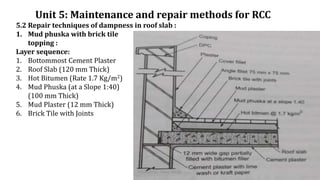
The document discusses various maintenance and repair methods for reinforced concrete cracks (RCC). It describes common locations of cracks in RCC columns, beams, slabs, and footings. These include diagonal, splitting, horizontal, and corrosion cracks in columns; shear and bending cracks in beams; and shrinkage cracks in slabs. It also lists causes of cracks like design/construction errors, chemical/mechanical damage, and dampness. Methods to repair cracks include epoxy injection, grouting, stitching, rebaring, and shotcrete. Mud phuska and lime concrete are techniques to repair dampness in roof slabs by providing insulation and waterproofing.