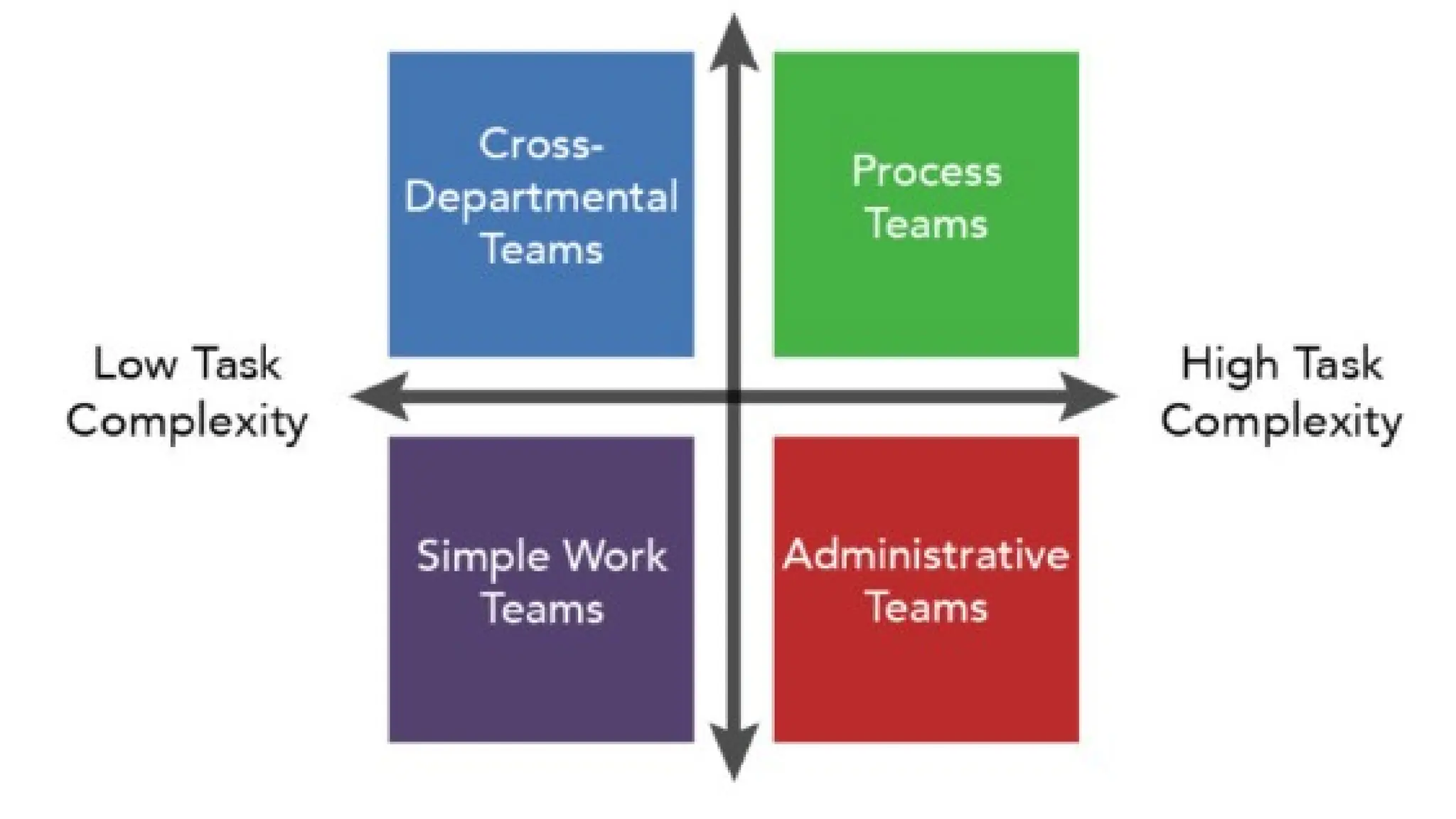
The document defines various types of teams in organizations, including simple work, administrative, cross-departmental, process, virtual, self-managed, and problem-solving teams, each with distinct characteristics and objectives. It highlights the advantages of cross-departmental teams, such as accelerating task completion and fostering creativity, and discusses factors that contribute to team effectiveness, including role clarity, collaborative spirit, and psychological safety. Additionally, the document emphasizes the importance of leadership in creating a supportive environment for team success.