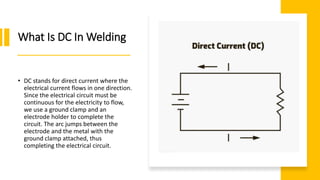
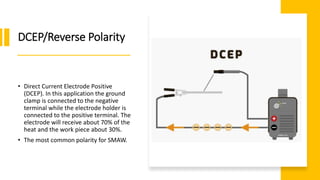
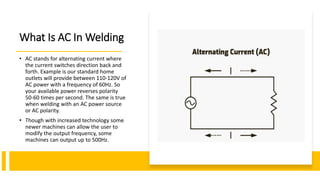
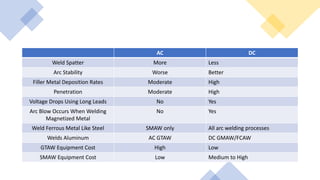
This document discusses the differences between AC and DC welding currents. It explains that DC current flows in one direction while AC current switches direction back and forth. DC provides a more stable arc with less spatter but is more prone to arc blow when welding magnetized metals. In contrast, AC has more spatter and a less stable arc for welding metals like steel, but is less prone to arc blow and can weld aluminum. The document outlines advantages and disadvantages of each type of current for different welding applications and processes.