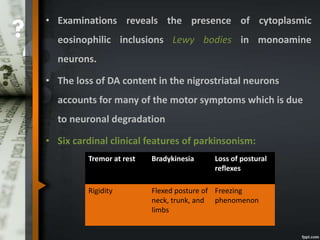
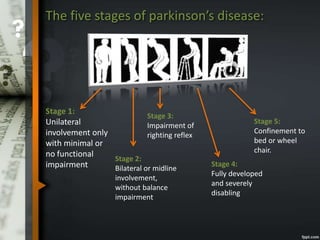
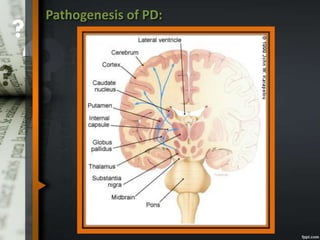
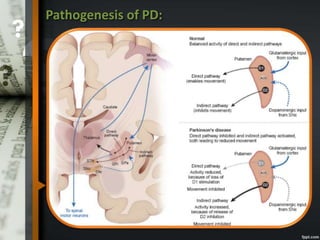
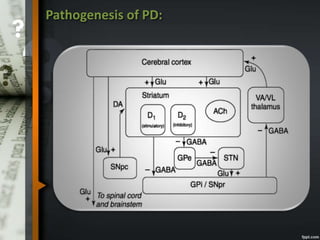
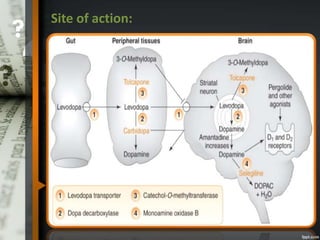
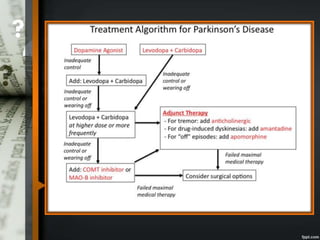
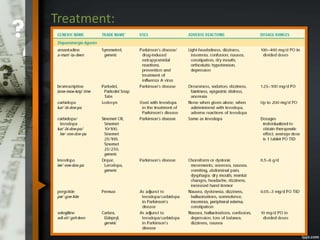
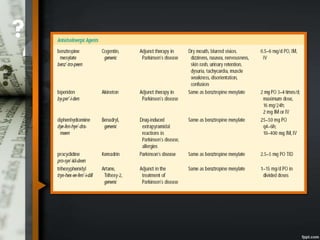
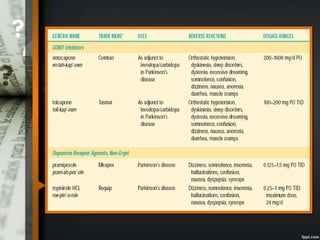
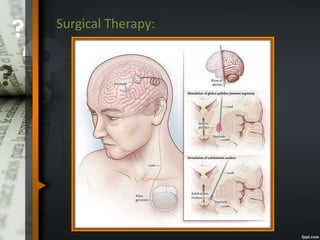
Parkinson's disease is a progressive neurological disorder caused by the loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra. The motor symptoms include tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia, and postural instability. Levodopa is the most effective drug for treating motor symptoms but causes adverse effects like involuntary movements. Other drugs used include dopamine agonists, COMT inhibitors, anticholinergics, and MAO-B inhibitors. Surgical therapies like deep brain stimulation may provide relief for advanced cases. The pathogenesis involves mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and protein aggregation.