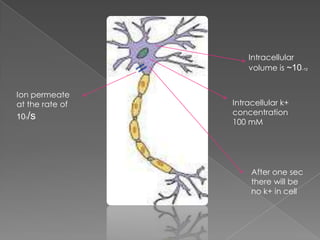
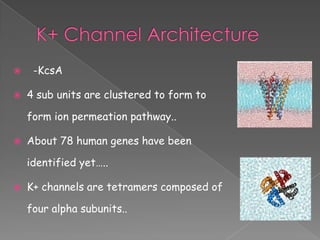
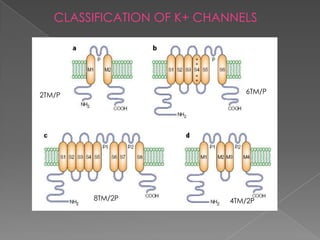
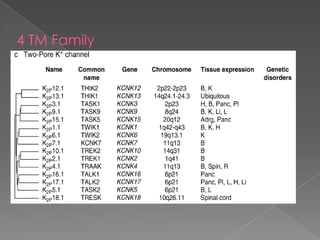
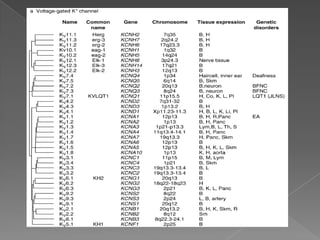
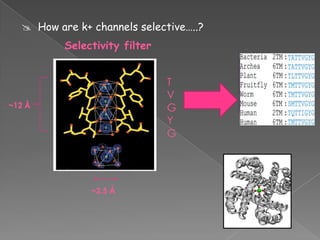
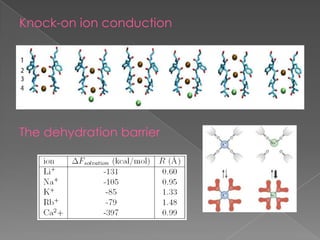
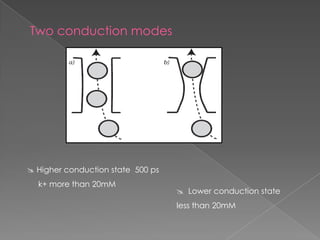
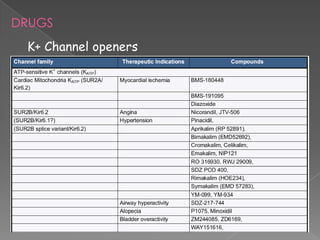
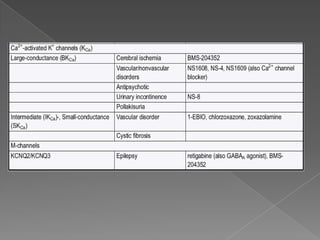
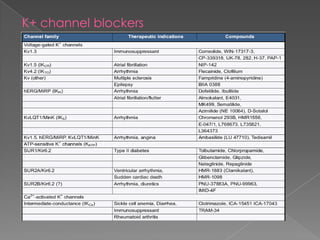
This document discusses potassium (K+) channels. It begins with an introduction and overview of K+ channel architecture and classification. It then covers the selectivity filter that allows for selective potassium ion permeation. The document discusses the structural basis of ion permeation and selectivity, including the knock-on ion conduction mechanism and dehydration barrier. It also addresses two conduction states that K+ channels can operate in and how they are selectively permeable while also operating quickly. The document concludes with sections on genetic K+ channelopathies and drugs that can open or block K+ channels.