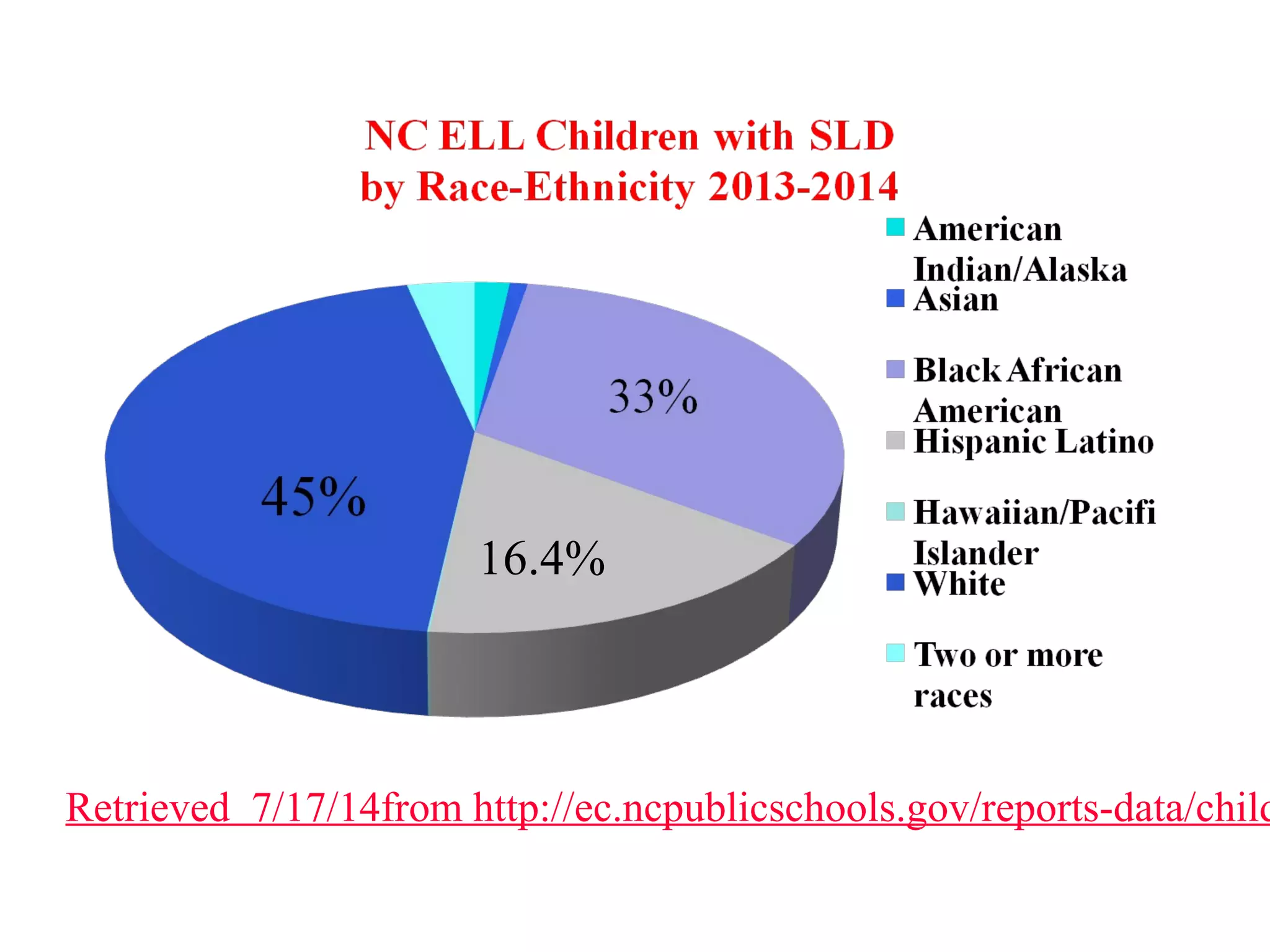
The document addresses the challenges faced by English Language Learners (ELLs) with specific learning disabilities in North Carolina's public schools, emphasizing the need for tailored instructional strategies and Response to Intervention (RTI) approaches. It outlines the characteristics of learning disabilities, the unique needs of ELLs, and effective methods for improving literacy skills among these students. The document also highlights the importance of collaboration between regular teachers, ESL teachers, and exceptional education teachers to support these learners effectively.