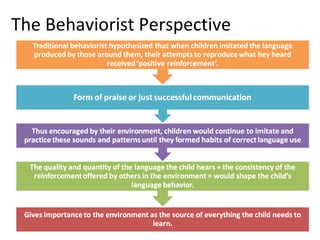
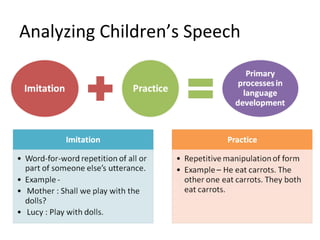
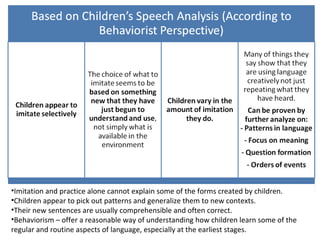
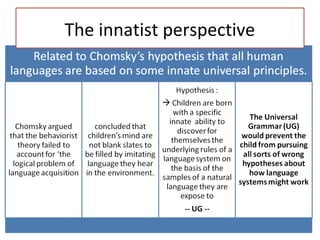
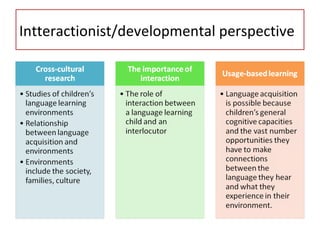
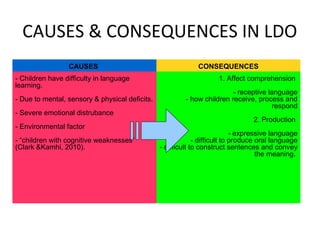
This chapter discusses language learning in early childhood. It covers topics such as first language acquisition milestones in the first three years including negation and question formation. It also discusses language development in pre-school and school-aged children. The chapter examines theoretical perspectives on first language acquisition such as behaviorist, innatist and interactionist views. It further discusses language disorders and delays in children as well as childhood bilingualism.