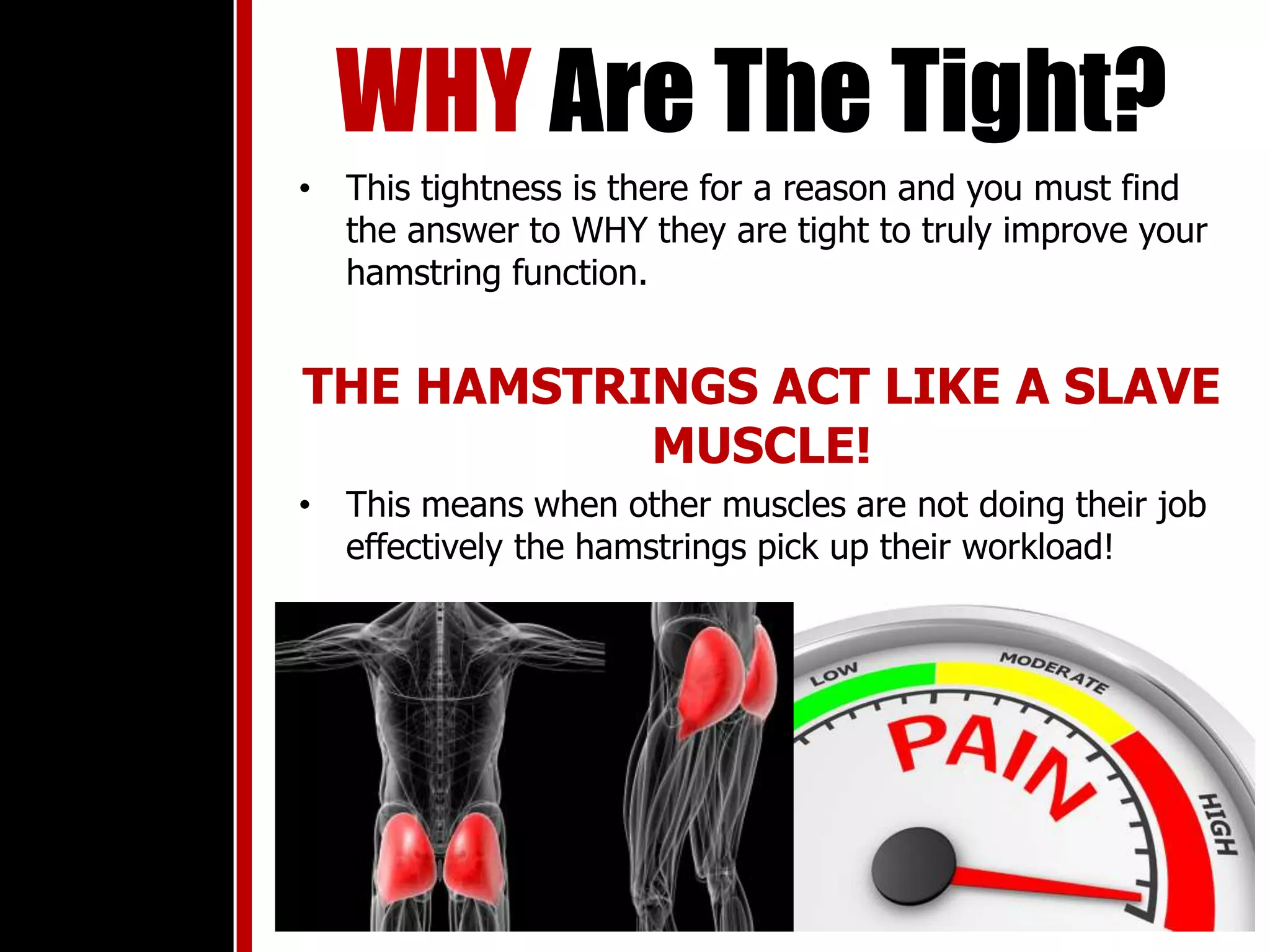
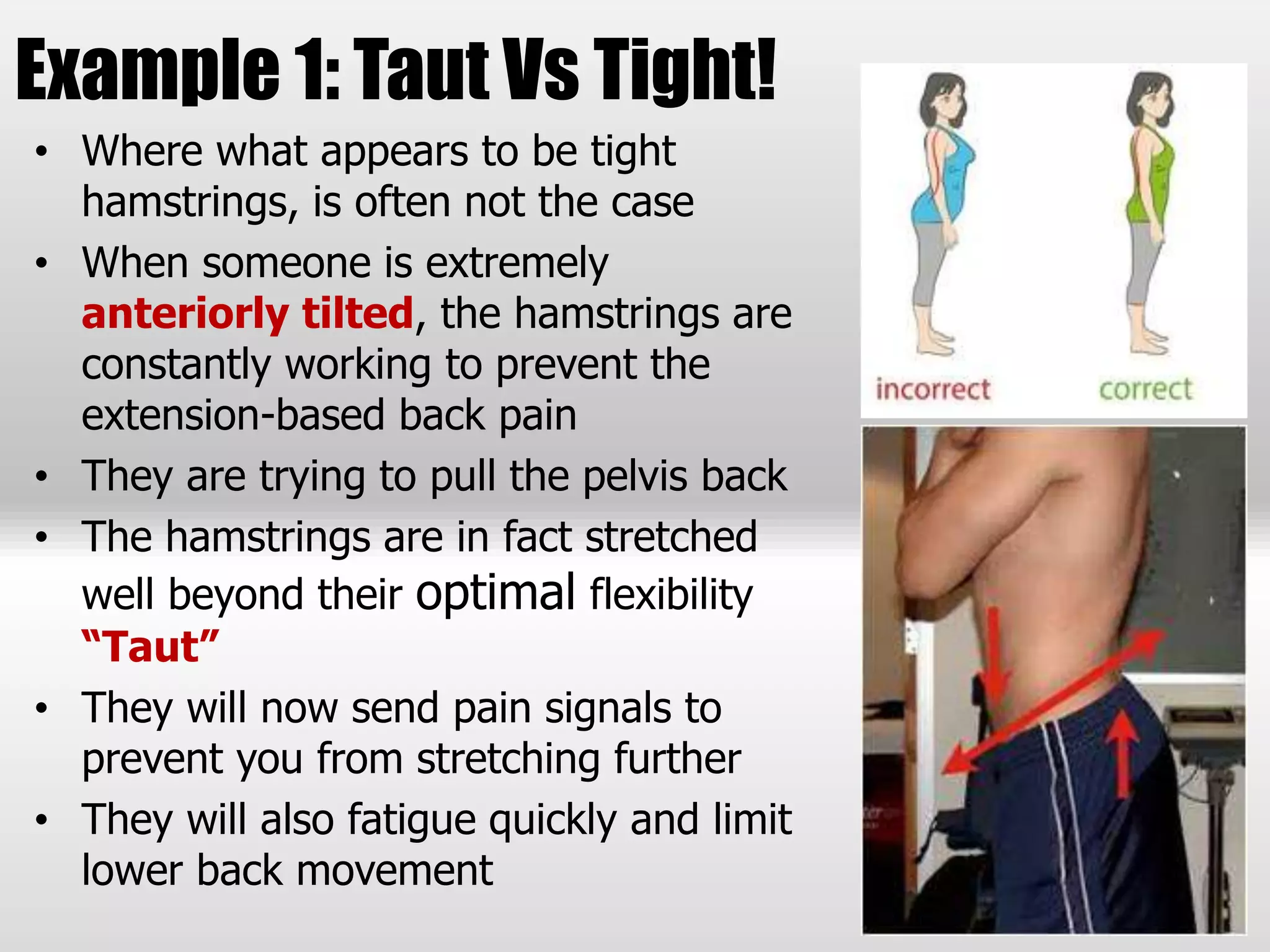
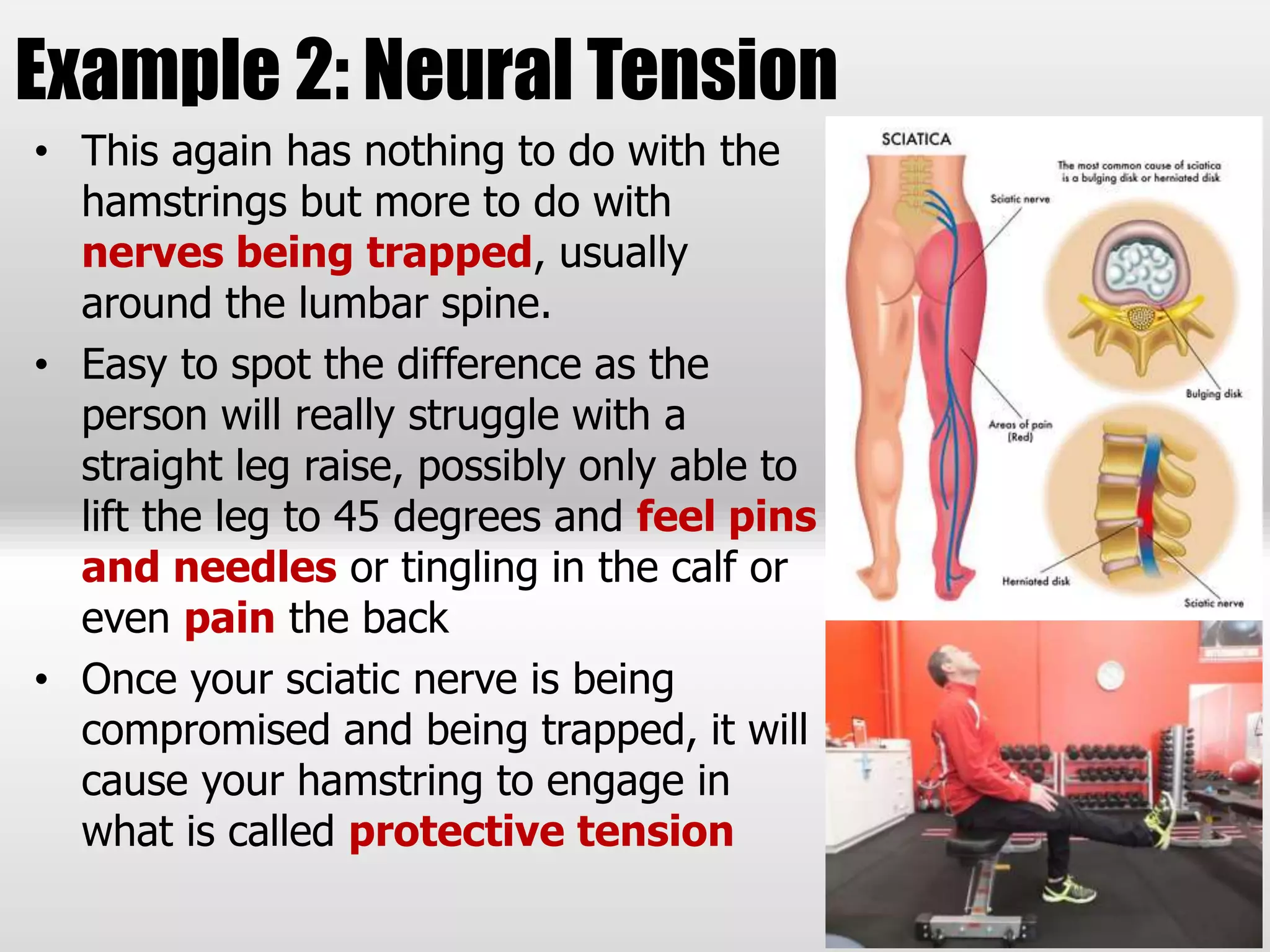
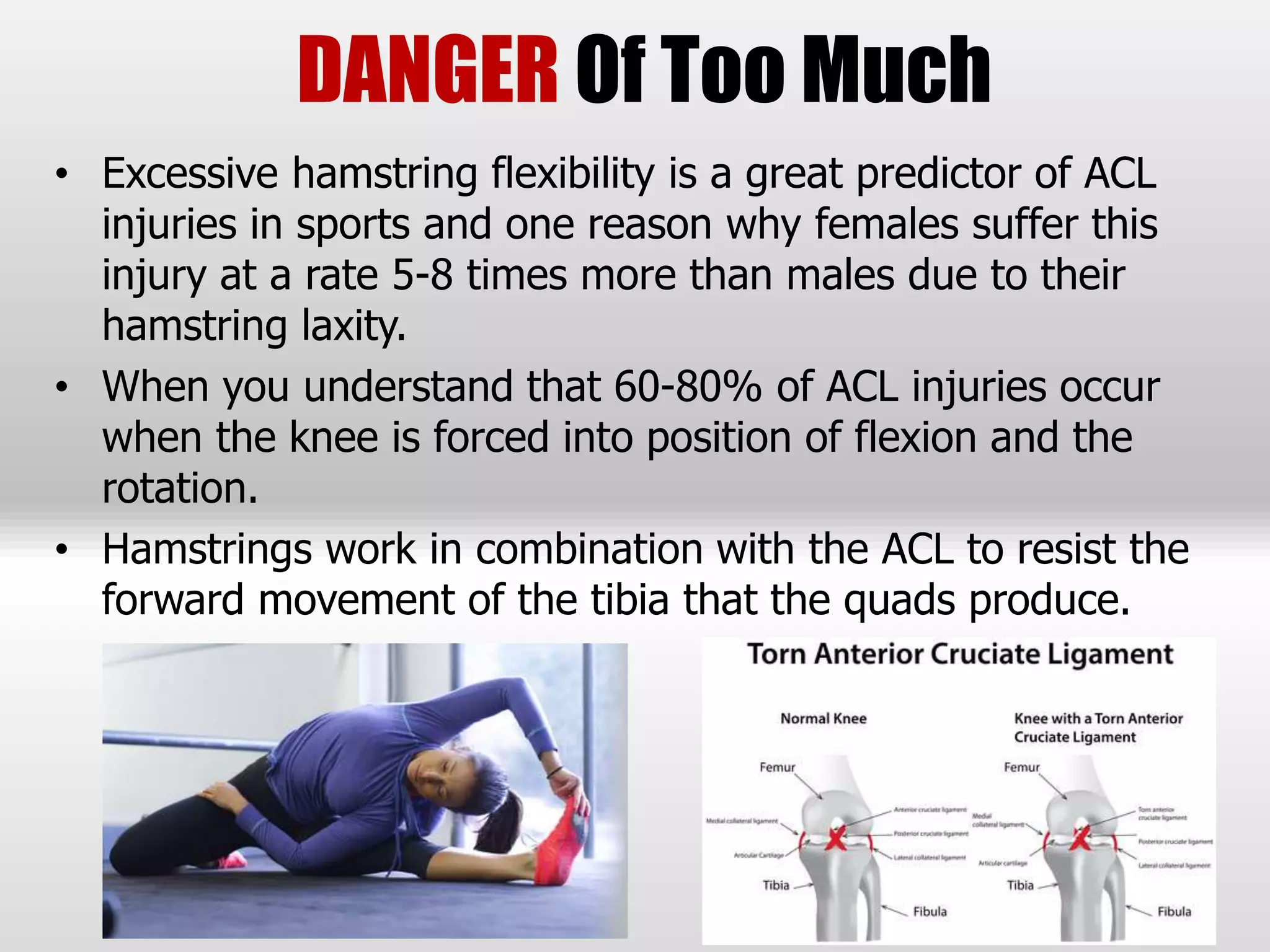
The document discusses the importance of hamstrings in movement and injury prevention, highlighting their role in activities like walking and running, and their function as stabilizers against the quadriceps. It addresses common misconceptions about hamstring tightness and suggests that issues may stem from pelvic tilt or nerve entrapment rather than actual tightness. To improve hamstring function, the document emphasizes the need for proper assessment, strengthening exercises targeting underlying issues, and cautions against excessive flexibility training which can lead to injuries.