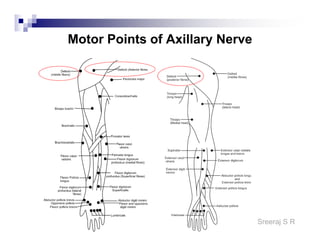
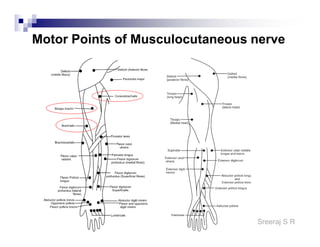
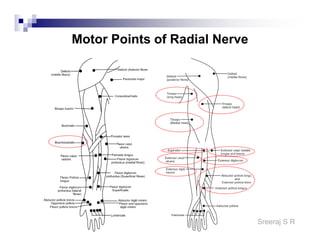
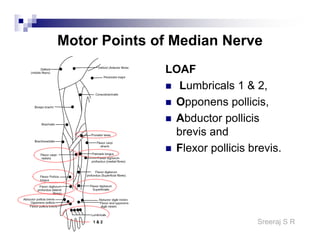
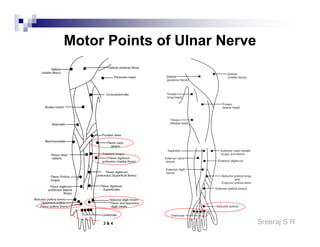
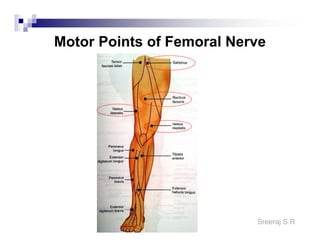
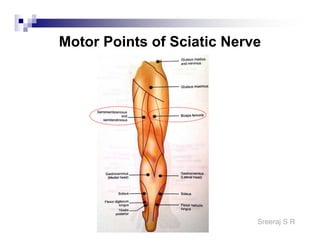
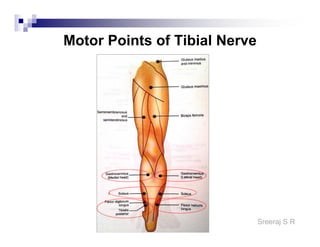
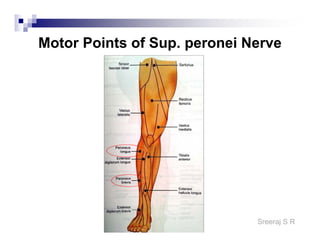
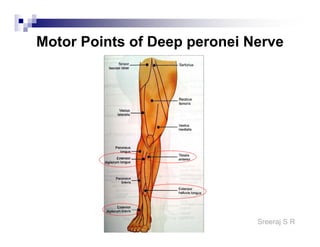
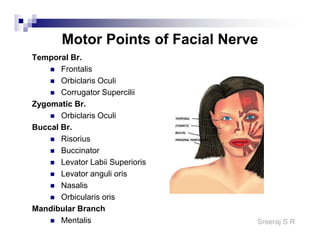
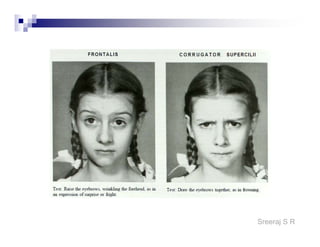
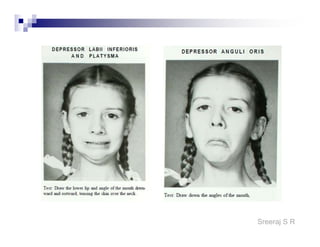
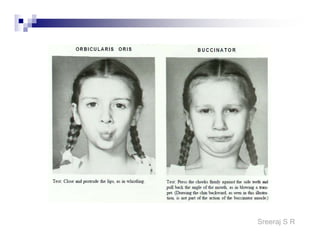
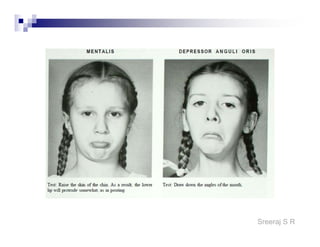
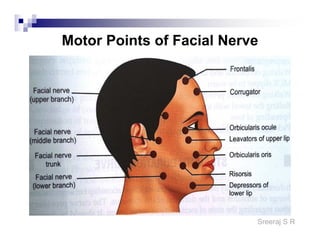
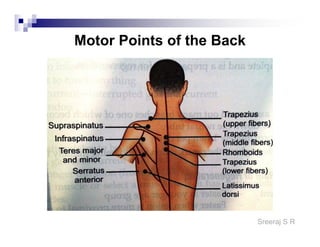
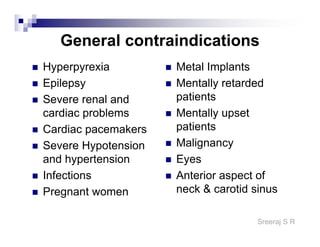
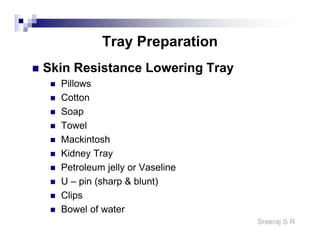
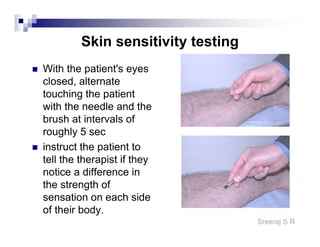
The document discusses the motor points of various nerves including the axillary, musculocutaneous, radial, median, ulnar, femoral, sciatic, tibial, superior peroneal, deep peroneal and facial nerves. It also discusses principles of electrical stimulation application such as patient positioning, skin preparation, testing the equipment, determining treatment parameters and monitoring the patient during treatment. Precautions, contraindications and procedures for initiating, conducting and terminating the treatment are provided.