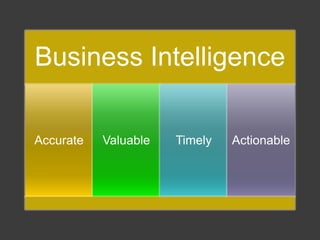
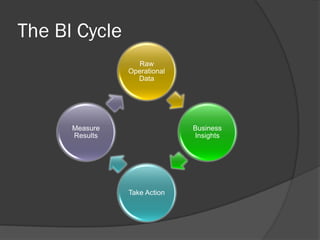
Business intelligence (BI) uses data about past and present to help companies make better decisions for the future. BI provides timely, accurate insights that are valuable and can be acted upon. It helps companies operate more efficiently and profitably by supporting better strategic and tactical decision making. As BI systems evolve to deliver analytics to mobile devices in near real-time, more companies are using BI to promote a data-driven culture and rational decision making processes.