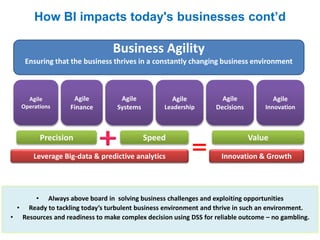
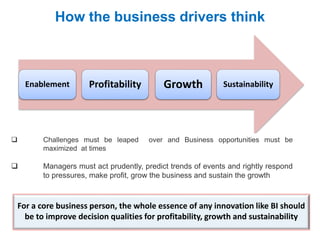
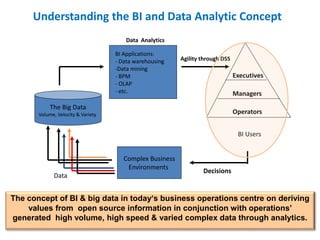
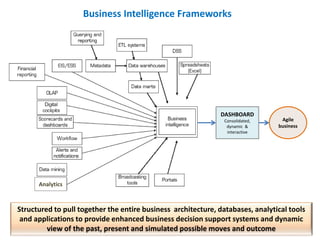
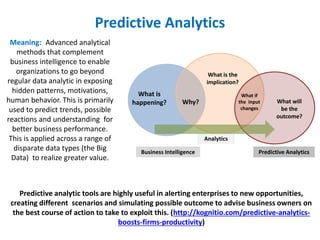
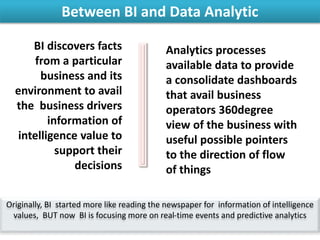
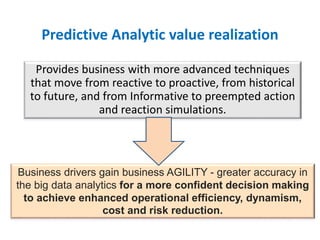
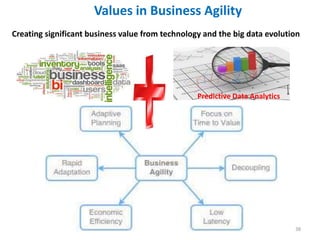
The document discusses the integration of business intelligence (BI) and data analytics to drive value realization within organizations. It emphasizes the importance of real-time data access and predictive analytics to enhance decision-making, operational efficiency, and business agility. The material covers various frameworks, challenges, user goals, and applications aimed at improving business strategies in a complex and competitive environment.