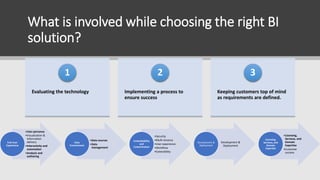
The document provides a checklist for evaluating Business Intelligence solutions. It covers key areas to consider like the data environment, end user experience, licensing and support, and features needed for data inquiry, manipulation, analysis, reporting, graphics, security, automation and collaboration. Choosing the right BI solution is important to turn data into insights, improve efficiency and gain competitive advantages. The evaluation process involves defining requirements, shortlisting options, seeing vendor demonstrations, and testing options.