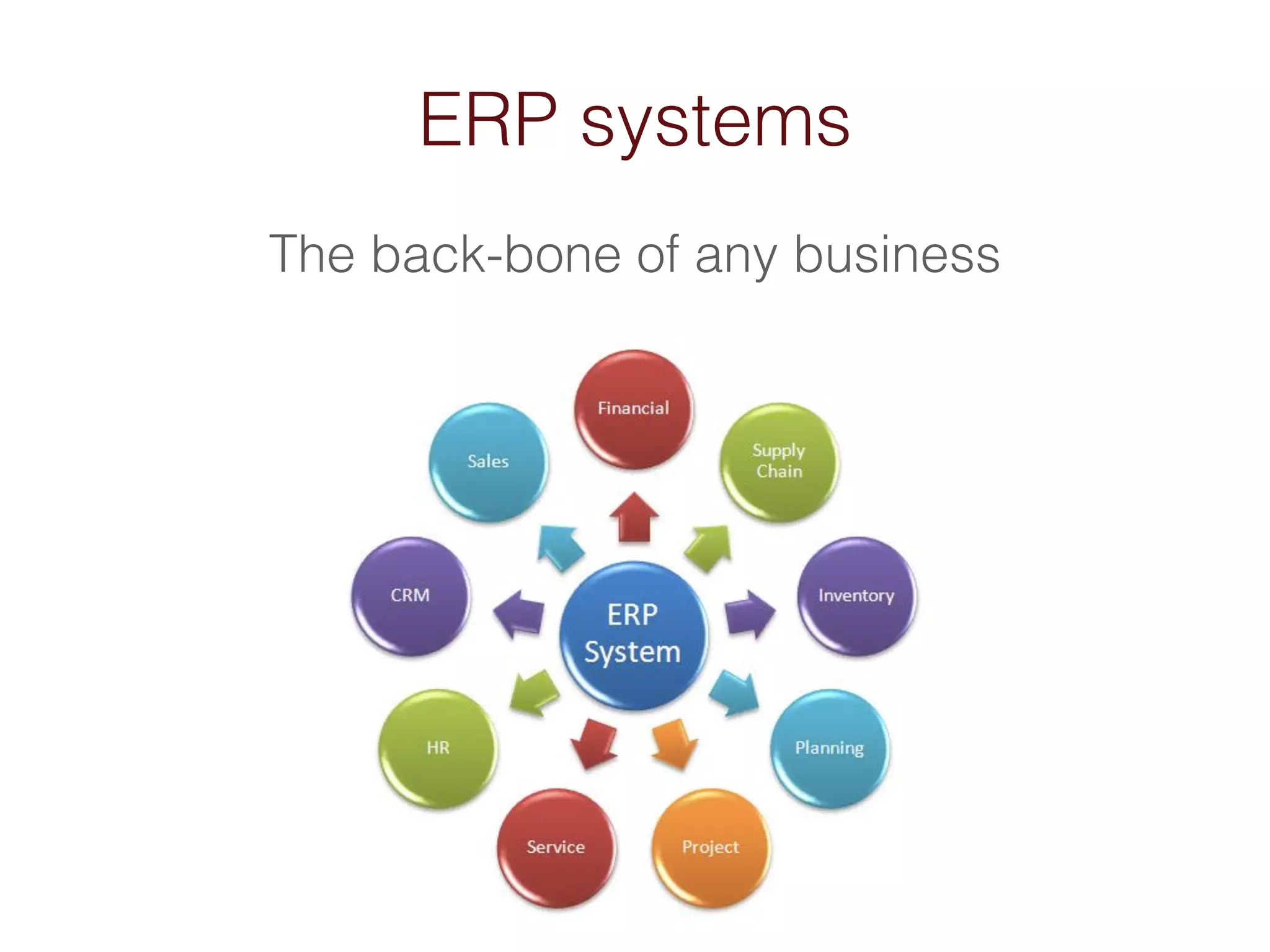
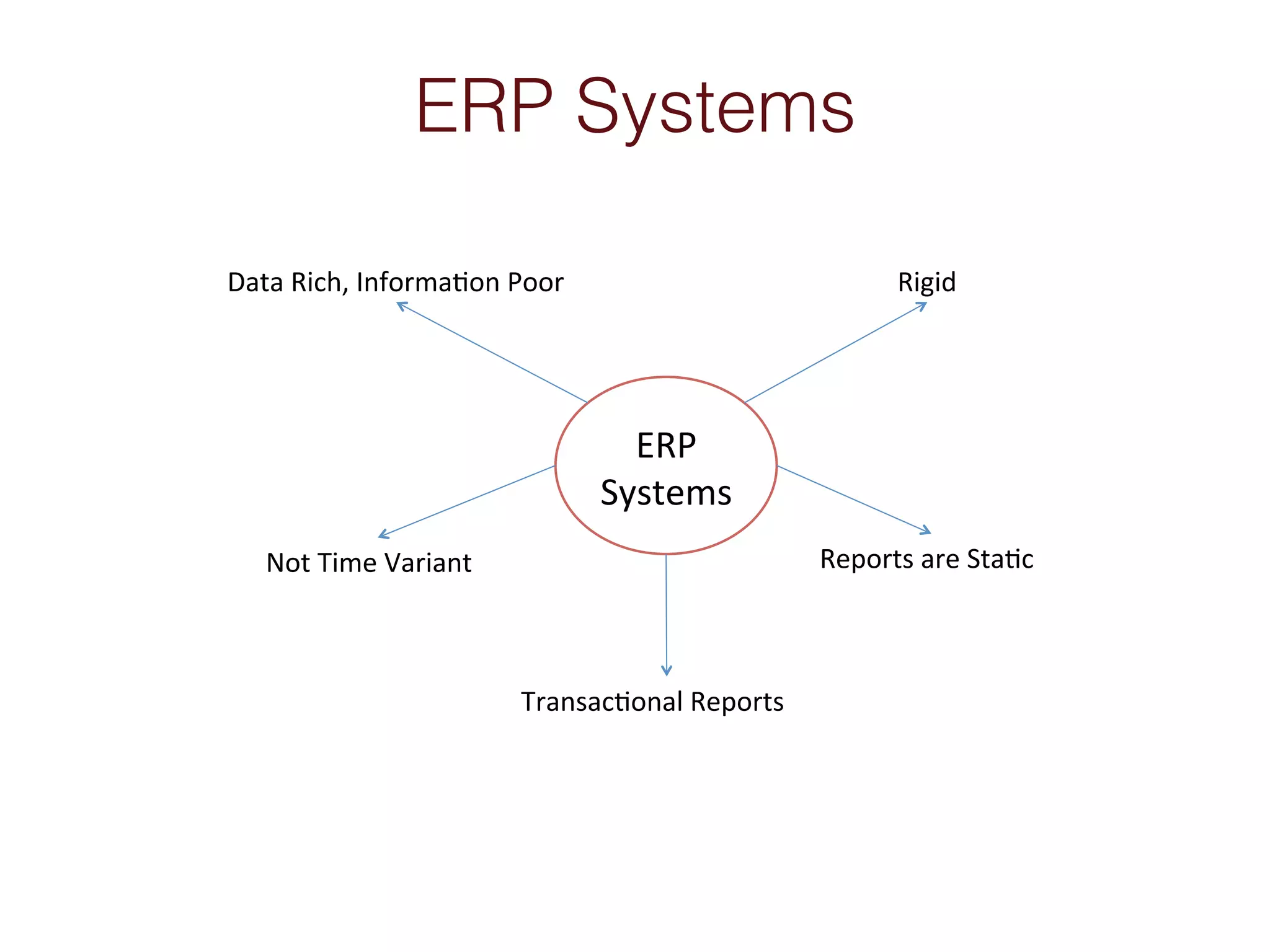
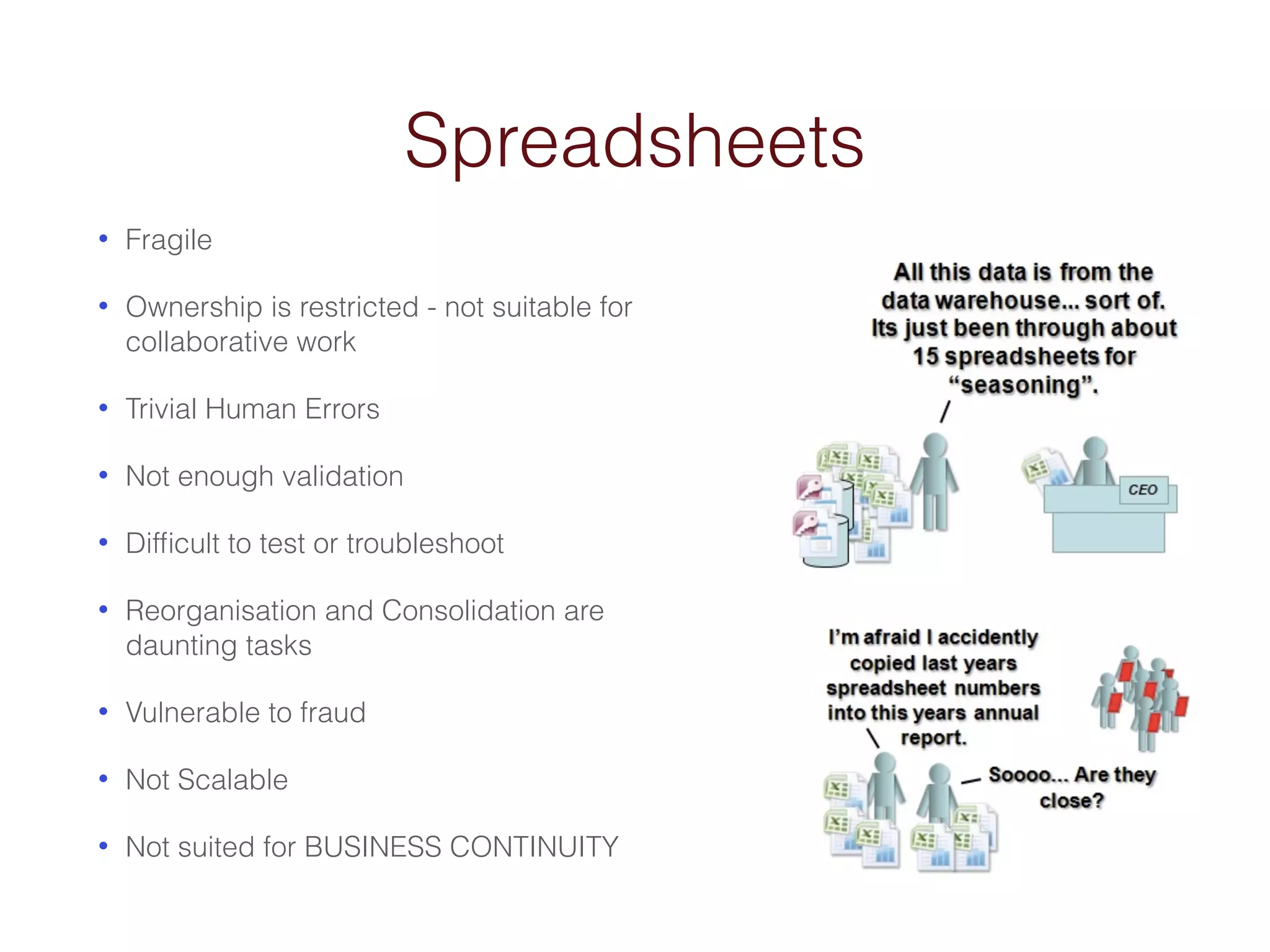
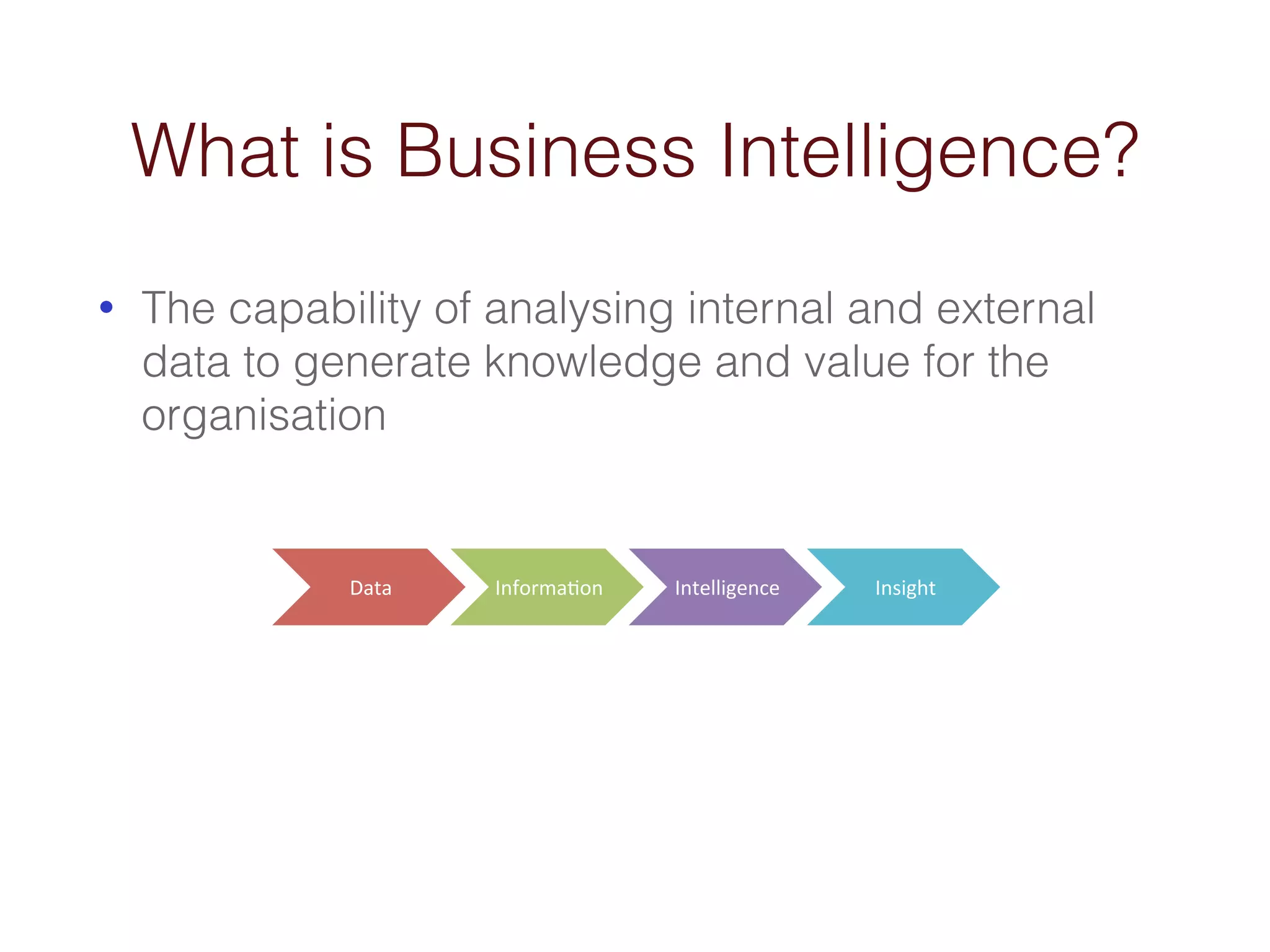
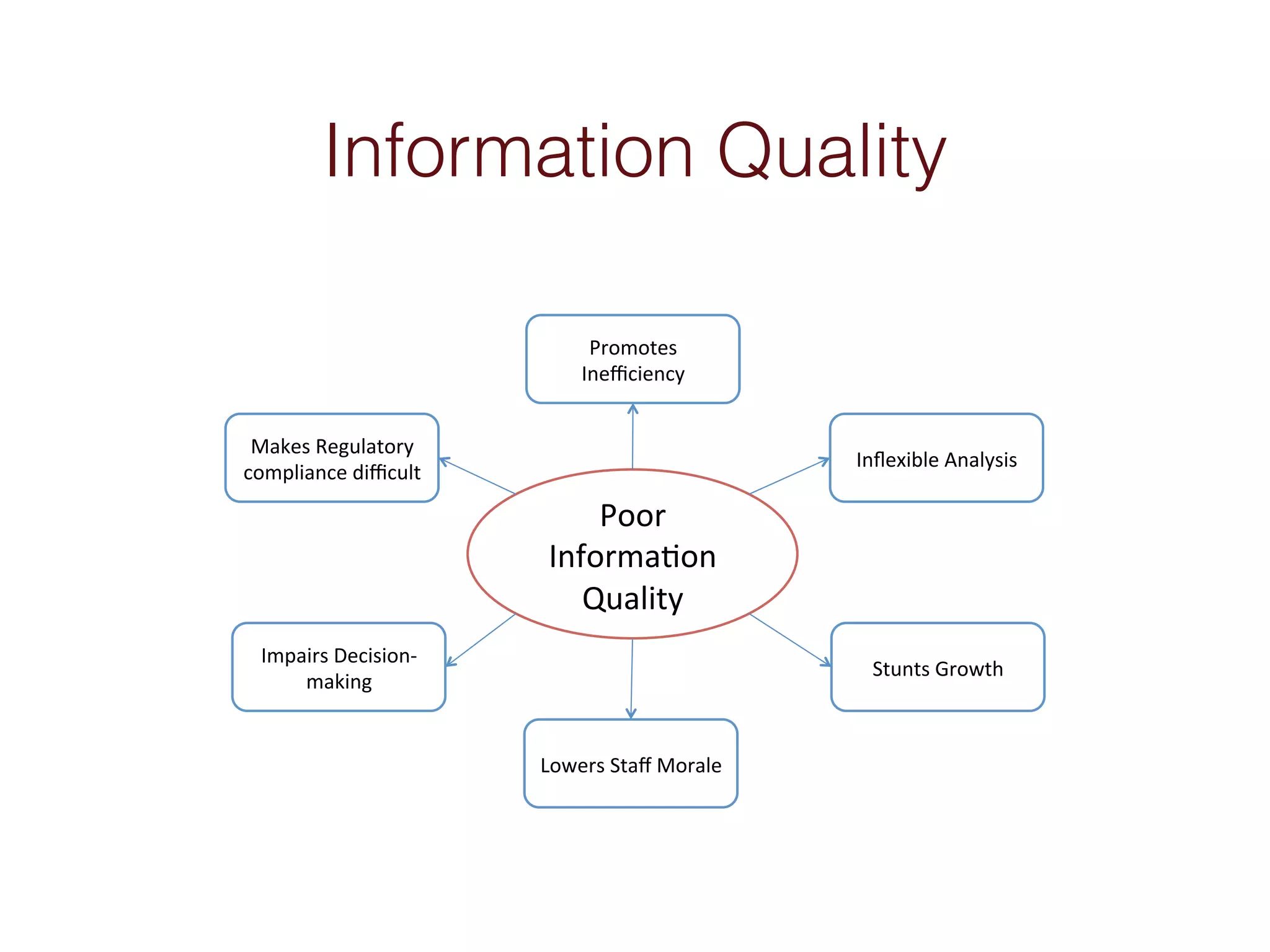
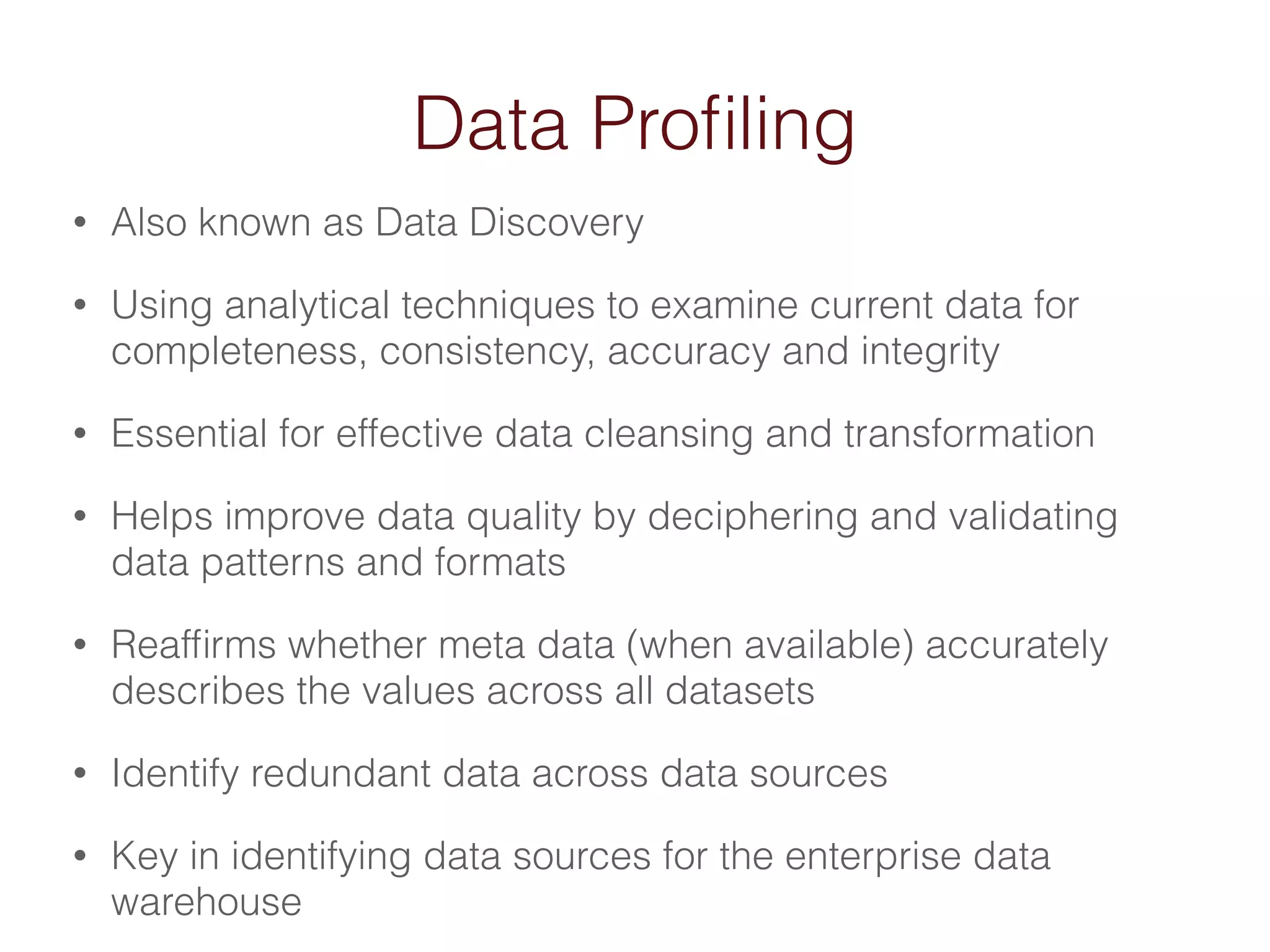
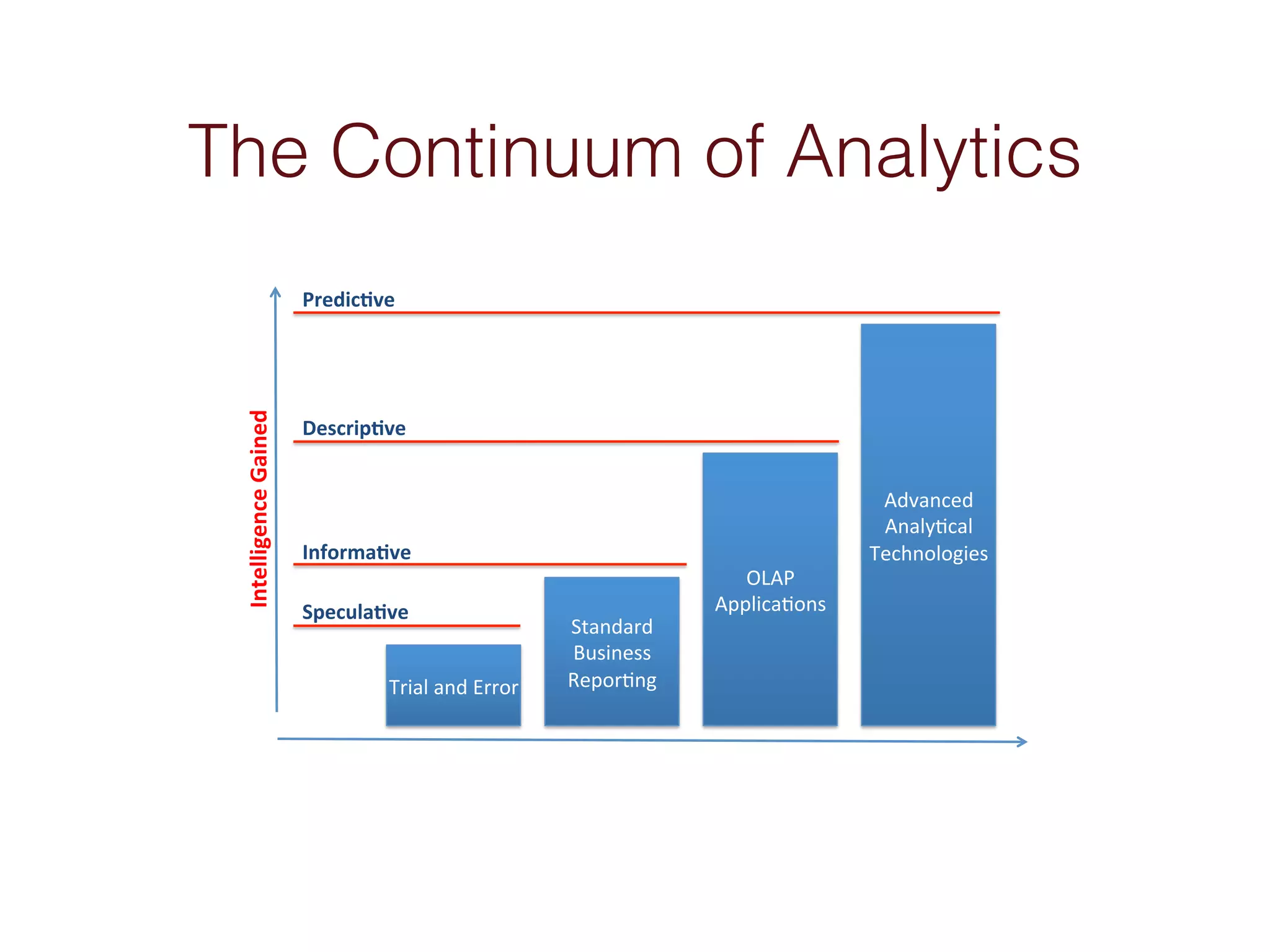
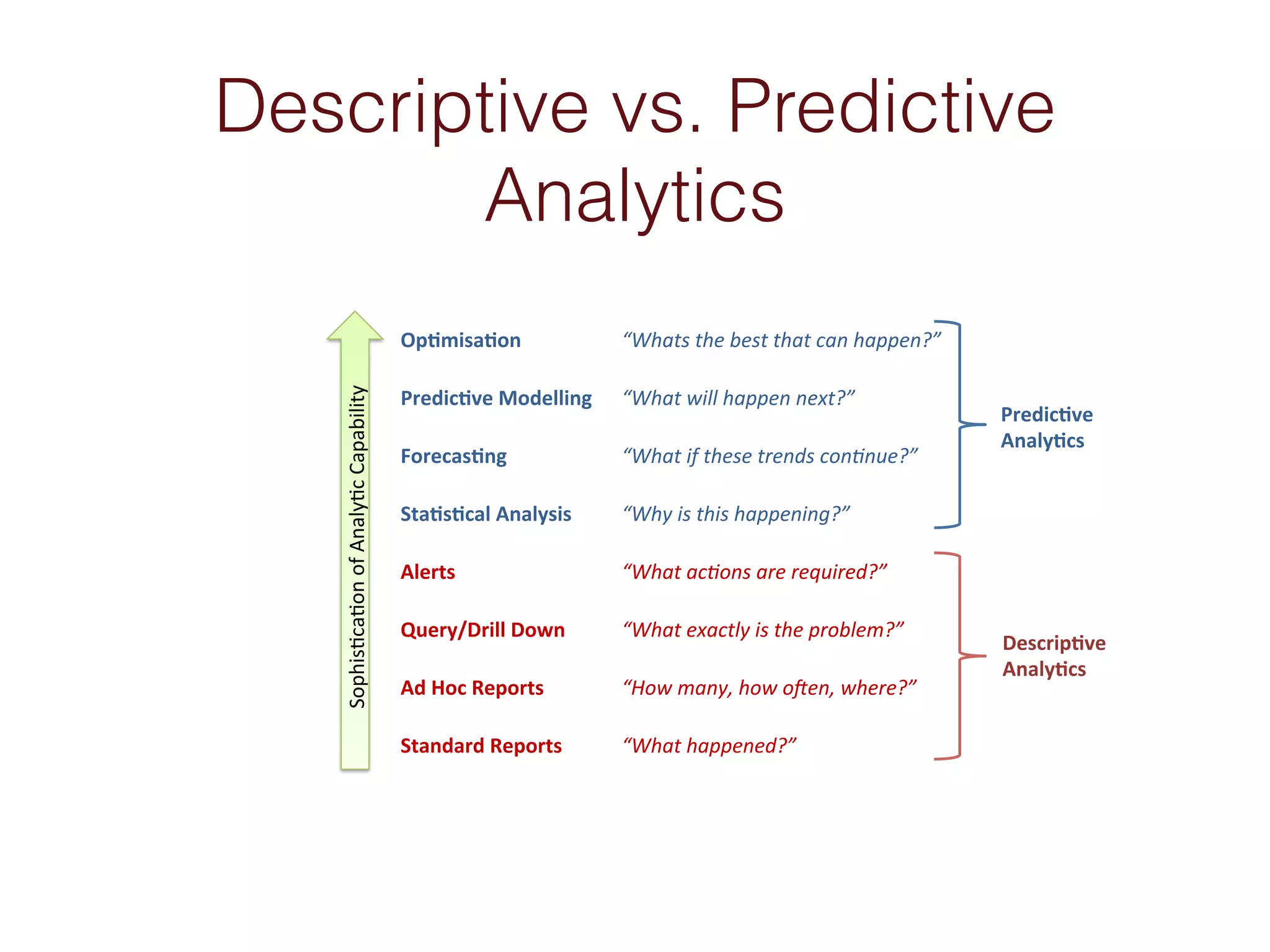
When an organization needs to make important decisions, business intelligence can help by analyzing internal and external data to generate knowledge. Business intelligence enables fact-based decisions by aggregating, enriching, and presenting data from sources like ERP systems and databases. The goals of a business intelligence implementation are to capture data from across the business to create a unified view, produce an integrated data warehouse to improve decision making, and enable ongoing analysis of data rather than just collecting it.