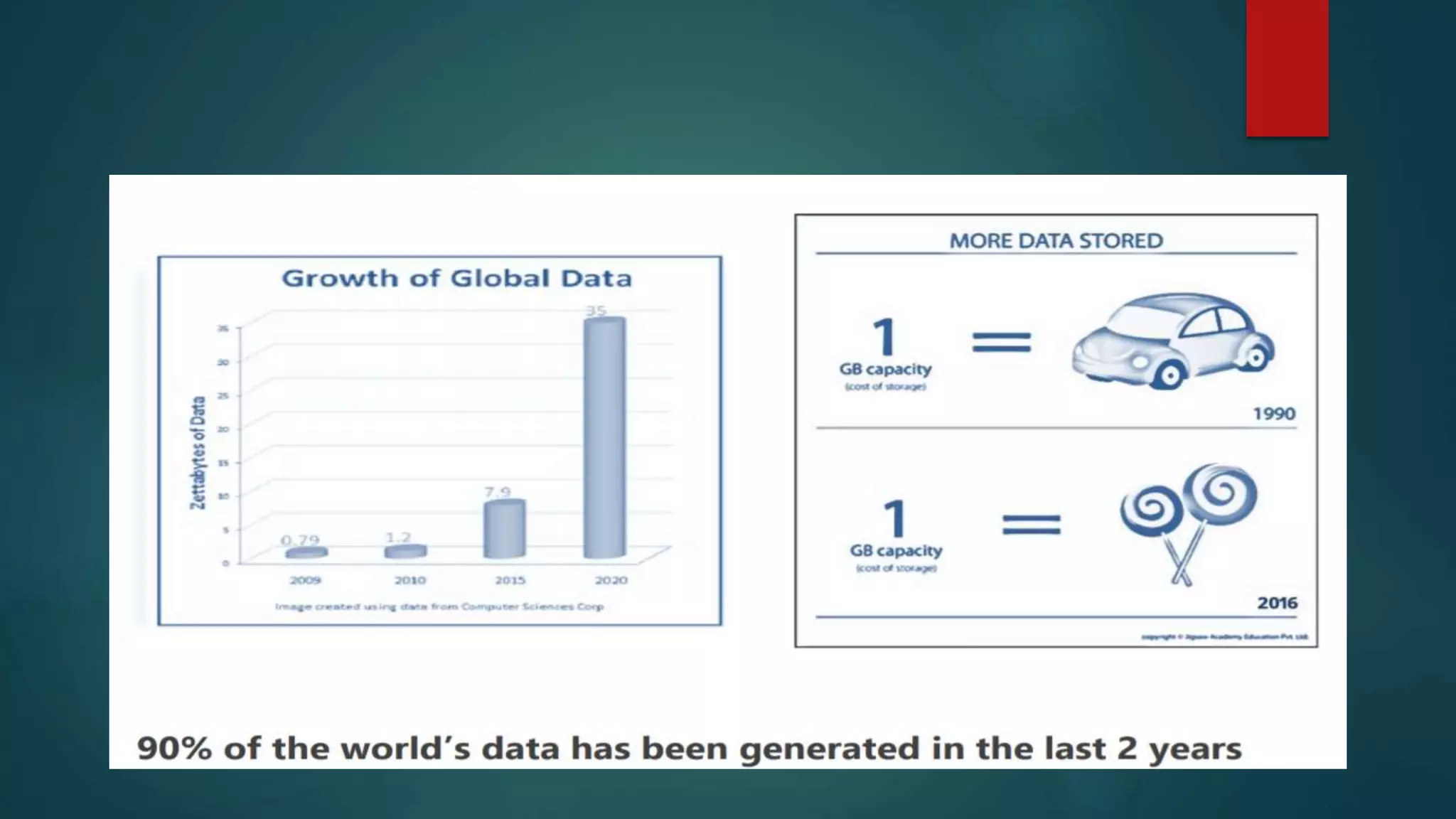
Business intelligence is a tool that transforms raw data into meaningful information to help businesses make better decisions. It helps managers and executives cut costs, identify opportunities, and improve processes. While the term was coined in 1865, business intelligence has grown more powerful due to increased data collection, storage capacity, and lower storage costs. Companies now use data from various digital sources for business intelligence. It provides benefits like accelerating decision making, optimizing processes, increasing efficiency, and gaining competitive advantages. Common business intelligence software tools are used to analyze historical, current, and predictive data for purposes like performance management and benchmarking against competitors. For successful implementation, companies must have clean data, effective training, clear ROI definitions, and focus on business objectives rather than