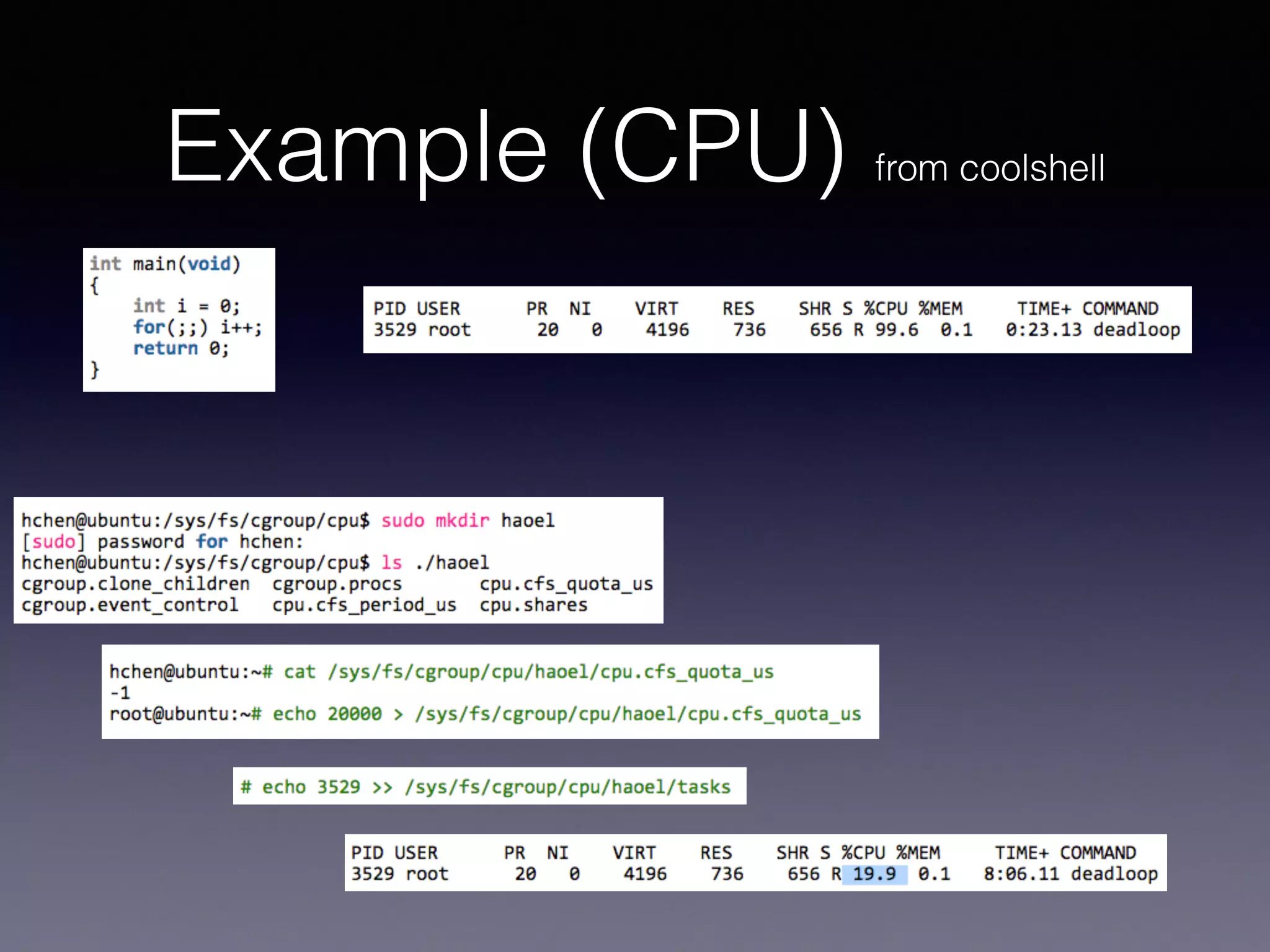
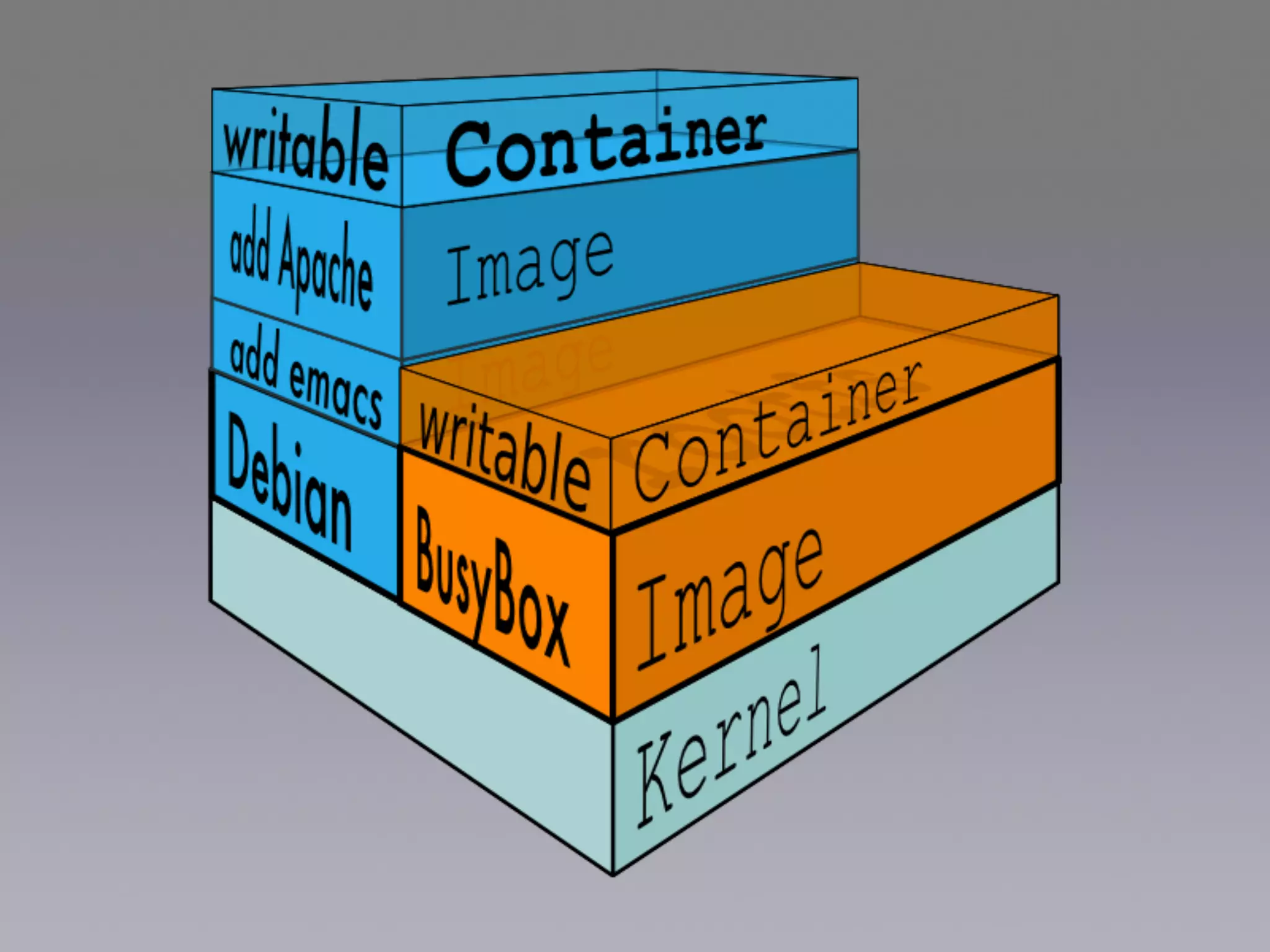
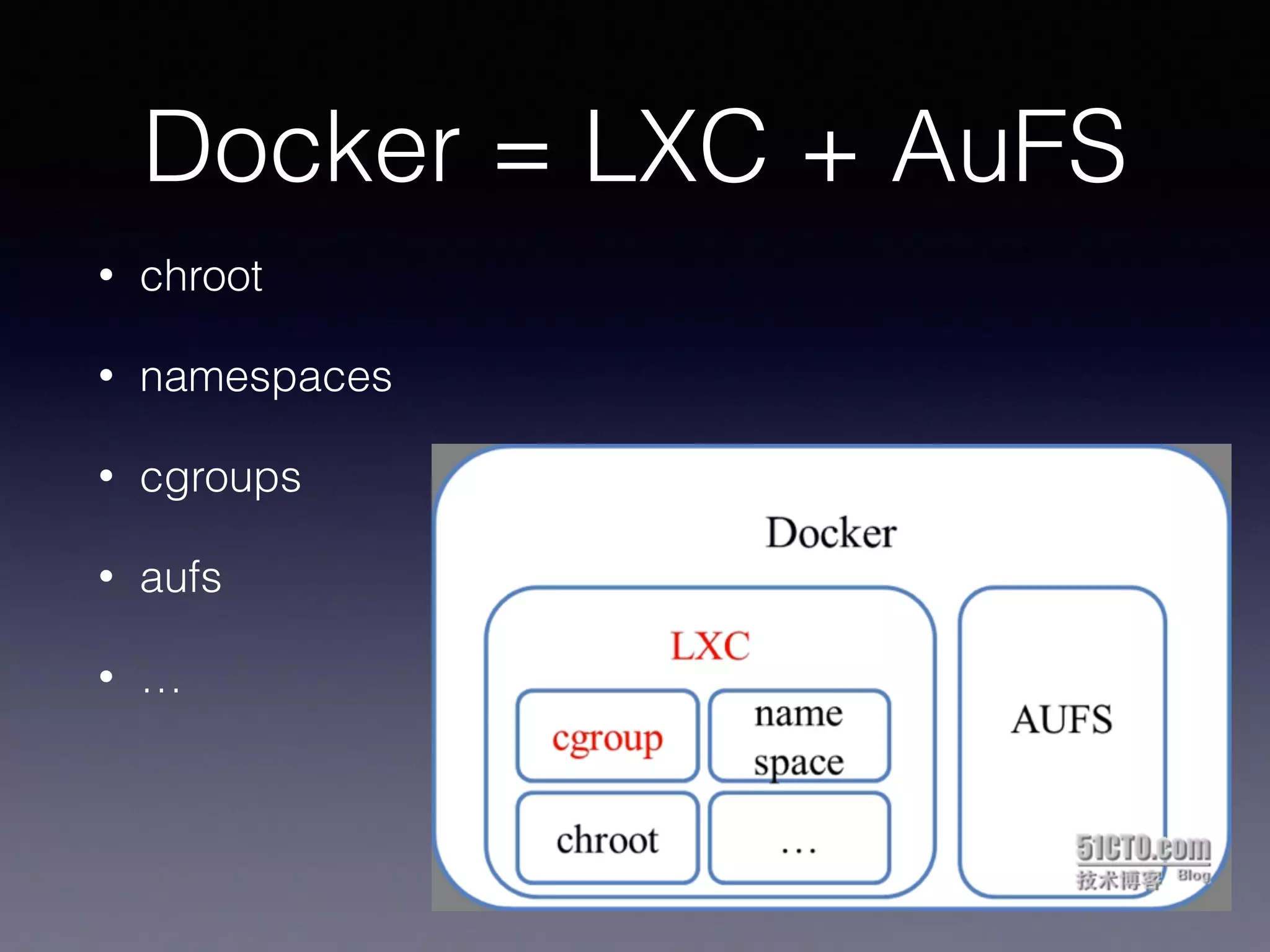
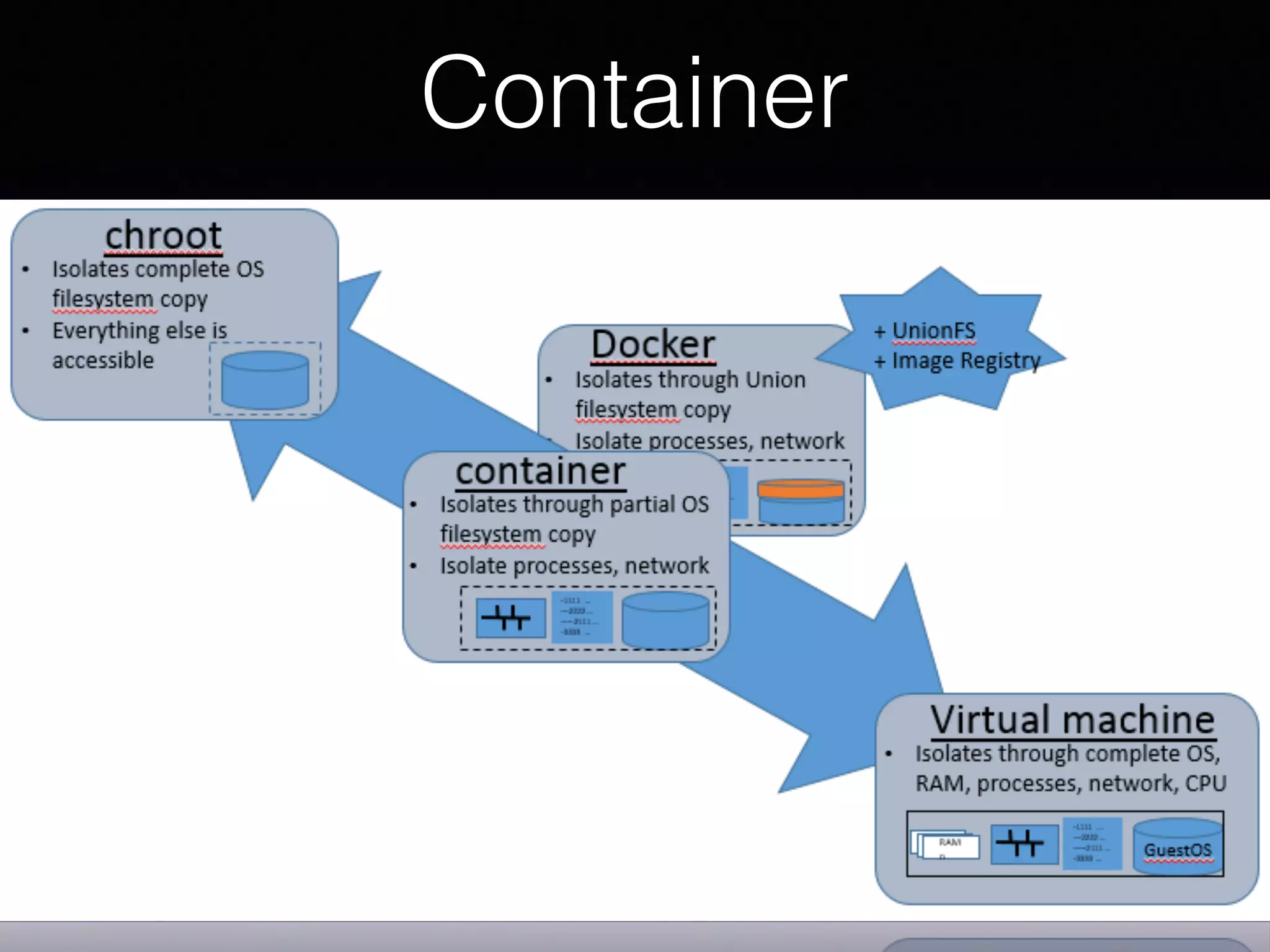
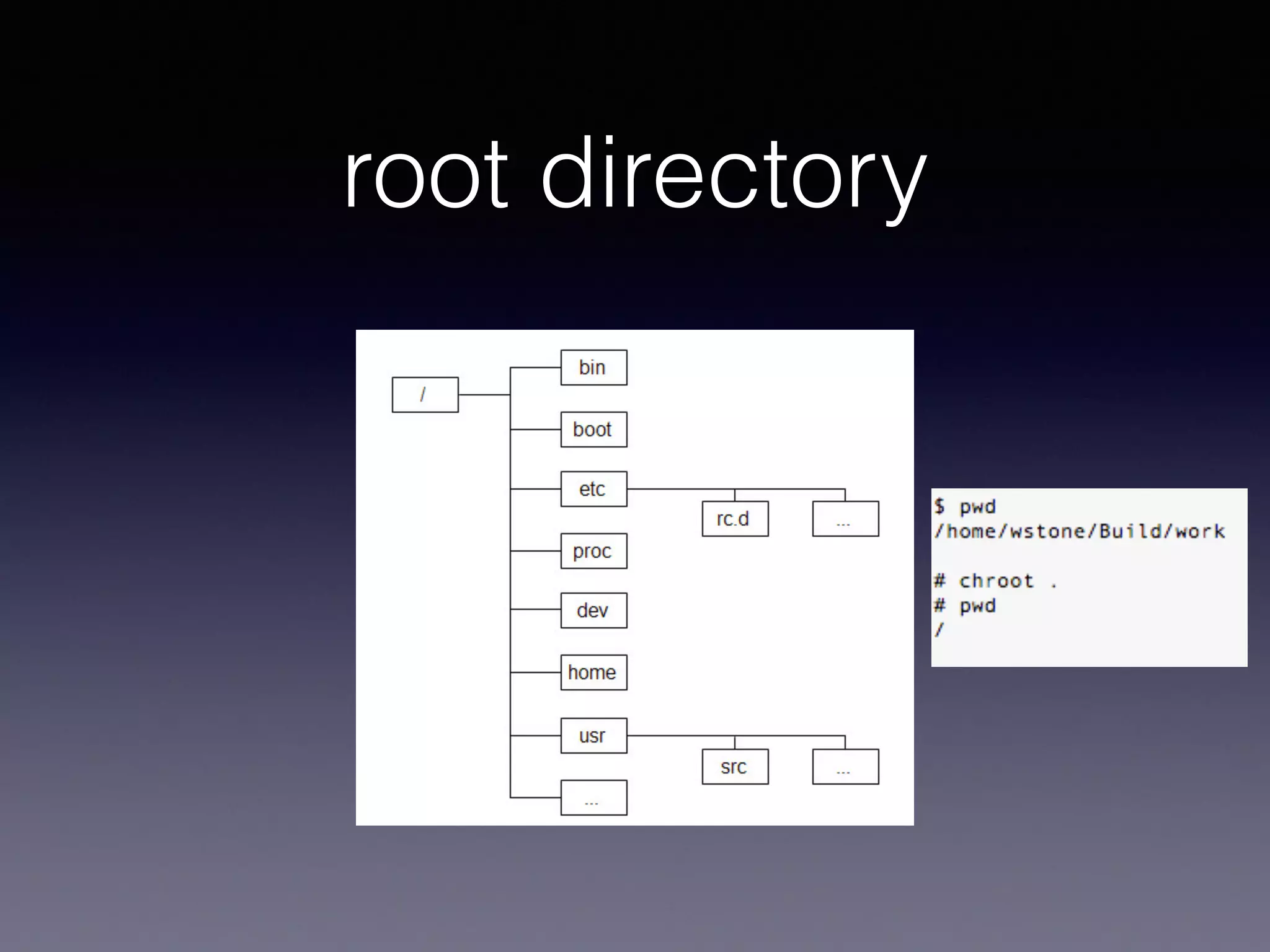
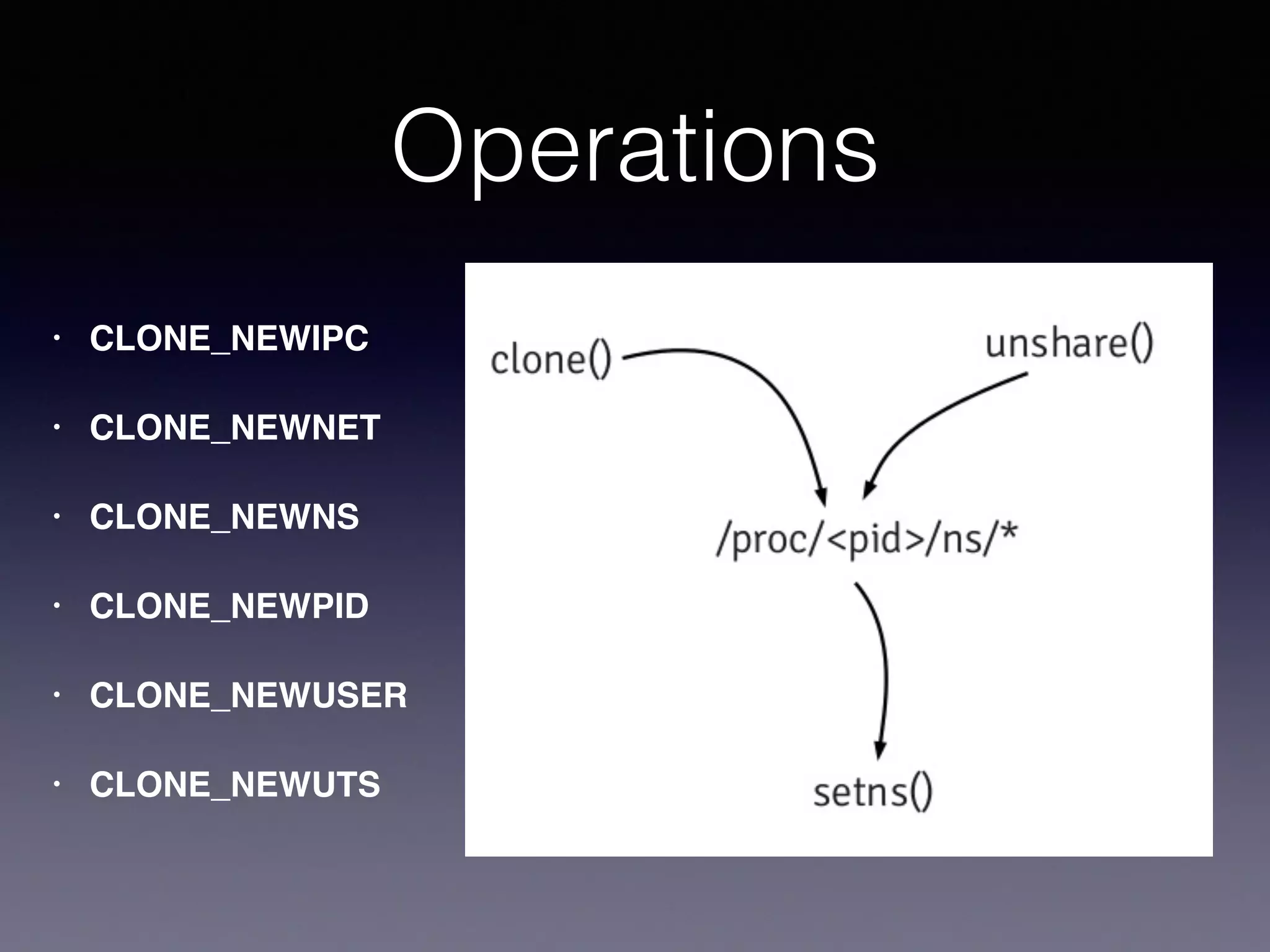
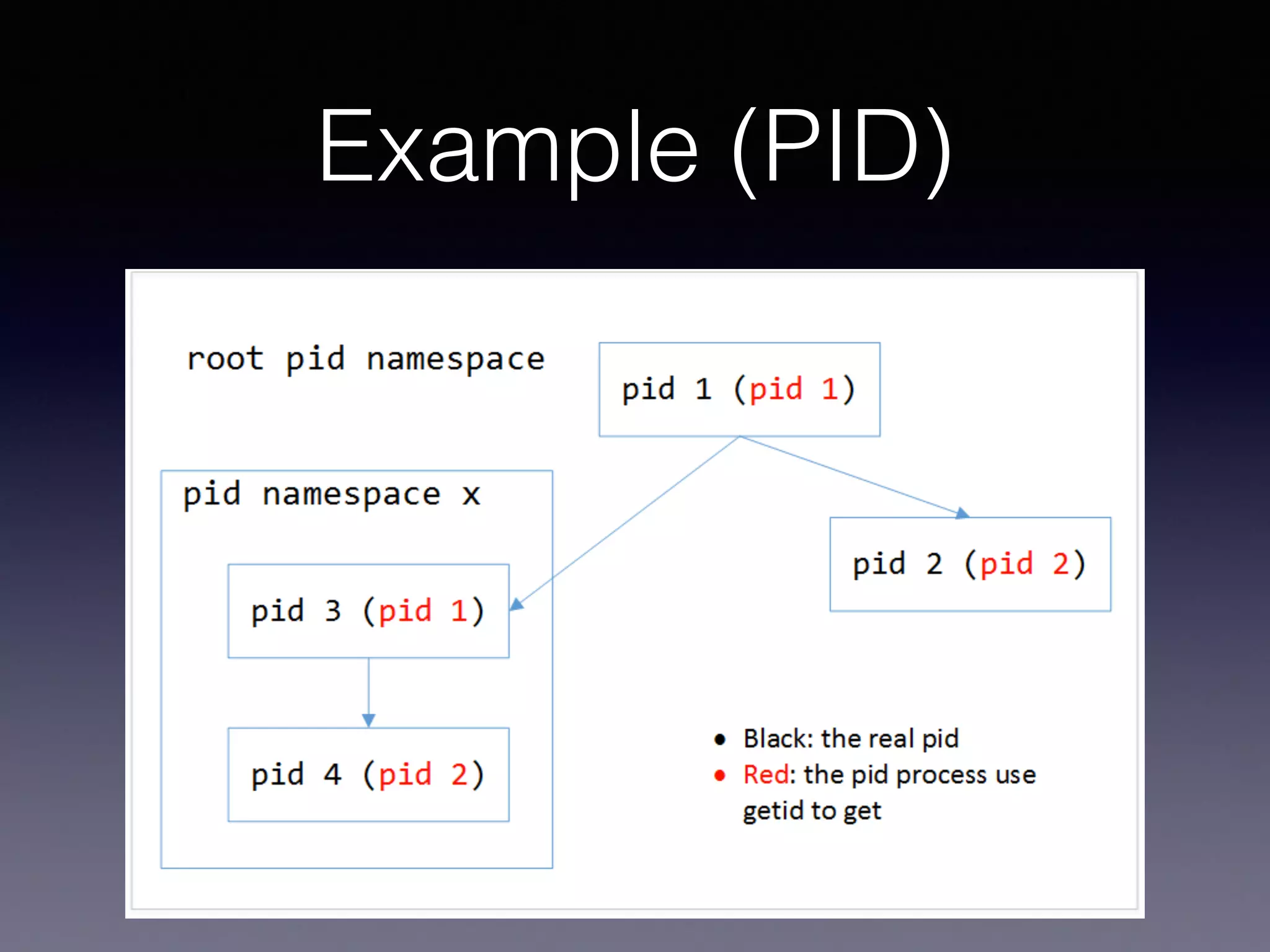
Docker uses virtualization techniques like namespaces and cgroups to isolate processes and share resources efficiently across multiple Linux containers. Namespaces allow processes to have isolated views of various systems like networking and process IDs. Cgroups limit and account for resource usage like CPU and memory. AuFS implements a union filesystem to overlay container filesystem changes over read-only base images. Docker combines these technologies into lightweight Linux containers that package code and dependencies to run reliably across environments.













![Features
• Resource limitation: groups can be set to not exceed a
configured memory limit, which also includes the file
system cache
• Prioritization: some groups may get a larger share of
CPU utilization[8] or disk I/O throughput
• Accounting: measures how much resources certain
systems use, which may be used, for example, for billing
purposes
• Control: freezing the groups of processes, their
checkpointing and restarting](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/understandhowdockerworks-151028103313-lva1-app6892/75/Understand-how-docker-works-22-2048.jpg)