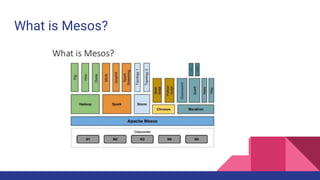
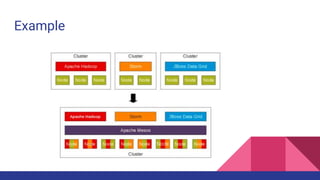
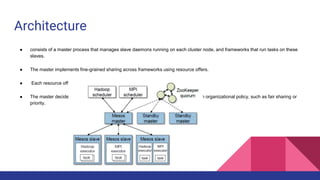
Mesos is a cluster manager that provides efficient resource sharing across distributed applications. It sits between applications and the operating system to make deploying and managing applications in large clusters more efficient. Mesos introduces distributed two-level scheduling where it decides how to allocate resources to frameworks, which then decide how to use those resources. It provides features like fault tolerance, scalability, resource isolation, and APIs for building distributed apps. Common uses include running Hadoop, Spark, Storm, Jenkins, and Docker on Mesos clusters.