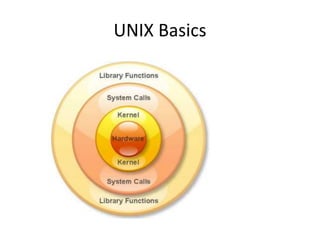
System administration involves tasks like maintaining computer systems and networks, setting up user accounts, monitoring performance and security, updating software, and troubleshooting issues. It requires broad technical knowledge as well as skills in areas like communication, problem solving, and planning for future needs of systems and users. While computer systems and the roles of system administrators have become more complex over time, the core goals remain ensuring systems and networks are operational, secure, and meeting the needs of users.