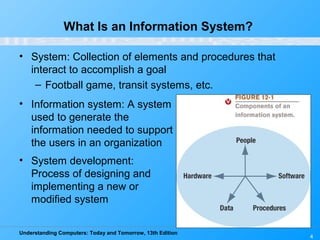
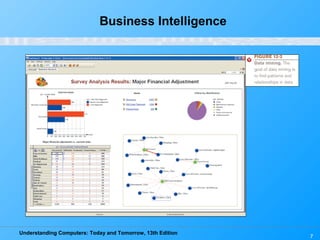
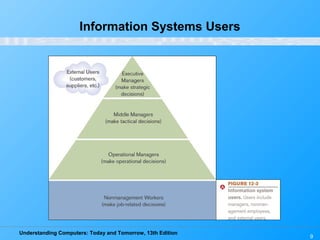
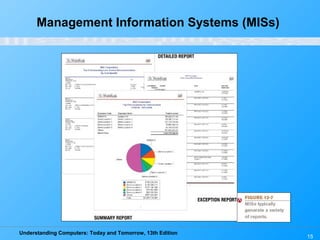
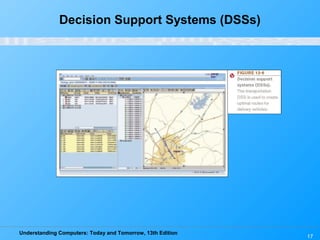
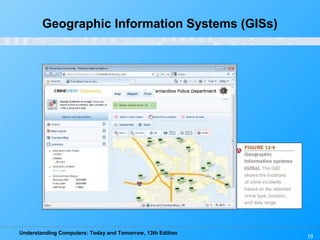
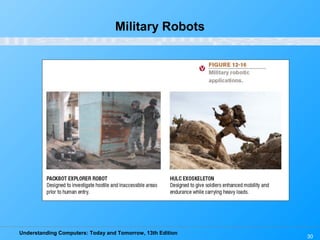
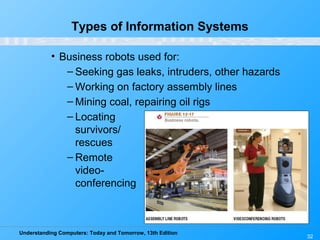
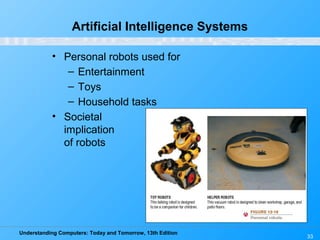
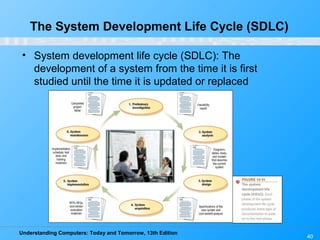
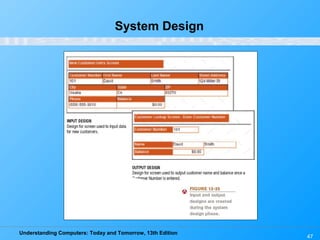
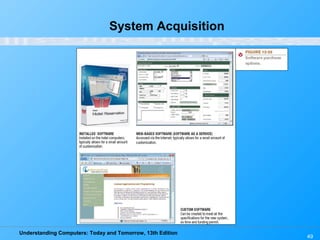
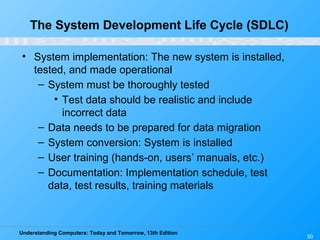
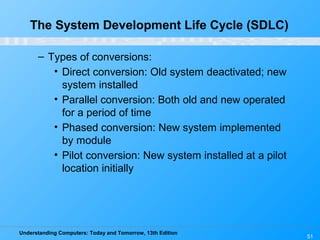
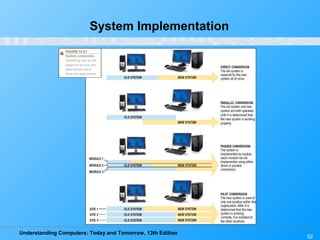
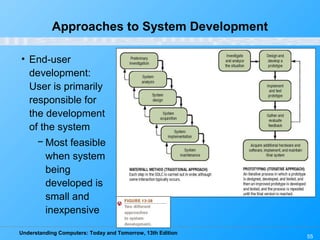
Chapter 12 of 'Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow' discusses information systems and their importance in organizations, outlining who uses them and the various types commonly found. It explains the system development life cycle (SDLC) and the roles of different individuals involved in system development, along with different strategies to approach system development. Additionally, the chapter covers business intelligence, data analysis, and the significance of computer professionals in managing and developing information systems.