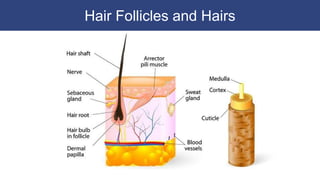
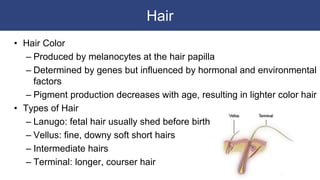
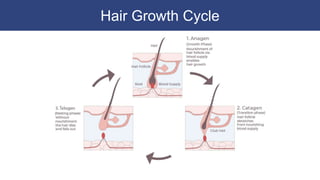
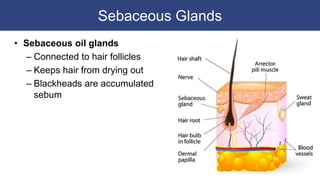
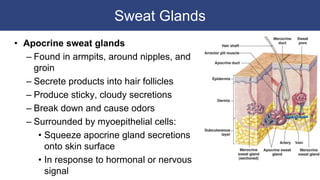
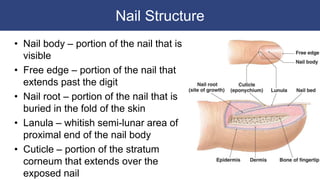
The integumentary system includes accessory structures like hair, hair follicles, sebaceous glands, sweat glands, and nails. Hair provides protection from injury, heat loss, and particles. It is composed of keratinized cells and grows from hair follicles in the dermis. Sebaceous and sweat glands secrete oils and fluids to cool and protect the skin. Nails cover the ends of fingers and toes and are made of packed dead keratinized cells.