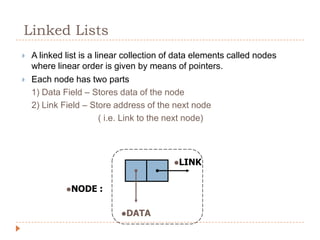
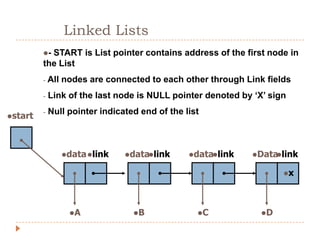
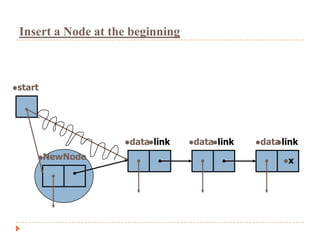
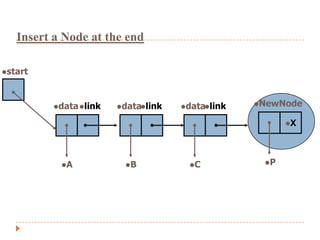
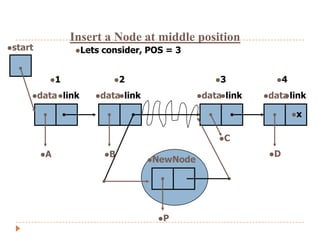
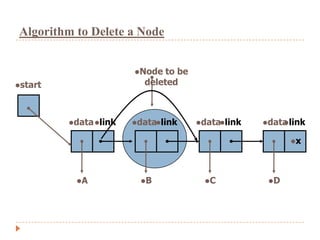
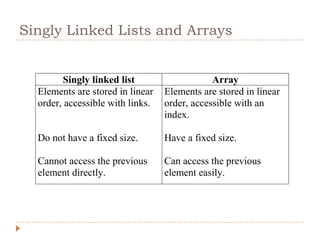
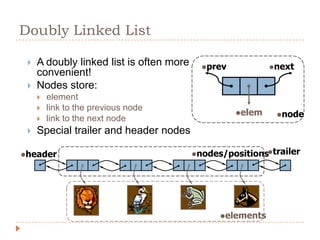
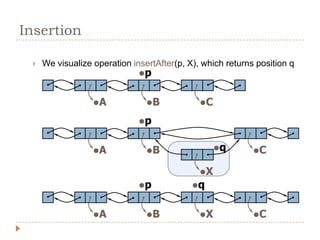
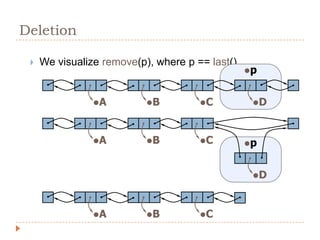
The document discusses lists and linked lists. It defines a list as an ordered collection of items that supports basic operations like adding, deleting, and accessing items. A linked list is a collection of links, where each link contains a data part and a link part pointing to the next link. Each node of a linked list contains a data field storing the data and a link field storing the address of the next node. The document then provides algorithms for common linked list operations like insertion, deletion, searching, and displaying all nodes.