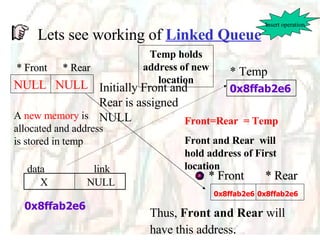
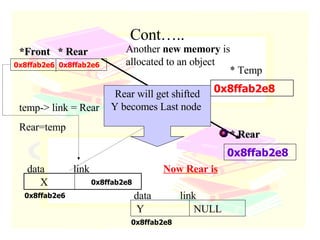
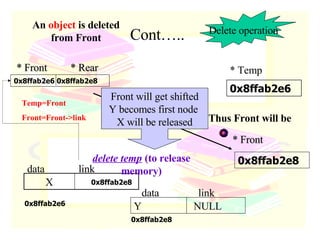
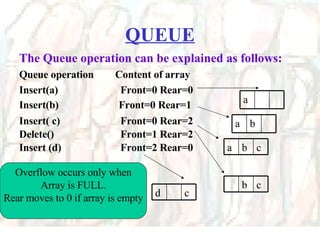
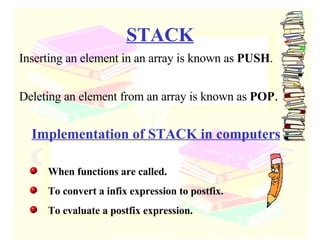
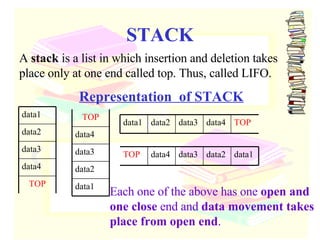
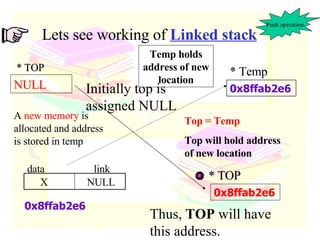
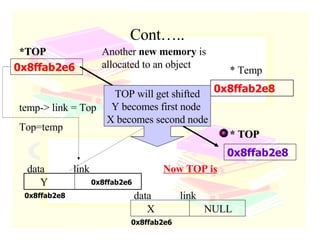
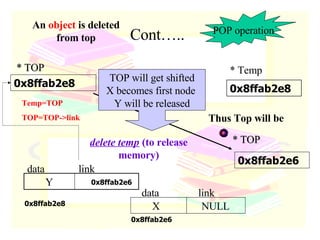
The document discusses stacks and queues as linear data structures. It defines stacks and queues, describes their common operations like push, pop, insert and delete, and ways to implement them using arrays and linked lists. Array implementation of stacks and queues is shown along with diagrams. Linked list implementation of stacks and queues is also discussed with diagrams showing the insertion and deletion of nodes. Sample programs to implement stacks and queues using both arrays and linked lists are mentioned.



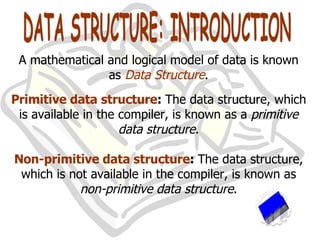
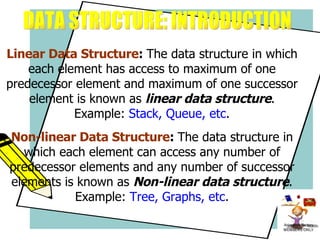
![It is a static data structure . It is a homogeneous collection of data. The elements in the array are stored on consecutive memory locations. Array is also known as a subscripted variable, e.g., A[i] is i th element of the array A. ARRAY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stacks-queues-1195489705431812-4/85/Stacks-Queues-7-320.jpg)



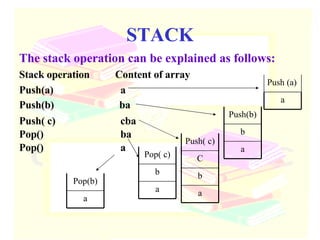

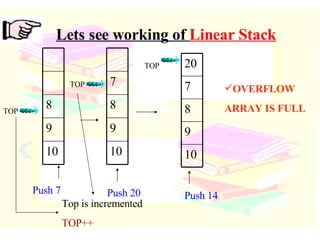
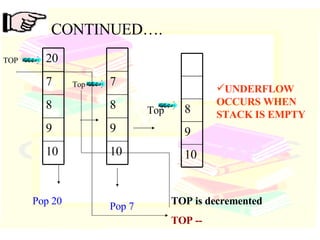
![Linear Stack int S[5]; When PUSH is selected, TOP is incremented, And data is added at that subscript location When POP is selected, TOP is decremented, And data is removed from that subscript location Stack array int TOP; To hold address of location where data is inserted or deleted](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stacks-queues-1195489705431812-4/85/Stacks-Queues-16-320.jpg)







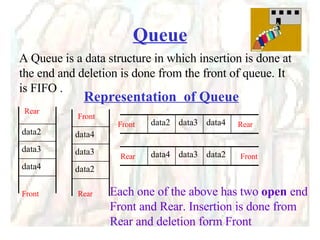


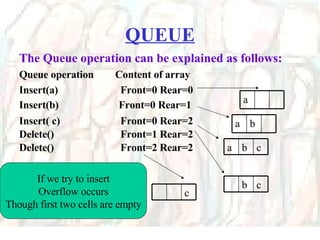
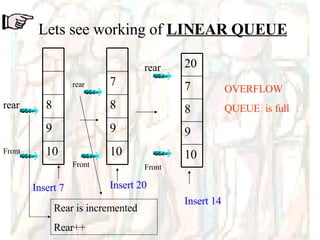
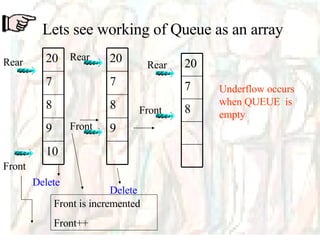
![Linear Queue int Q[5]; When INSERT is selected, Rear is incremented, And data is added at that subscript location When DELETE is selected, Front is decremented, And data is removed from that subscript location Queue array int Front, Rear; To hold address of location where data is inserted or deleted](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stacks-queues-1195489705431812-4/85/Stacks-Queues-34-320.jpg)