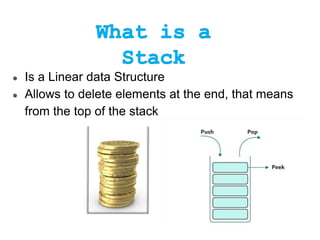
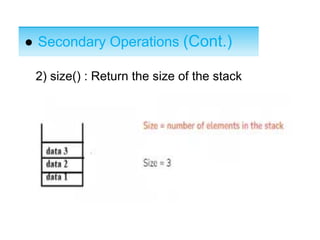
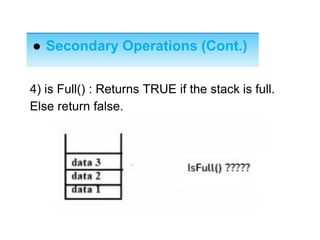
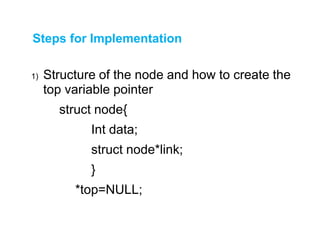
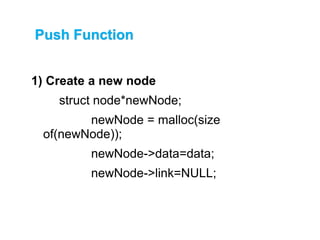
This document describes stacks and their implementation using linked lists. It discusses that stacks are linear data structures that allow deletion from one end only. It outlines primary operations like push and pop and secondary operations like top, size, isEmpty and isFull. It then discusses implementing stacks using arrays or linked lists, with linked lists being preferable when size is unknown. It provides pseudocode for implementing push, pop and peek functions for a linked list stack.