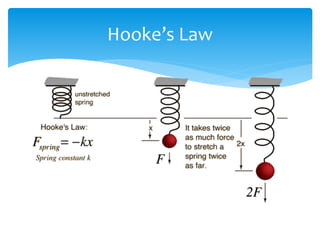
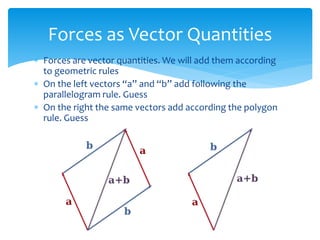
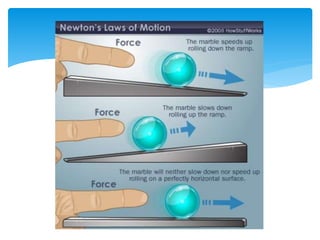
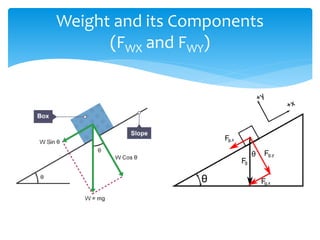
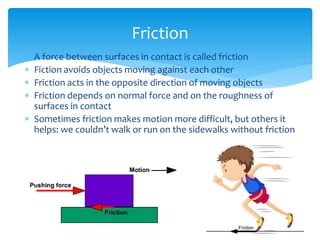
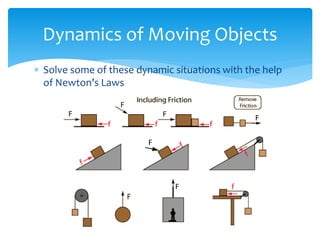
Forces act on objects and can cause changes in motion or shape. Hooke's law states that the force needed to extend or compress a spring is proportional to the distance changed. Forces are vector quantities that combine according to geometric rules. Newton's three laws of motion describe how forces cause changes in motion: the first law states an object in motion stays in motion unless acted on by a net force, the second law relates net force, mass, and acceleration, and the third law states that every force induces an equal and opposite reaction force. Friction and tension are types of contact forces that influence motion. Dynamics problems apply Newton's laws to analyze forces and motion in physical situations.