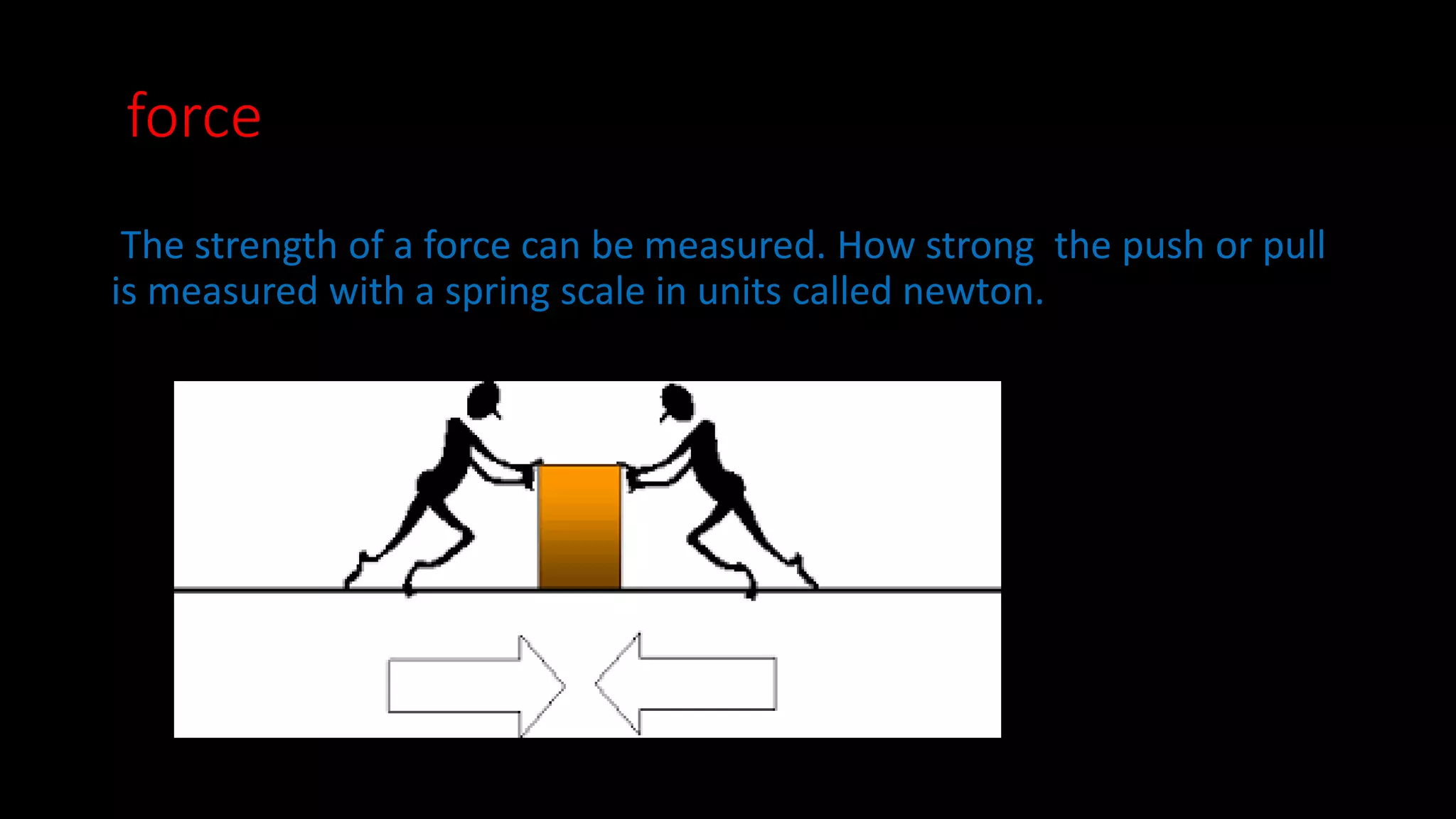
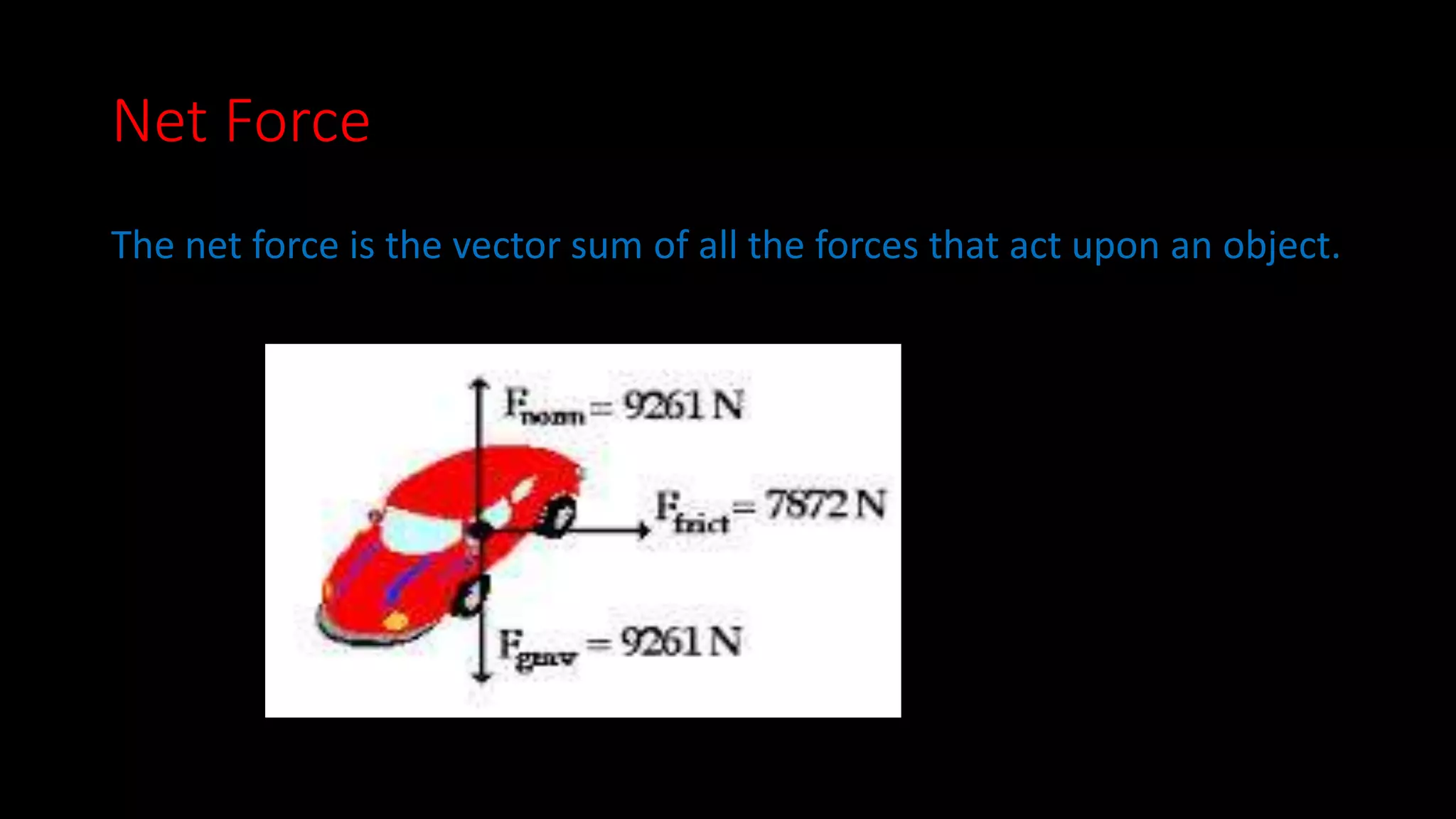
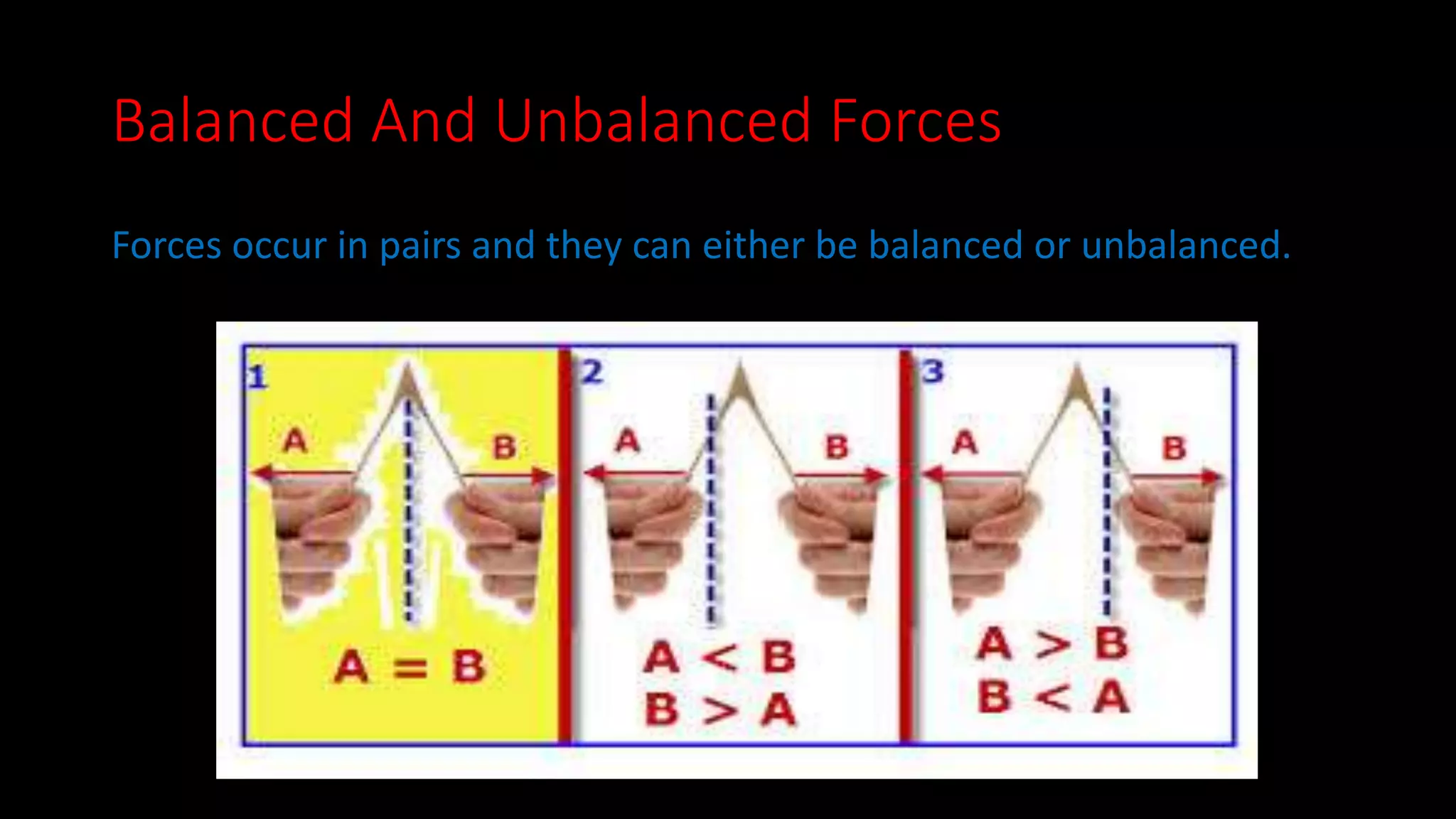
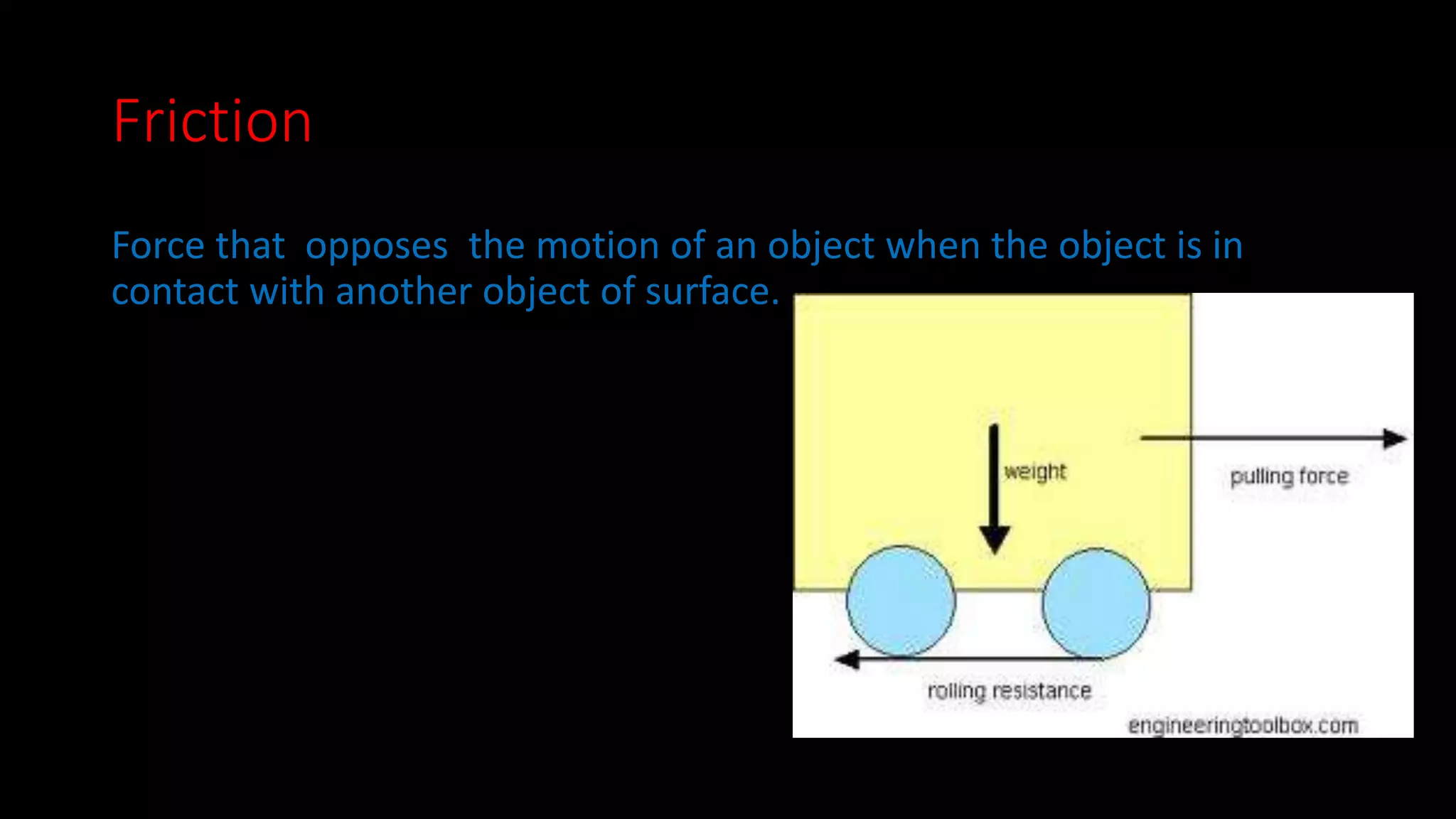
This document provides an overview of key concepts in Newtonian mechanics including Newton's laws of motion, force, inertia, balanced and unbalanced forces, friction, net force, mass, acceleration, and force diagrams. Newton's first law states that objects in motion stay in motion and objects at rest stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton's second law establishes the relationship between net force, mass, and acceleration. Newton's third law describes that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.