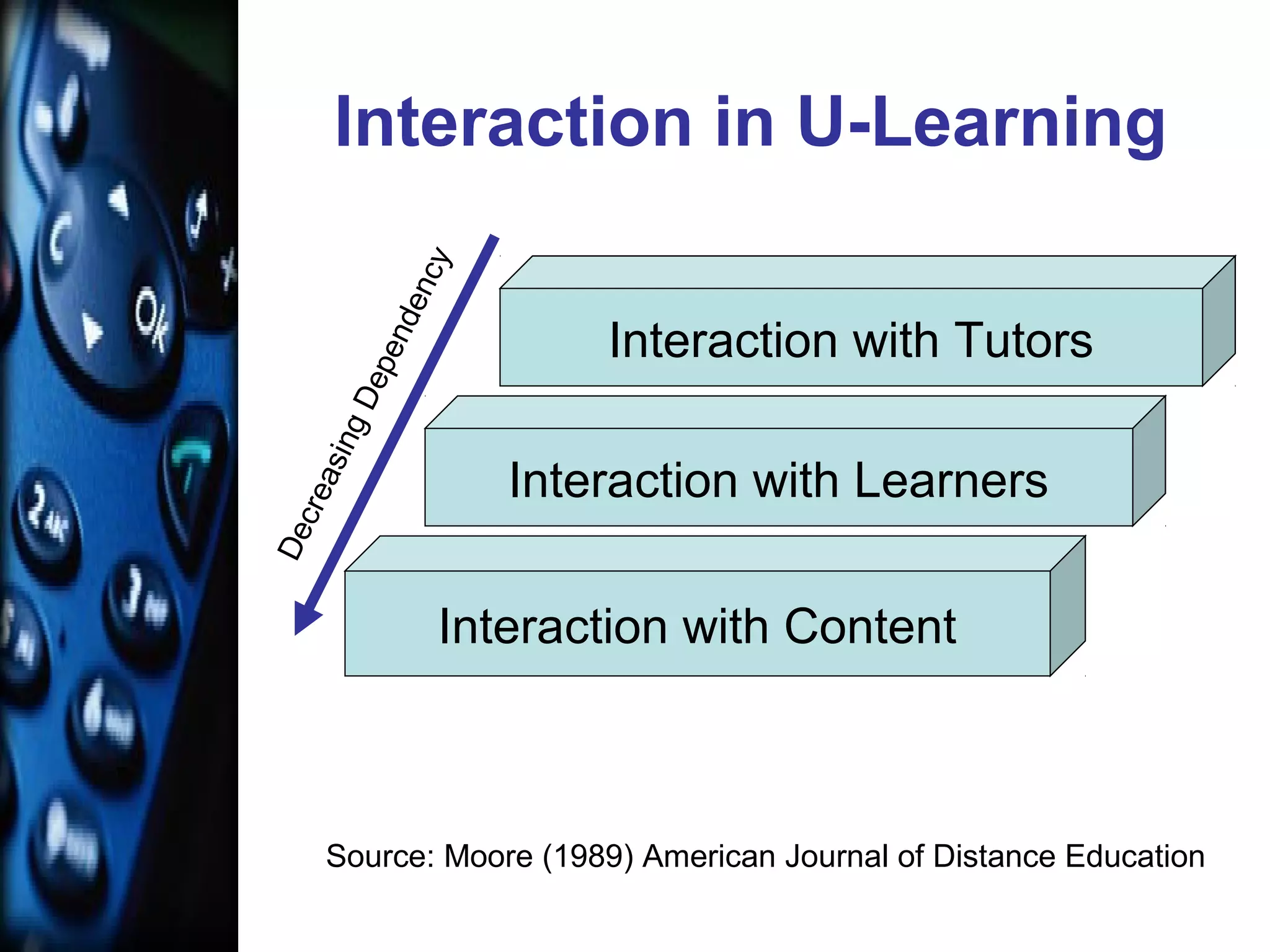
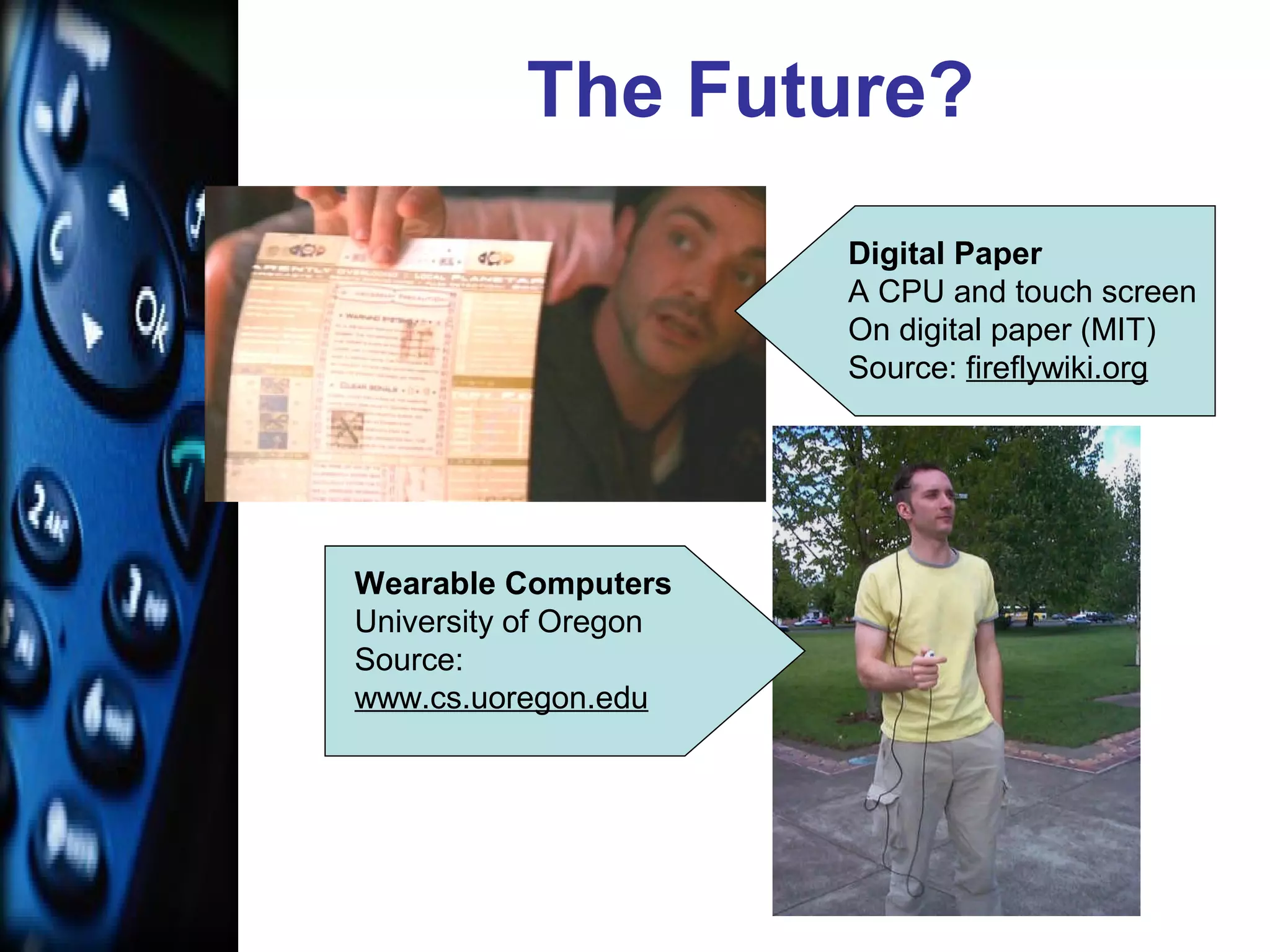
This document discusses the rise of mobile learning or "u-learning" due to changing habits of digital native students. It notes that students now spend much more time engaged with digital media like games and phones than traditional activities like reading. This has caused a paradigm shift where educators must adapt to students who are comfortable multi-tasking and learning on the go using mobile devices. The mobile phone is predicted to become the main platform for u-learning in the next five years as phones converge different functions and allow learning interactions and access to content anywhere through wireless networks. The document outlines some current mobile learning applications and resources for educators wanting to implement u-learning.