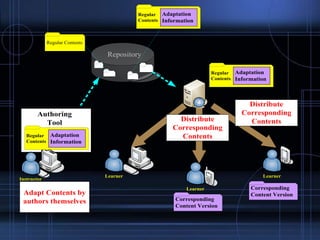
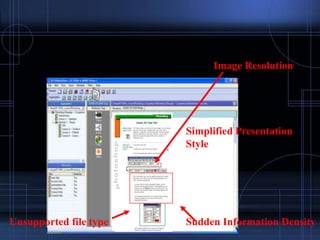
Mobile learning has evolved from using laptops to now utilizing various mobile devices like smartphones. It allows learning to occur independently of location and time. Various mobile learning systems have been developed for specific domains like museum tours or outdoor activities. Challenges include cost, compatibility across devices and platforms, and intermittent network connections. New technologies like moblogging, podcasting, and QR codes are expanding mobile learning opportunities. Businesses can benefit from just-in-time, job site training on mobile devices. The future of mobile learning involves ubiquitous access to information through voice and location-aware devices tailored to individual interests.