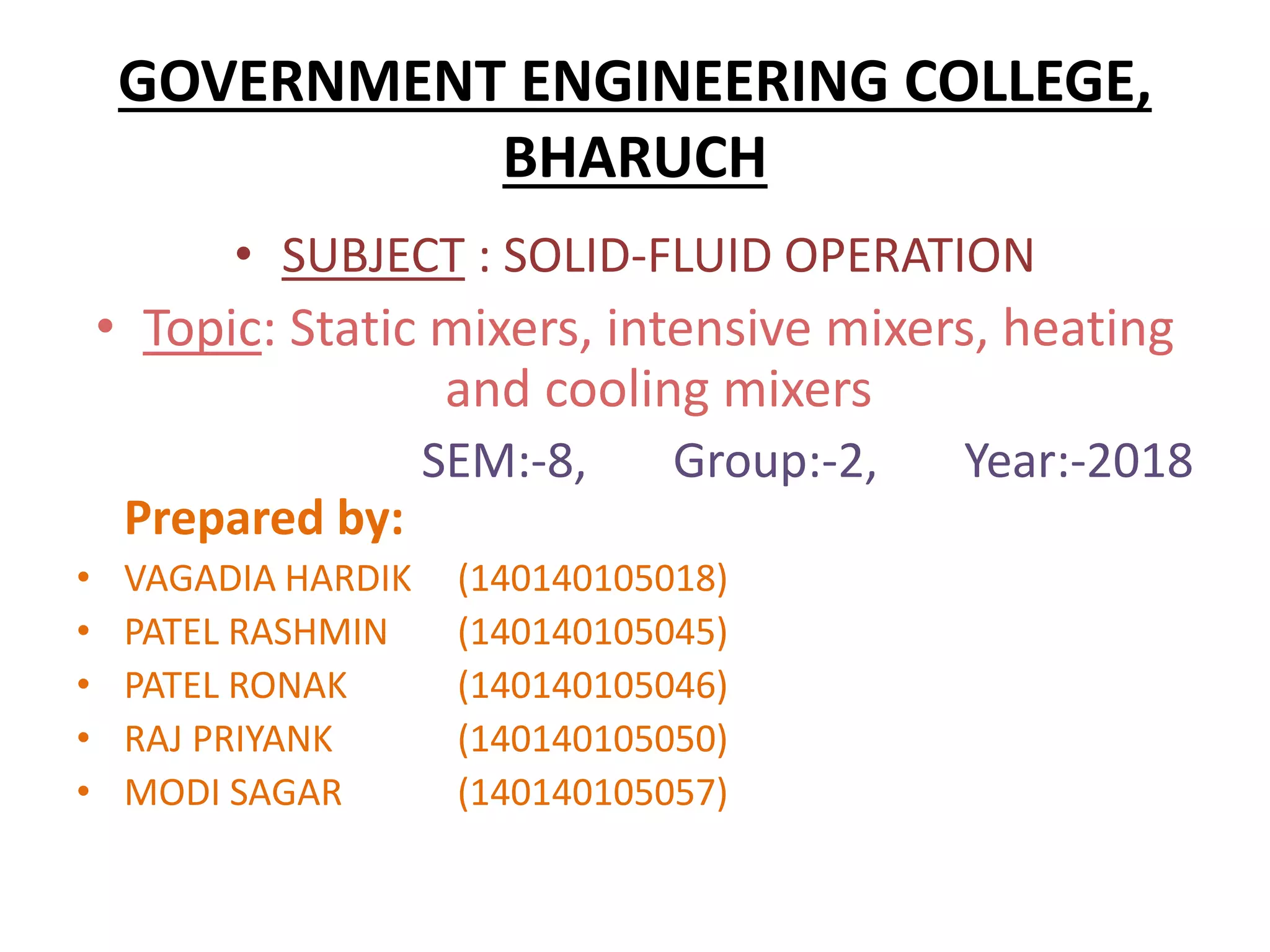
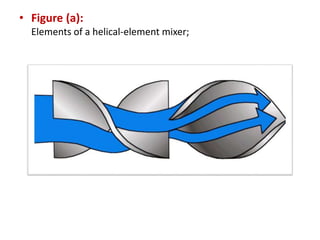
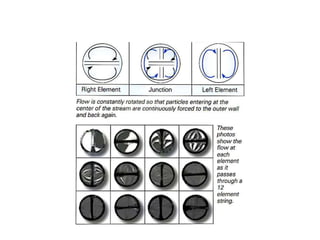
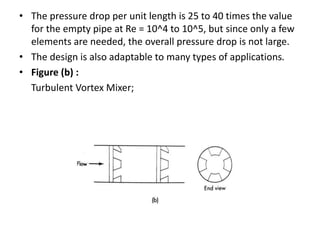
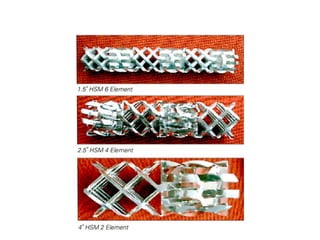
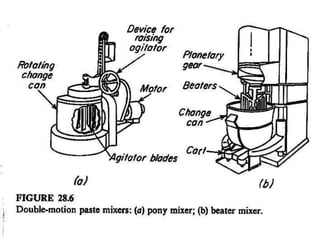
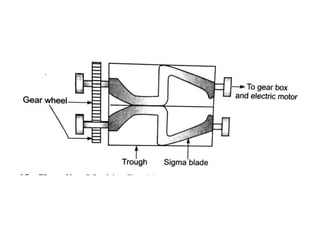
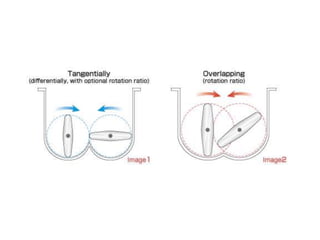
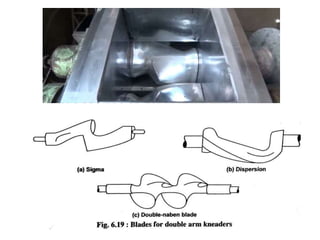
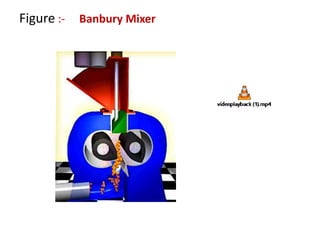
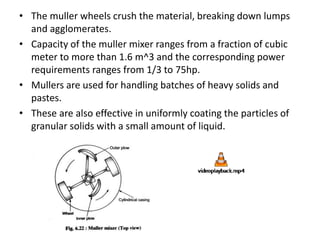
This document summarizes different types of mixers used in industrial processes. It describes static mixers, which mix fluids using inserts in pipes without moving parts, including helical element mixers and turbulent vortex mixers. It also describes intensive mixers like change-can mixers, kneaders including sigma and Banbury mixers, mixer extruders, and muller mixers. Finally, it discusses heating and cooling mixers like high speed mixers and cooling mixers used to precisely control temperature during industrial mixing.