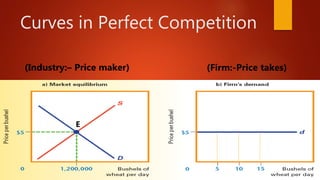
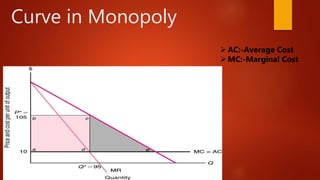
This document discusses market structure and defines the key types: perfect competition, monopoly, and monopolistic competition. Perfect competition has many small sellers and buyers, homogeneous products, free entry and exit, and transparent information. A monopoly has a single seller with a unique product and controls price and quantity. Monopolistic competition has multiple firms producing differentiated products facing downward sloping demand curves. The main differences are around the number of buyers and sellers, product homogeneity, and price uniformity across the types.