Embed presentation
Downloaded 19 times



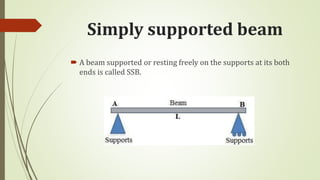

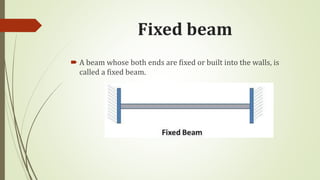
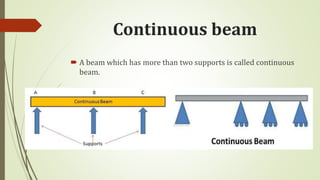

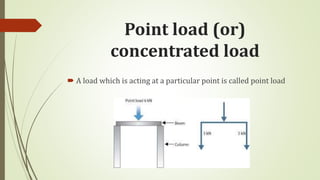





A beam is a structural member that is supported along its length and subjected to external forces acting perpendicularly to its central axis. There are different types of beams including cantilever, simply supported, overhanging, fixed, and continuous beams. Beams can experience different types of transverse loading such as point loads, uniformly distributed loads, and uniformly varying loads.













