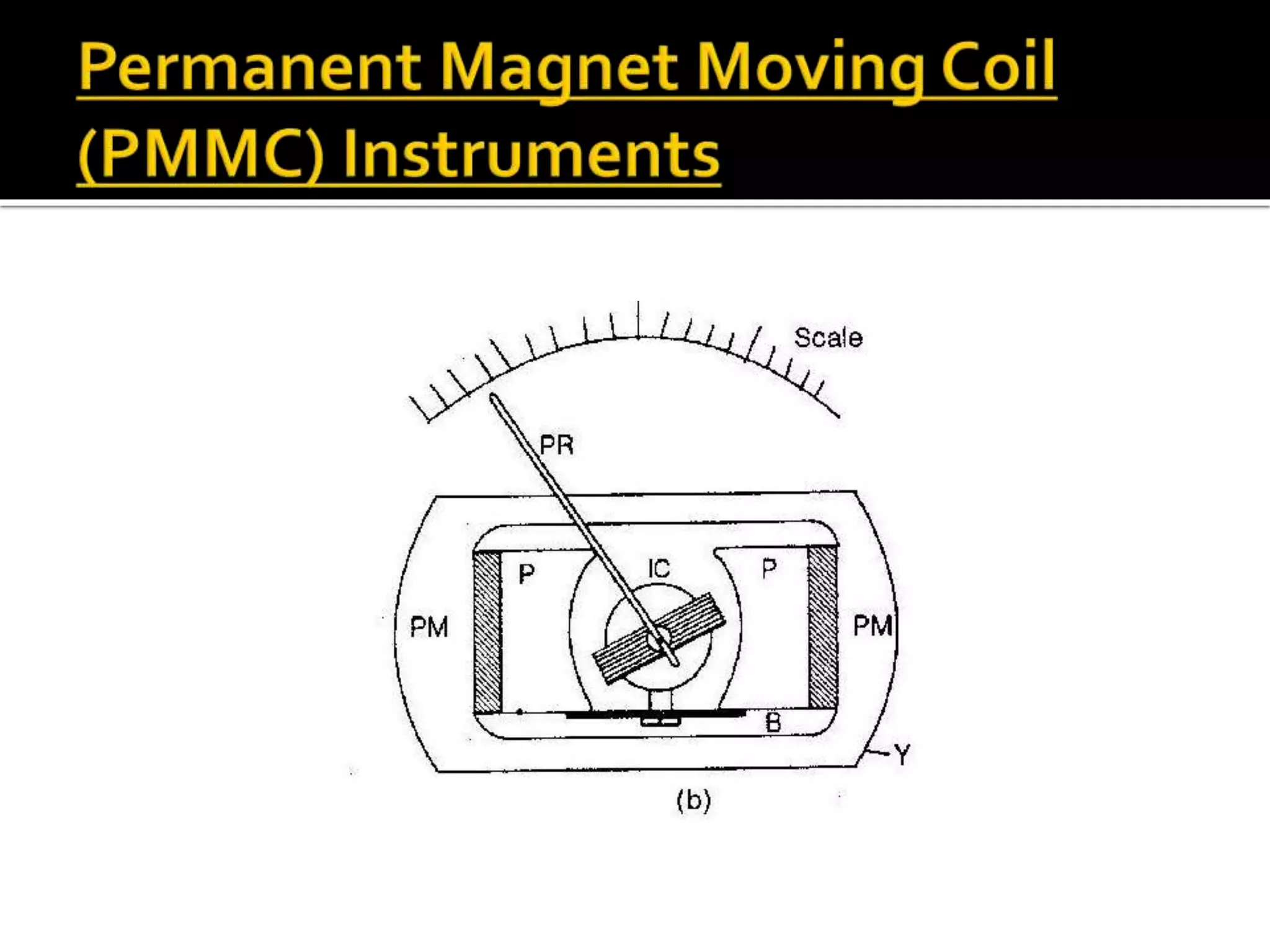
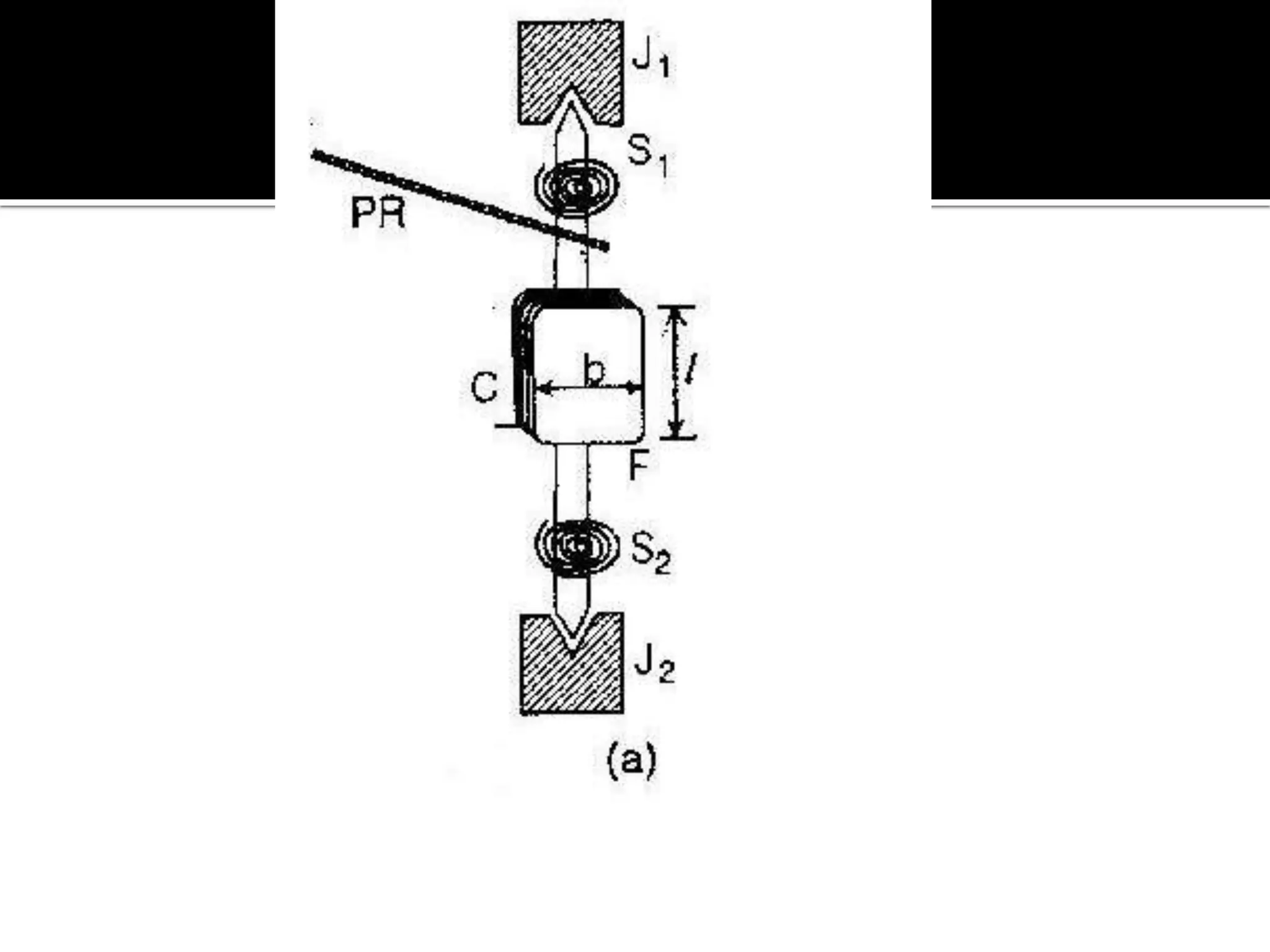
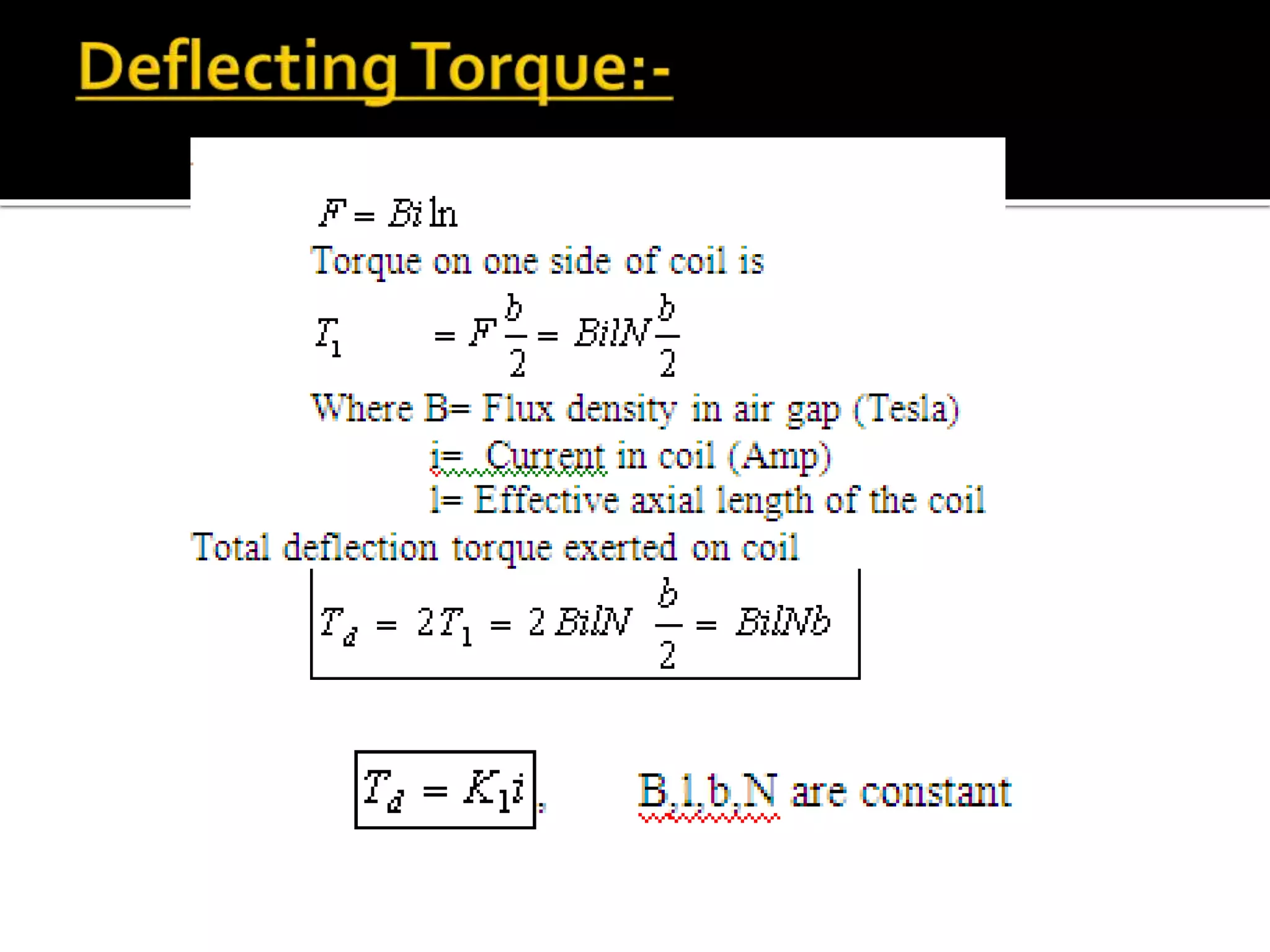
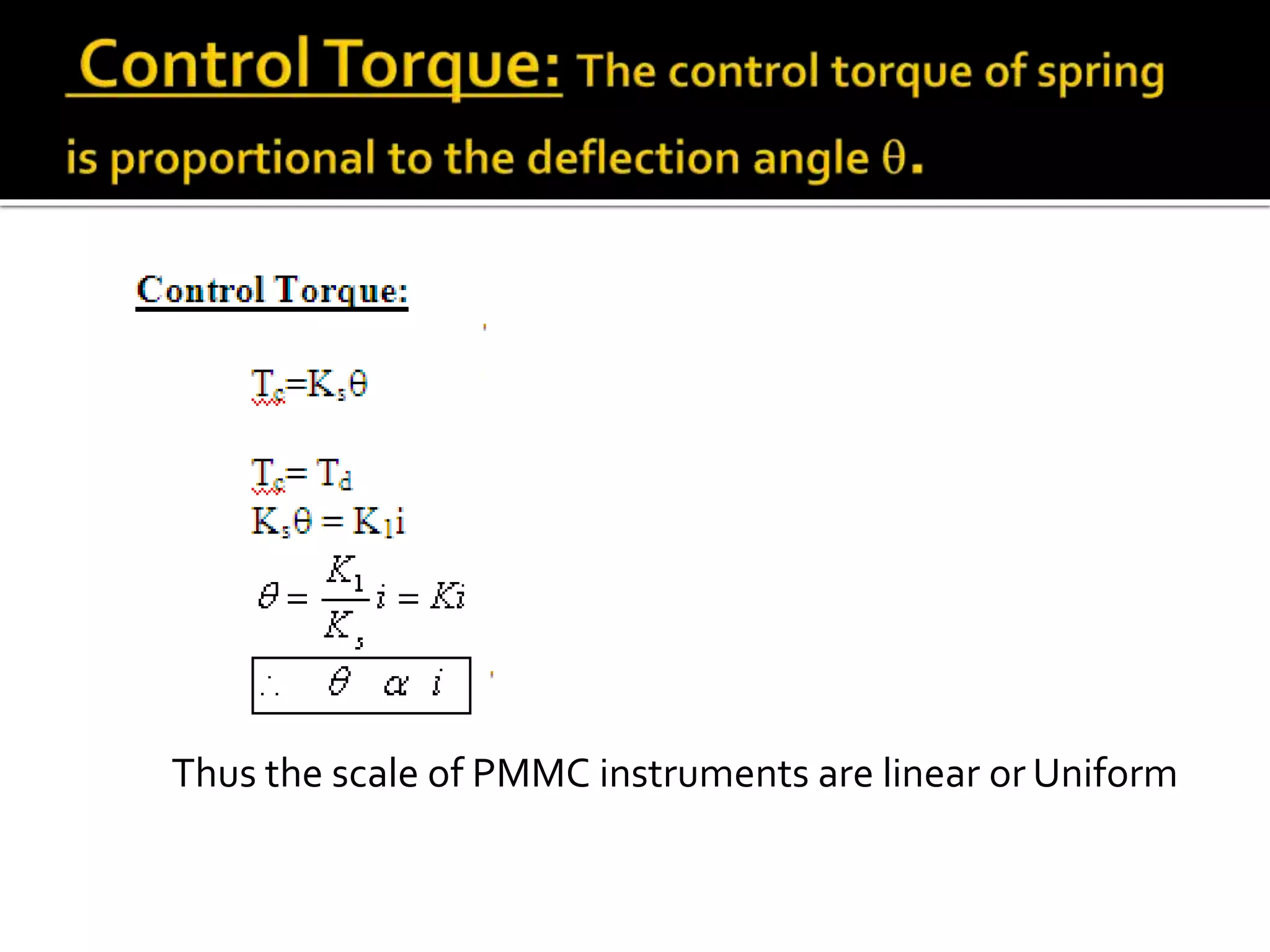
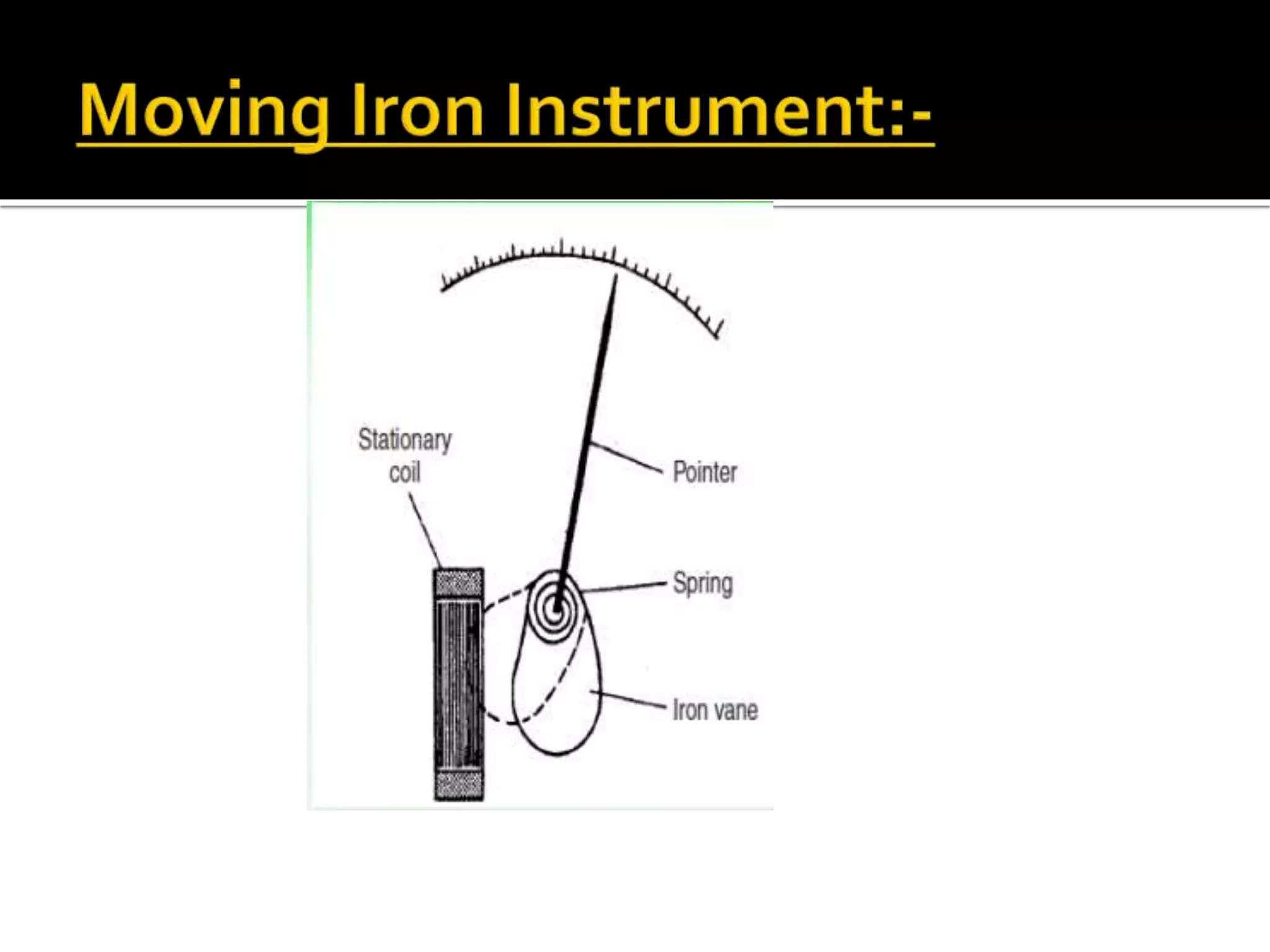
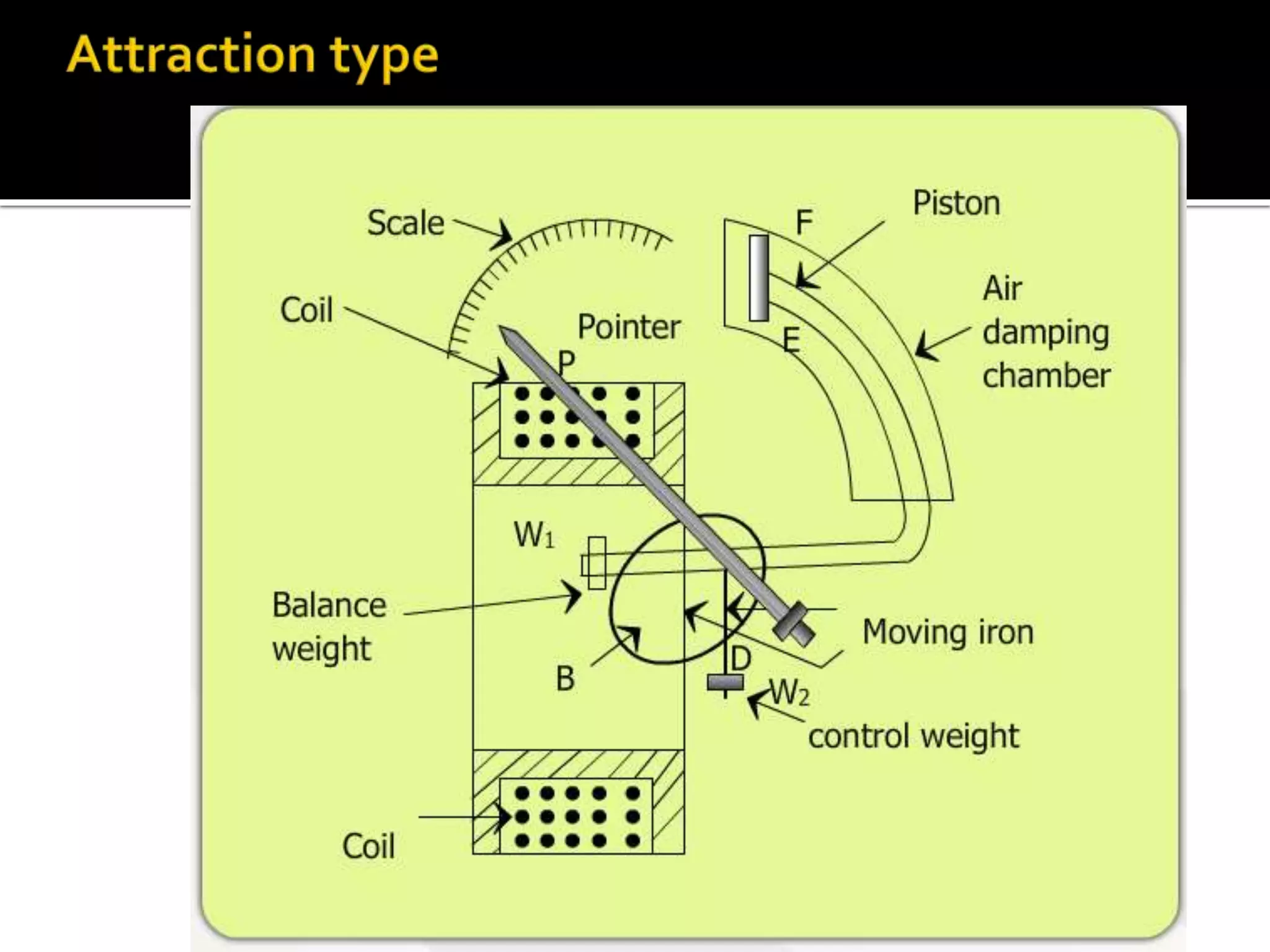
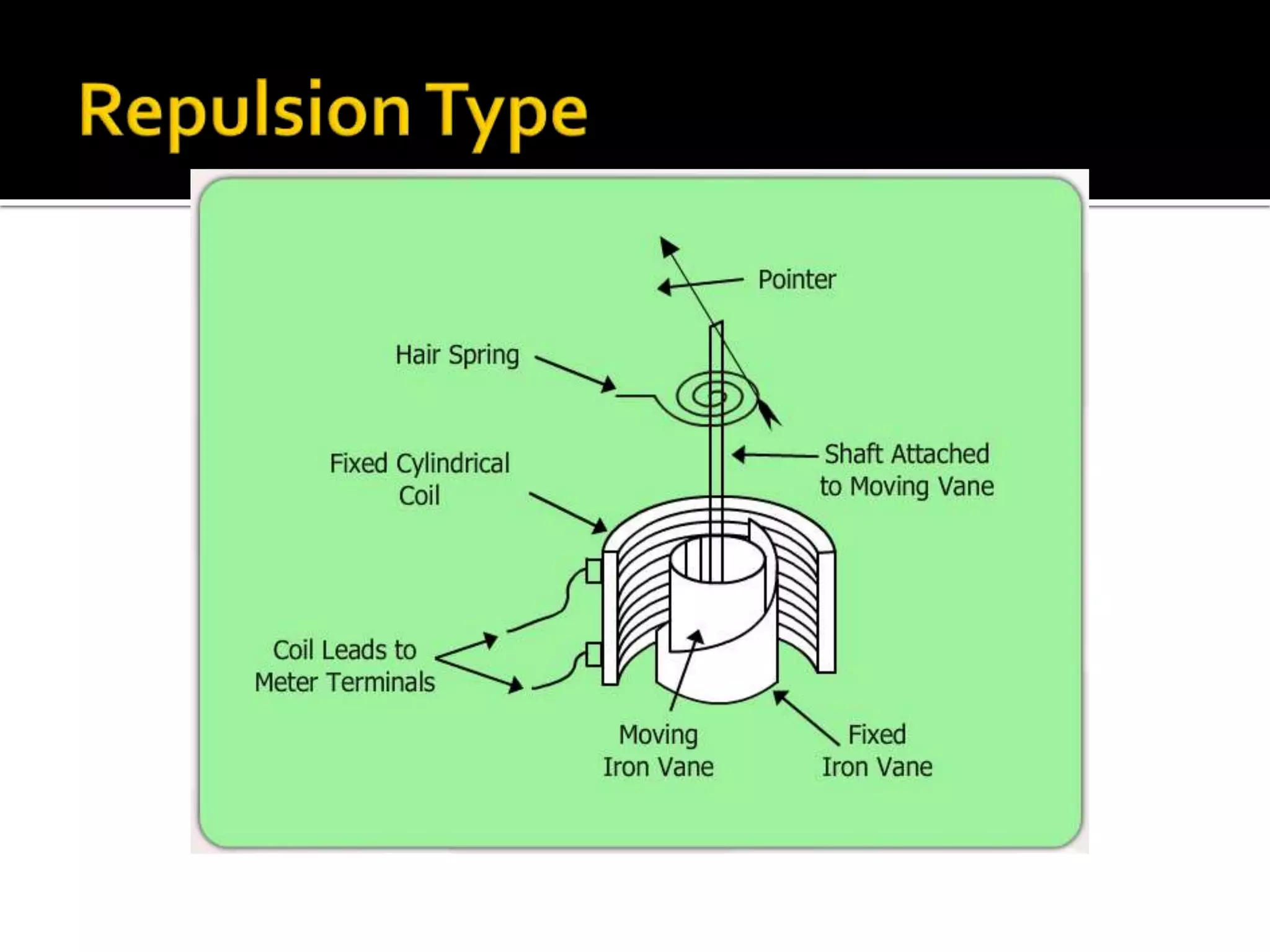
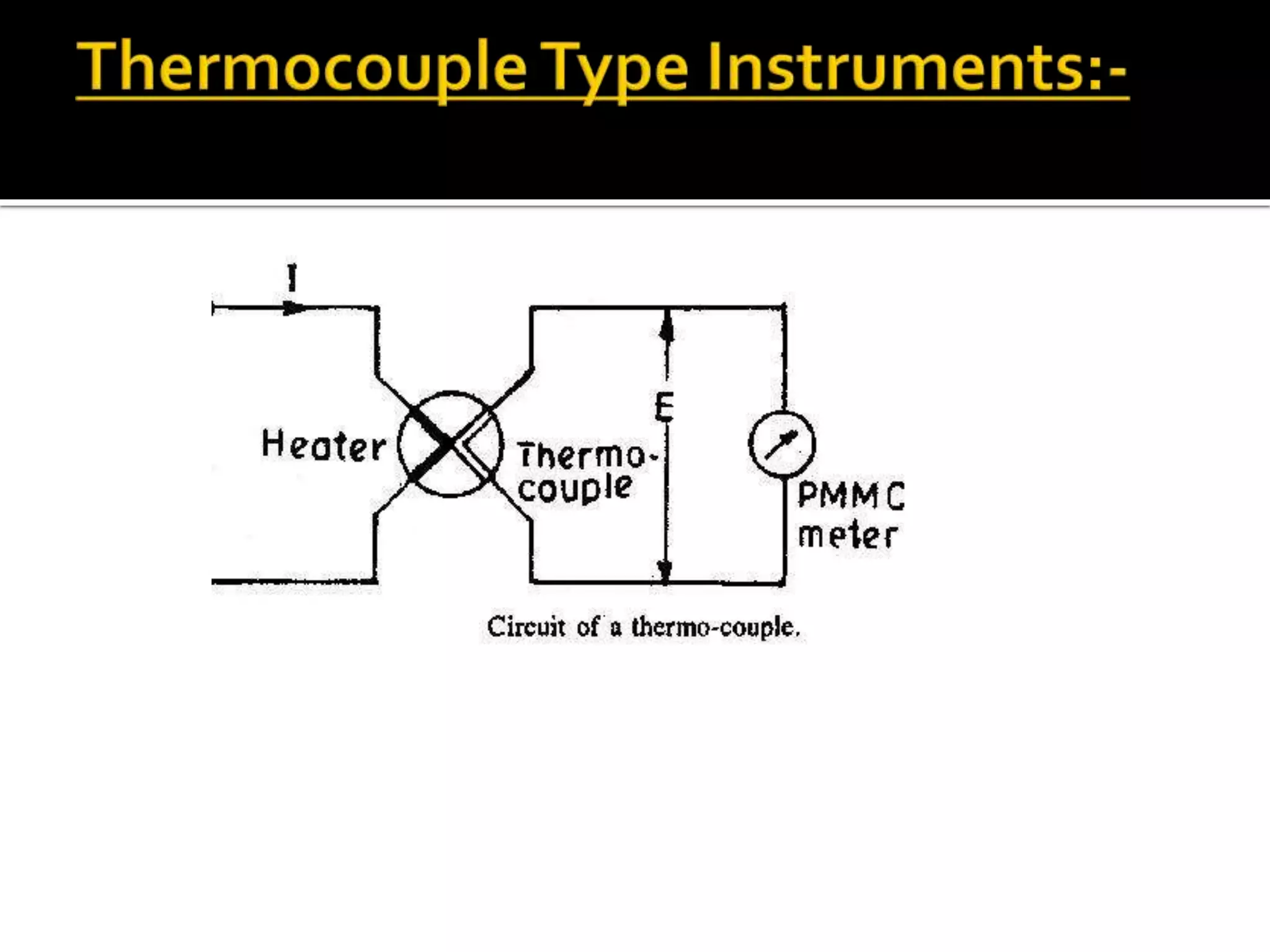
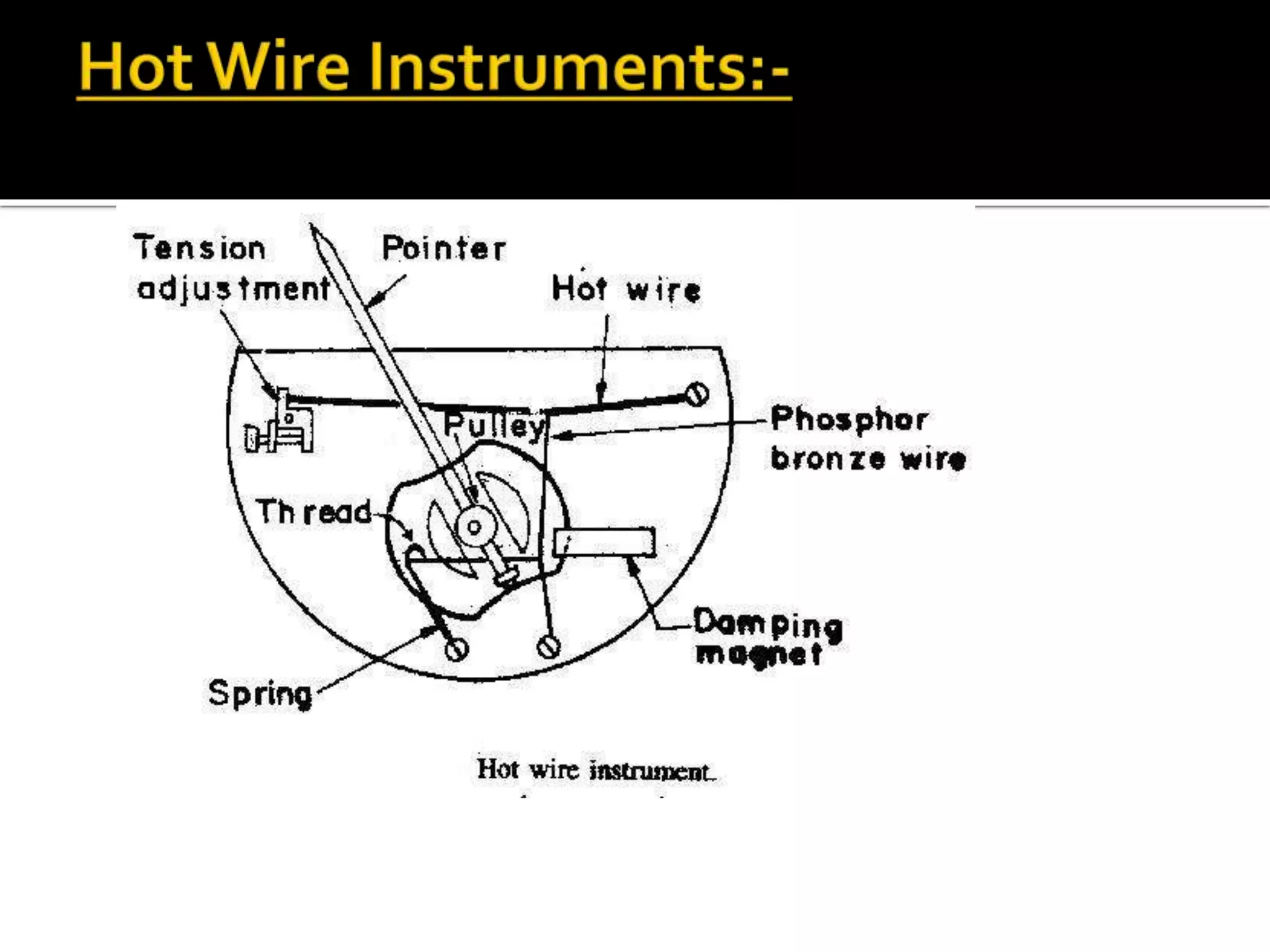
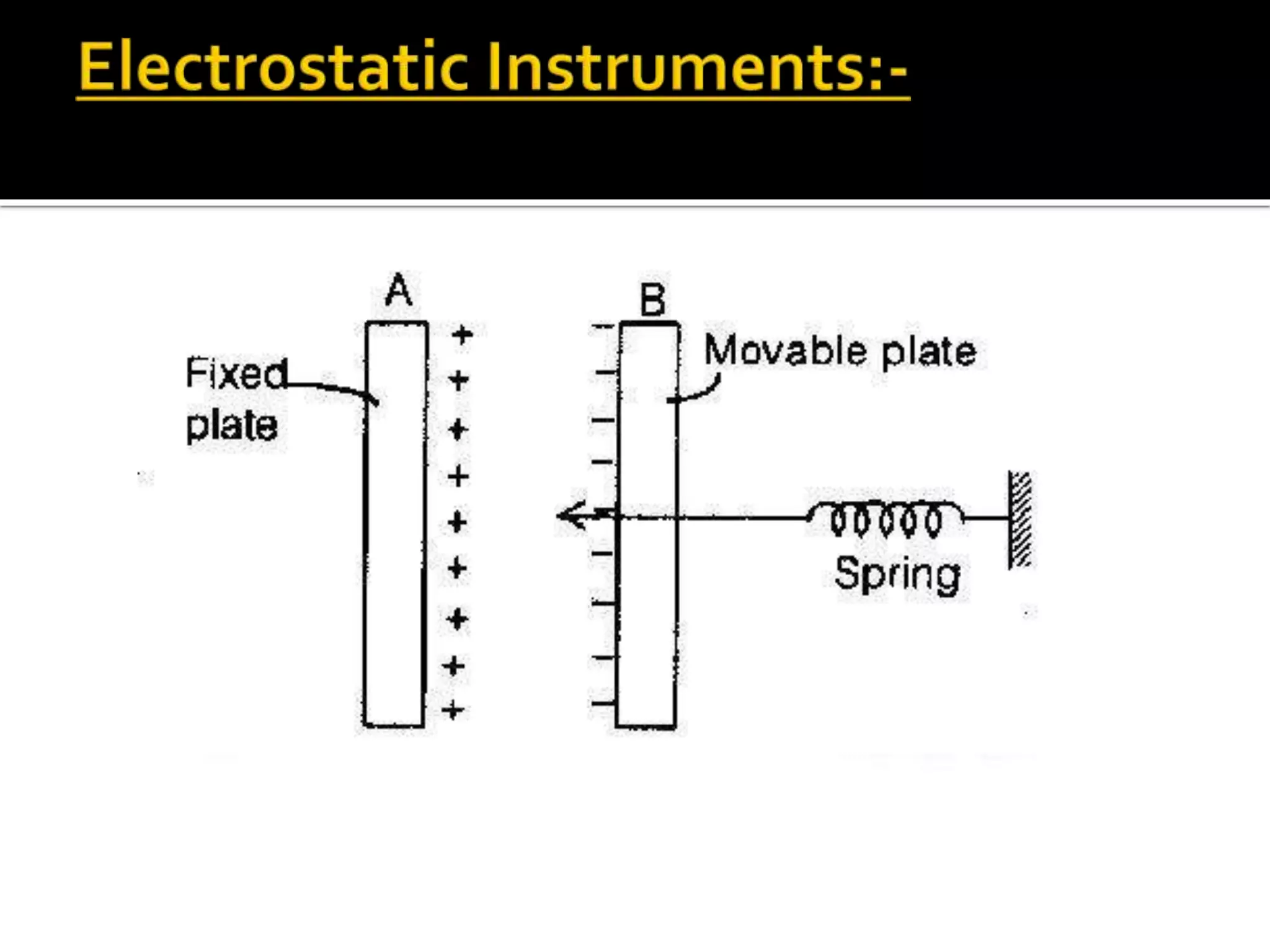
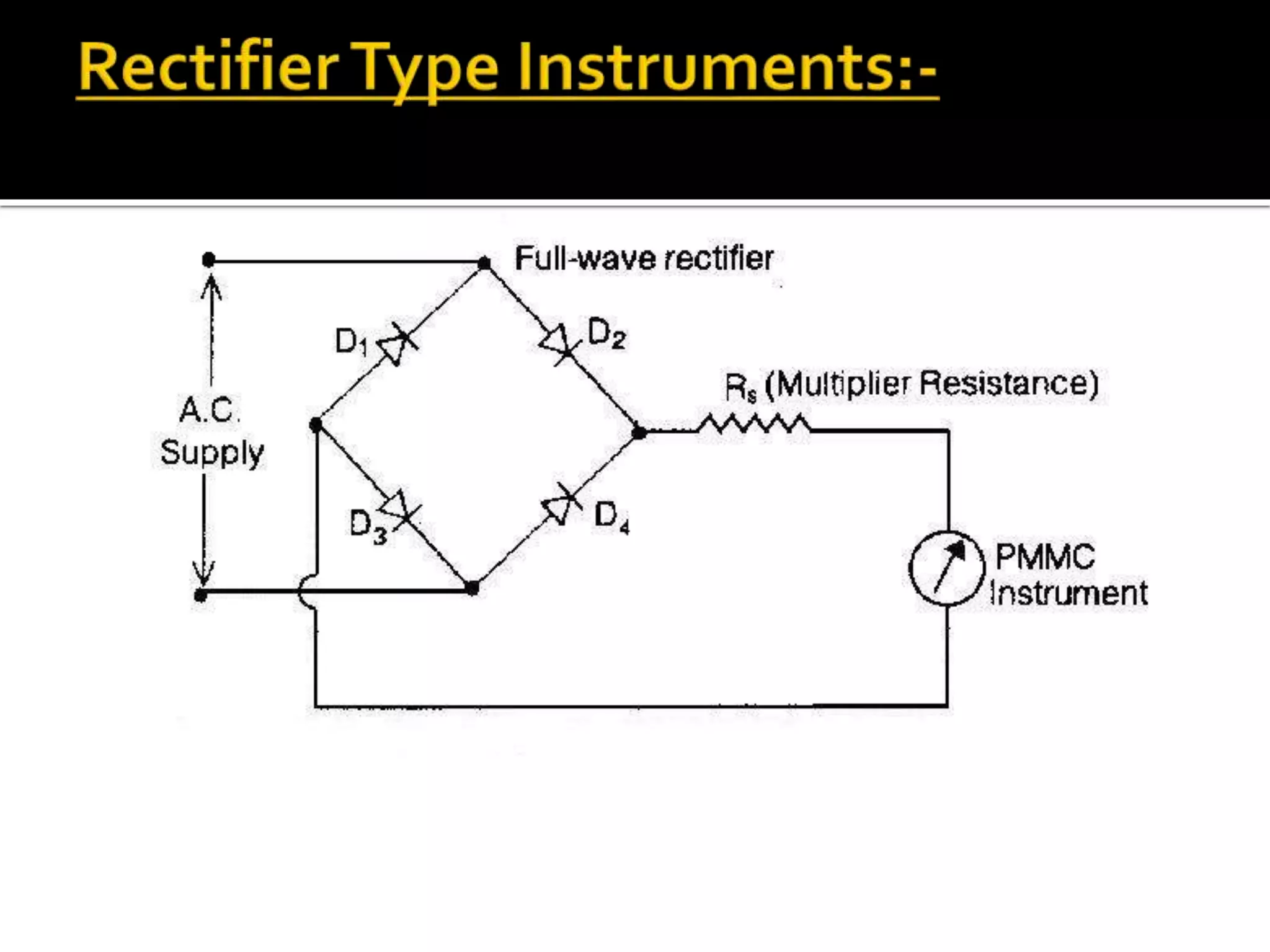
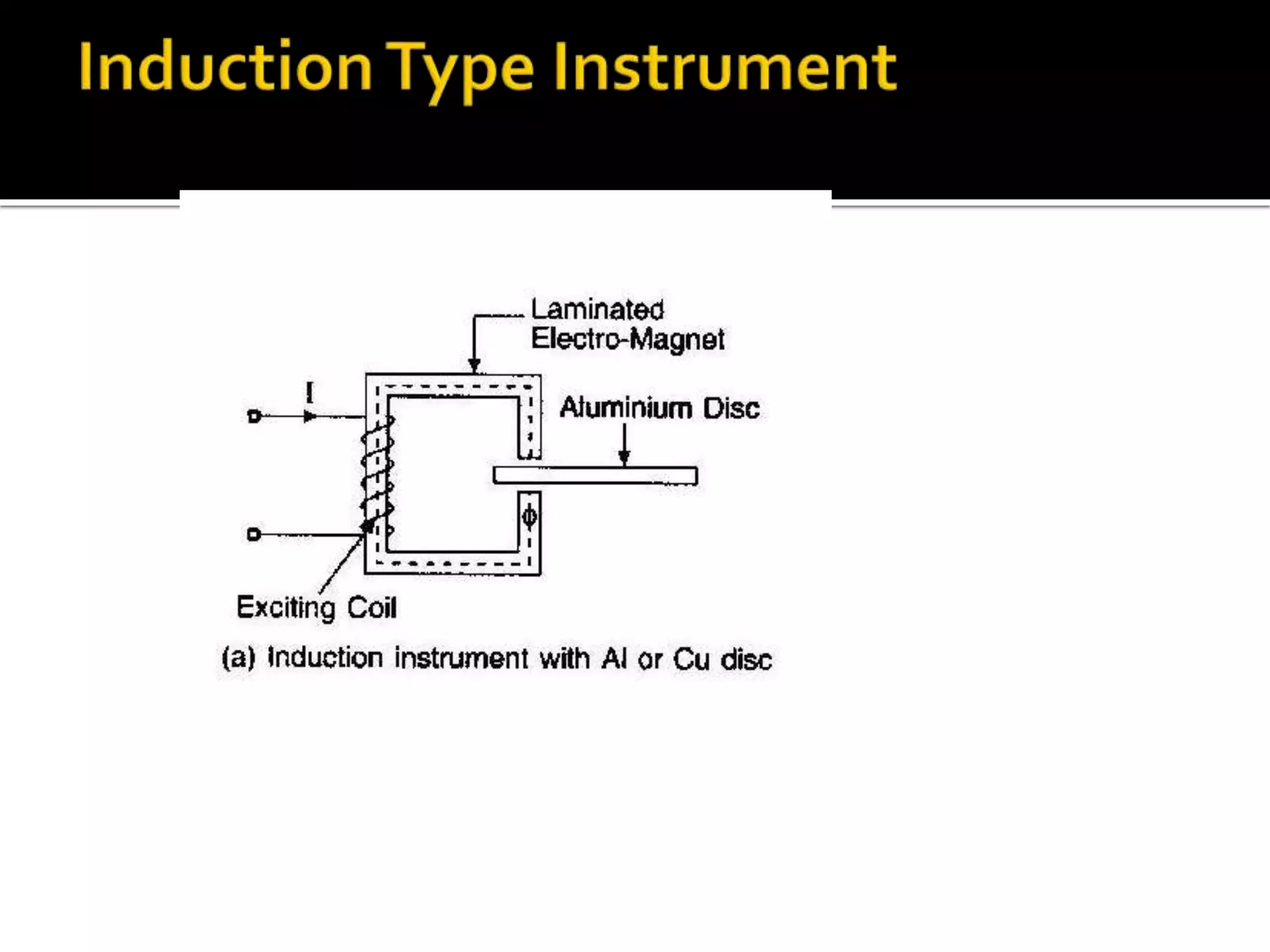
This document describes different types of instruments used for measurement of electrical quantities including permanent magnet moving coil instruments, moving iron instruments, electrodynamic instruments, hot-wire instruments, thermocouple instruments, induction-type instruments, electrostatic instruments, and rectifier-type instruments. It provides details on the working principles, advantages, disadvantages and applications of these instruments.