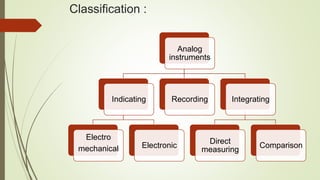
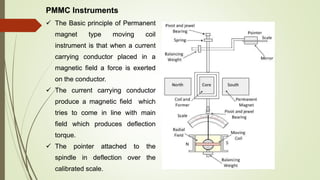
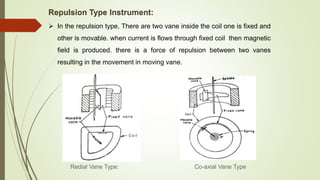
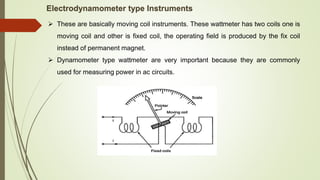
Analog instruments measure continuous variables like voltage and current. Common analog instruments include moving coil, moving iron, and dynamometer types. Moving coil instruments use a permanent magnet field to induce torque on a current-carrying coil. Moving iron instruments operate on attraction or repulsion of an iron core. Dynamometer instruments have fixed and moving coils to measure power. Energy meters also use induction to rotate a disk and register consumption. Instrument transformers like current and potential transformers allow measurement of high voltages and currents safely at lower levels suited for instruments.