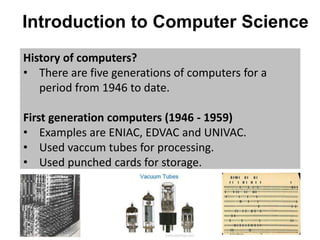
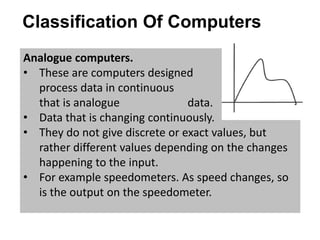
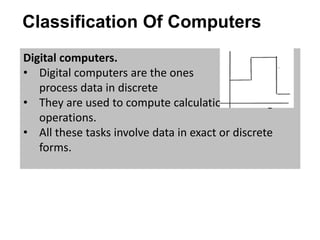
The document provides an overview of computer science, including a definition of computers and their history through five generations from 1946 to the present. It covers different classifications of computers based on size, type, and purpose, highlighting supercomputers, mainframe computers, mini computers, and microcomputers, as well as digital, analogue, and hybrid computers. Additionally, it explains the usage of general-purpose and special-purpose computers in various fields, along with applications for each type.