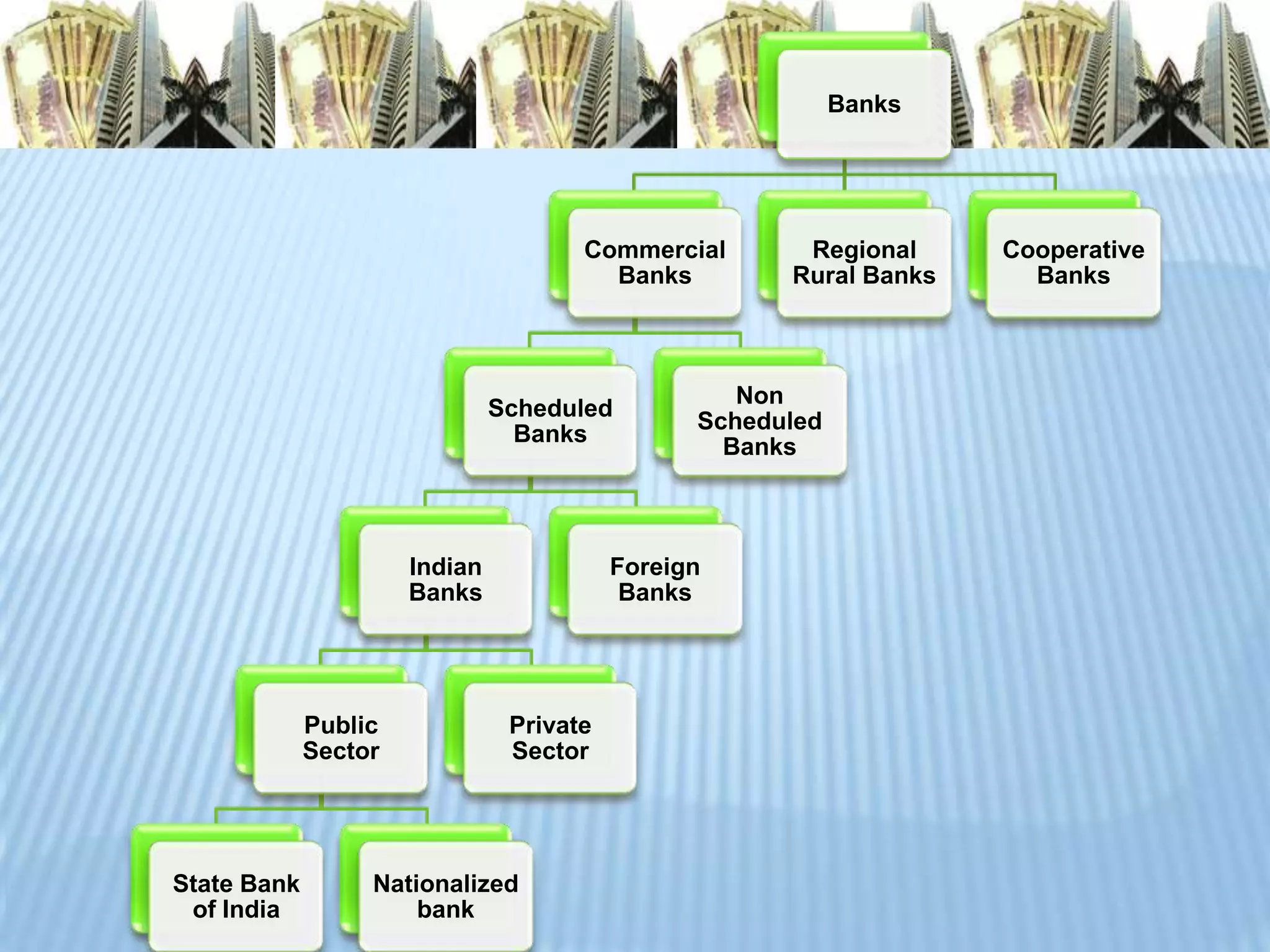
There are several types of banks in India. The main types are scheduled banks, which must meet certain criteria to be included in the second schedule of the RBI Act, and non-scheduled banks. Scheduled banks can be further divided into public sector banks that are majority owned by the government, private sector banks owned by private individuals, foreign banks registered abroad but operating in India, and cooperative banks established under the Cooperative Credit Societies Act. Other bank types include regional rural banks focused on rural agriculture financing, and the State Bank of India which was formed when the government took over the Imperial Bank of India.