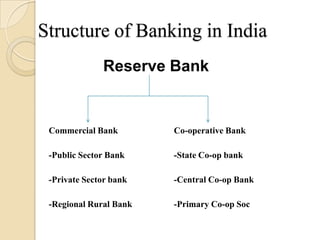
This document provides an overview of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). It discusses the RBI's history, governance structure, key roles as the central bank and monetary authority of India including regulating the financial system, managing foreign exchange and currency, and its developmental functions. The document also outlines the RBI's objectives in being established, its subsidiaries, and instruments used for credit control.