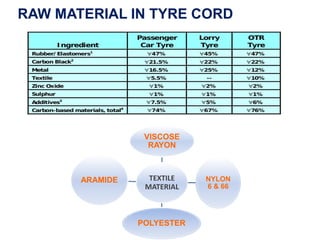
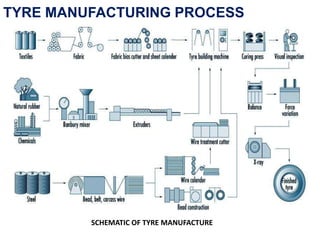
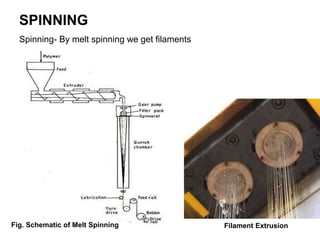
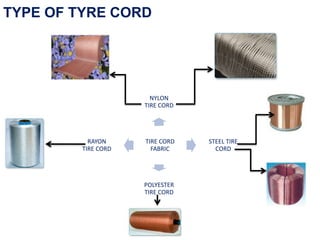
The document discusses the manufacturing process of tyre cord. It begins with an introduction to tyre cord and its important functions. It then describes the raw materials used, which include polyester, rayon, nylon, aramid and steel. The manufacturing process involves steps like spinning, twisting, cabling, weaving, dipping and vulcanization. Key properties that tyre cord provides are high tenacity, toughness and fatigue resistance. Finally, the document notes that tyre cord finds application in automotive tires for passenger cars, trucks, buses and other off-road vehicles.