This lab report summarizes 3 experiments on the mechanisms of a conventional loom:
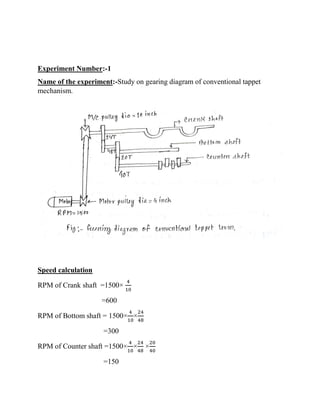
1) Studying the gearing diagram and calculating shaft speeds and gear teeth numbers.
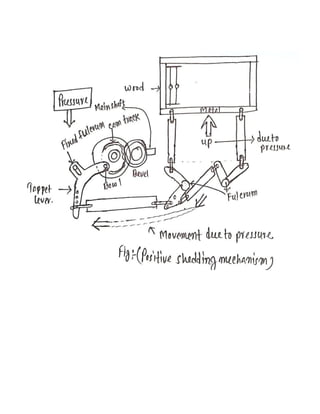
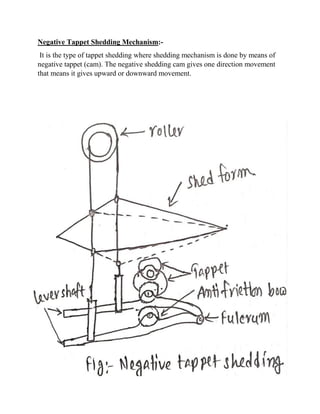
2) Studying positive and negative tappet shedding mechanisms and their parts.
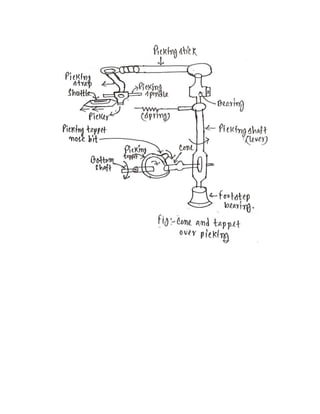
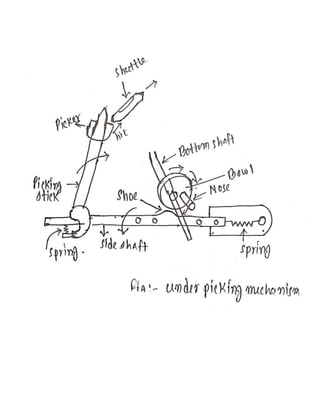
3) Studying overpicking and underpicking mechanisms, identifying their parts, and explaining how each works.
The report provides details on the objectives, parts, principles, and uses of each mechanism studied. The commentary reflects on learning about important loom components and how the experience could apply to future work.