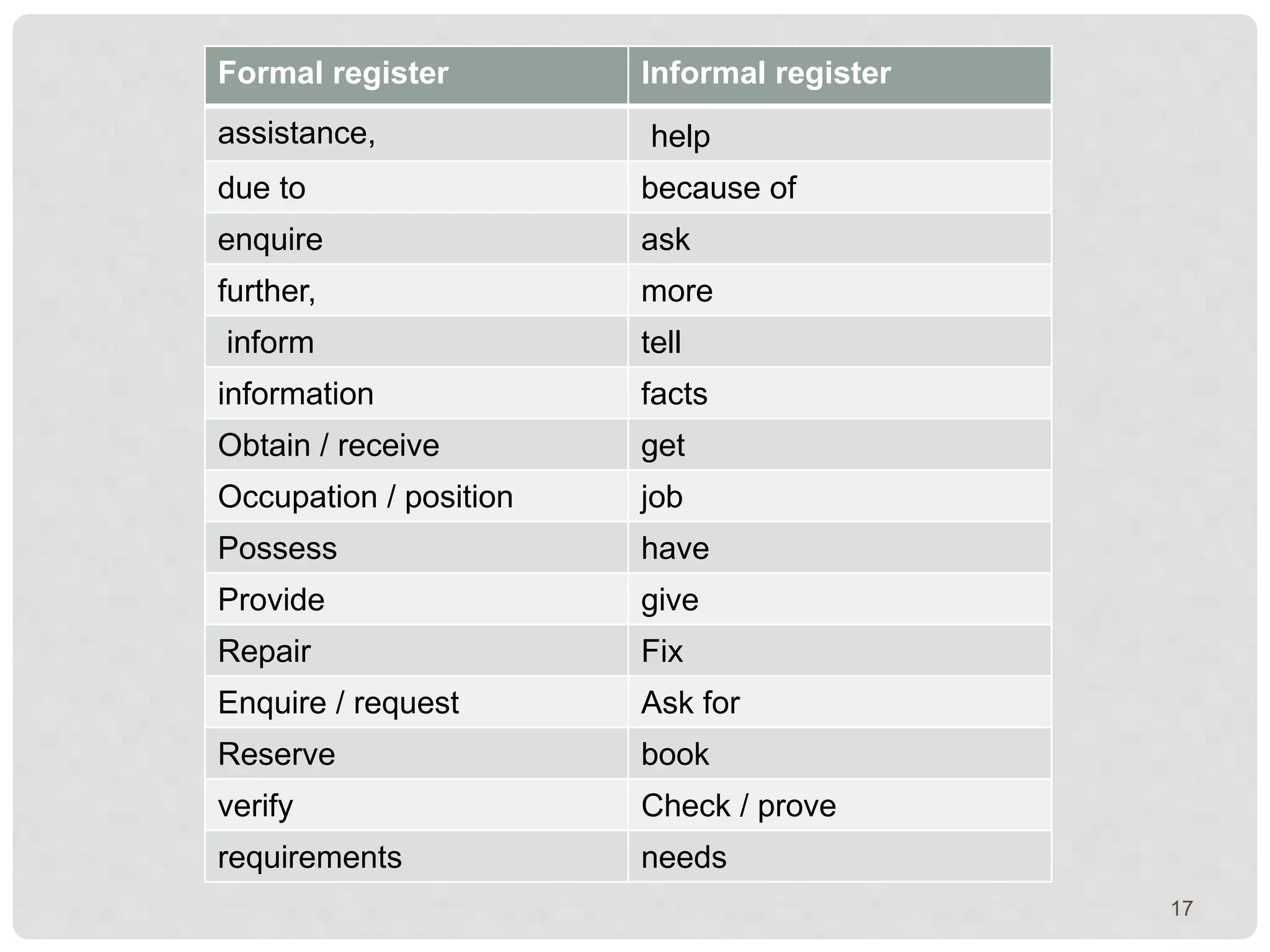
This document provides information on conditional clauses and ethics. It discusses different types of conditional clauses including zero, first, second, and third conditionals. It explains how to use each conditional to talk about the present, future, or past. The document also provides examples of conditional clauses. Additionally, it discusses strategies for writing for and against essays, making suggestions, greetings and closings in formal letters, and includes lists of useful phrases for business correspondence.