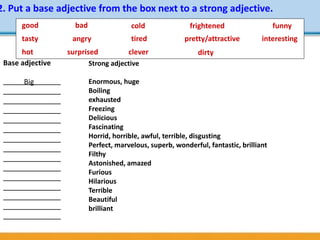
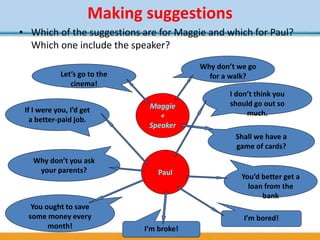
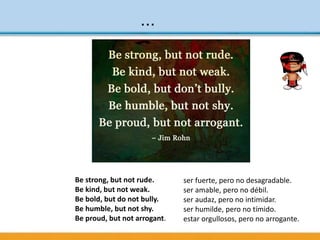
Unidad 8 covers key English language concepts including conditionals, time clauses, base and strong adjectives, and making suggestions. It includes exercises to practice these concepts through dialogues and grammar tests, emphasizing their application in real-life situations. The document also features motivational quotes and resources such as links to additional materials and bibliographies.