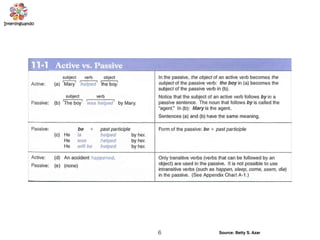
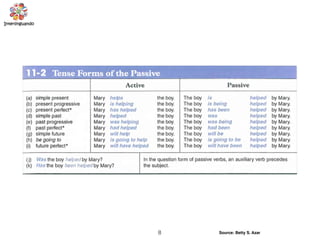
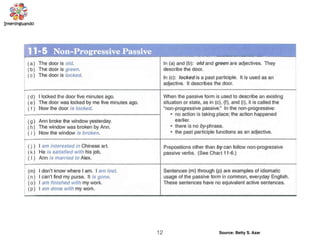
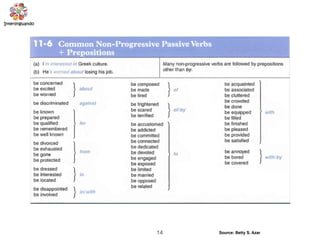
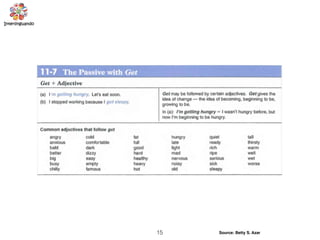
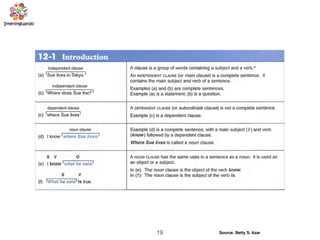
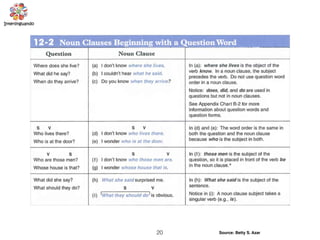
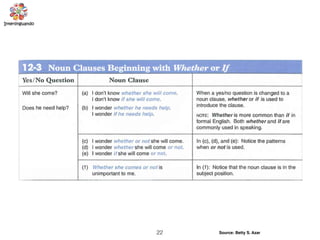
The document discusses the passive voice and noun clauses in grammar. It explains that the passive voice focuses on the action rather than the subject and is used when the subject is unknown or unimportant. It also notes that the passive voice is mandatory in scientific reports. The document then defines a noun clause as a dependent clause that acts as a noun and can serve as the subject, object, or complement of a sentence. Examples are provided to illustrate how noun clauses function within sentences.