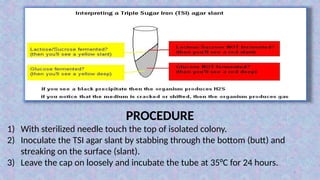
This document presents a lab presentation on biochemical tests for bacterial identification, specifically focusing on the Triple Sugar Iron (TSI) test. It details the components, principles, procedures, and interpretations of test results to differentiate enteric bacteria like Salmonella, E. coli, and Shigella. The TSI test assesses sugar fermentation, hydrogen sulfide production, and gas generation through color changes and precipitate formations.