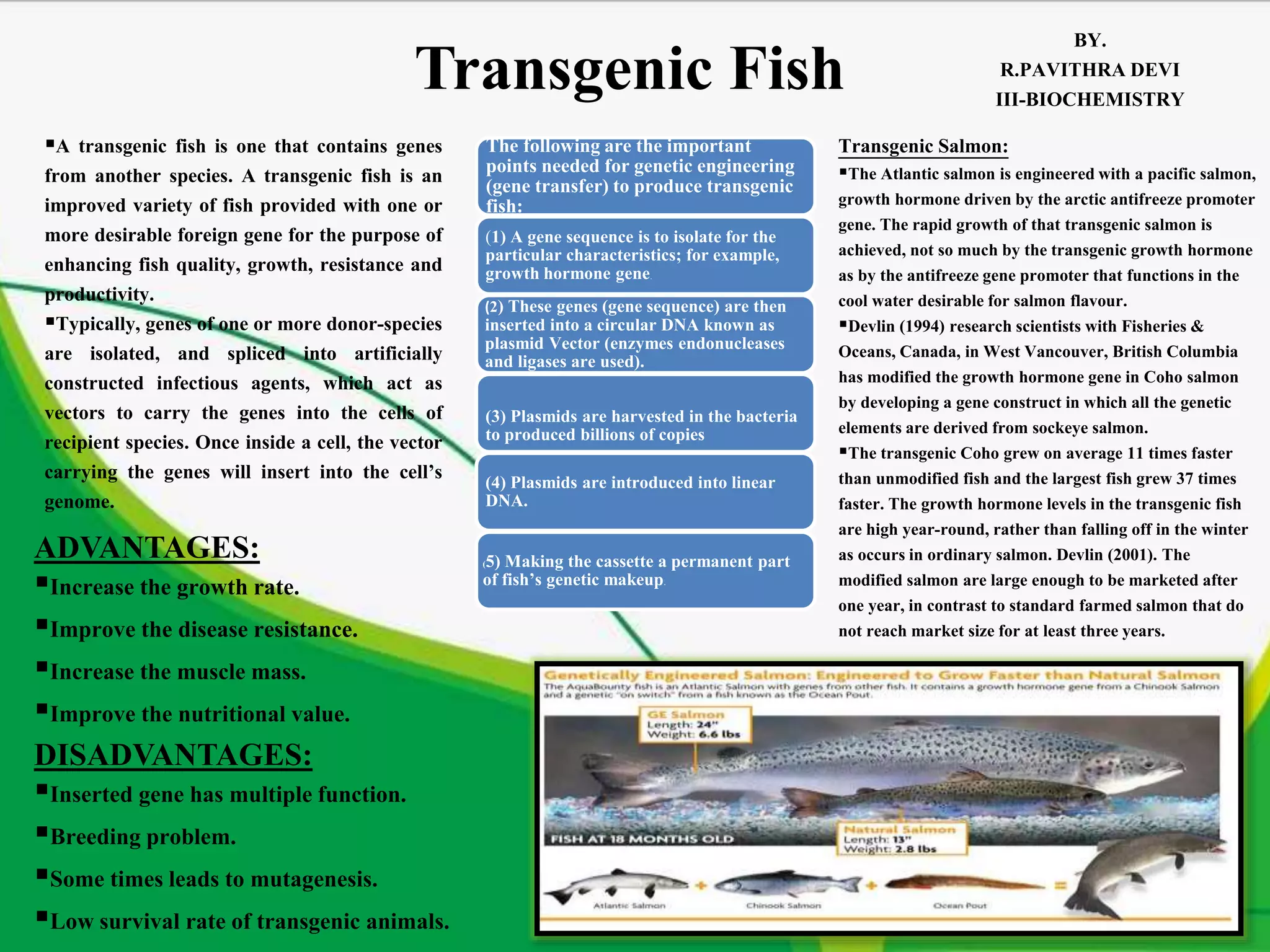
A transgenic fish is one that contains genes from another species inserted into its genome. Genes from donor species are isolated and inserted into vectors like plasmids, which are then introduced into fish cells. This allows the transfer of genes into the fish's genome to produce desirable traits like increased growth, disease resistance, or nutritional value. For example, growth hormone genes inserted into salmon can lead to fish that grow 11 times faster than unmodified salmon and reach market size in just one year. However, there are also risks like multiple gene functions, breeding problems, and low survival rates in transgenic fish.