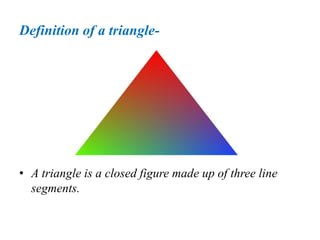
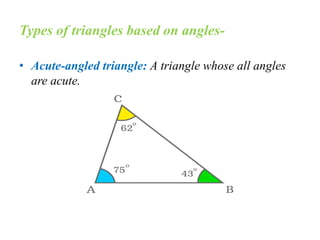
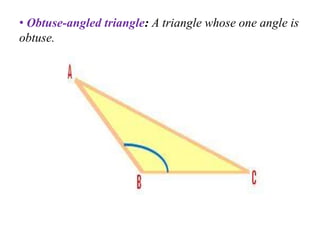
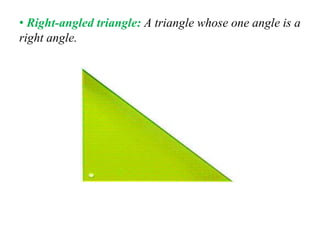
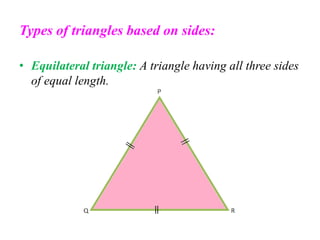
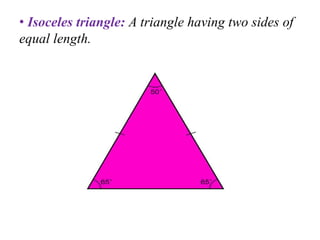
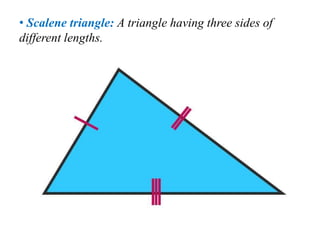
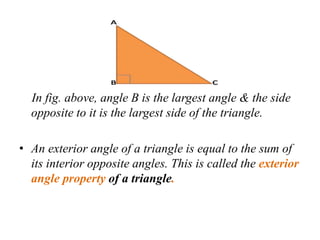
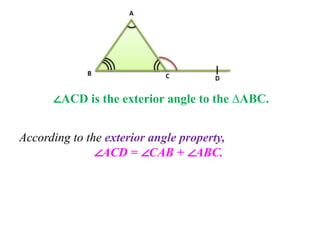
A triangle is defined as a closed figure made up of three line segments and has key properties such as vertices, base, altitude, median, centroid, perimeter, and angles. Triangles can be classified based on their angles (acute, obtuse, right) and their sides (equilateral, isosceles, scalene). Important properties include the angle-sum property (sum of angles equals 180 degrees) and the exterior angle property (an exterior angle is equal to the sum of its interior opposite angles).