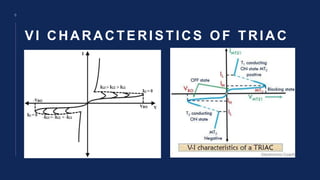
A triac is a three-terminal semiconductor device composed of two thyristors connected in parallel. It can switch alternating current power in both directions by triggering its gate terminal. It has four operating modes depending on the polarity of the voltage applied between its main terminals and the polarity of the gate signal. Triacs are commonly used for AC power control applications like lamp dimmers due to their ability to conduct current in both directions.