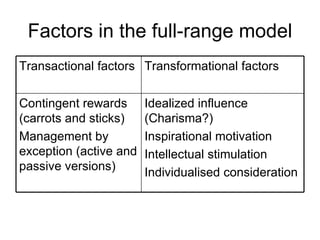
The document discusses trends in leadership thought over time. It begins with early theories that focused on heroic or trait-based leadership. Later theories examined leadership styles and contingency approaches. Current approaches emphasize transformational and distributed leadership. The document traces how leadership theories have evolved from focusing on great individuals to emphasizing relational and collaborative approaches.





![Definitions: It depends what you mean by leadership .. Influence processes Mobilizing resources to arouse, engage, satisfy the motives of followers Making sense [of what people are doing] …articulating purpose and values](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trends-in-leadership-thought-1196018202752432-2/85/Trends-In-Leadership-Thought-6-320.jpg)







![DECLINE IN TRAIT THEORIES The multiplicity of traits identified became a problem Stogdill’s Handbook called for a new approach (1960s) This helped in the rise of Style theories, and other Transactional theories [Co-editor Bass later associated with transformational leadership]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trends-in-leadership-thought-1196018202752432-2/85/Trends-In-Leadership-Thought-14-320.jpg)
![STOGDILL AND STYLE THEORIES Stogdill’s group at Ohio State pioneered style (what leaders do) over traits (what leaders are) Labelled main styles as consideration [towards others], and initiation of structure (‘People, and Task ‘ styles)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trends-in-leadership-thought-1196018202752432-2/85/Trends-In-Leadership-Thought-15-320.jpg)