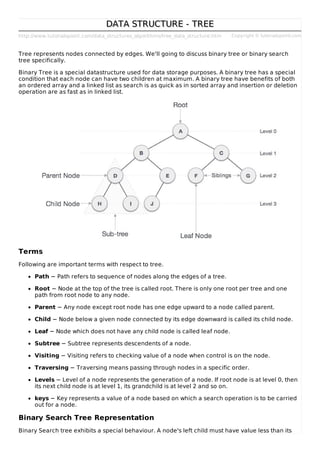
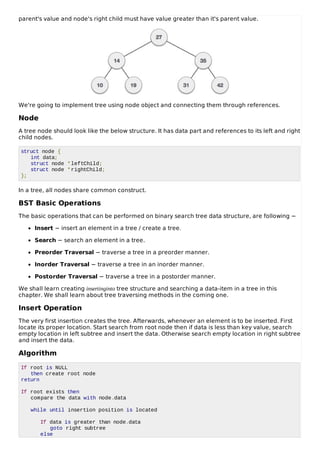
Binary trees are a data structure where nodes are connected in a parent-child relationship. Each node can have up to two children. Binary search trees have the additional property that the value of each node's left child is less than its own value, and the value of its right child is greater. This structure allows efficient search, insertion, and deletion operations. Basic tree operations include traversing the tree in different orders (pre-order, in-order, post-order) and searching for a node by its value. New nodes are inserted by finding the correct position based on value comparison to existing nodes.

![while data not found
If data is greater than node.data
goto right subtree
else
goto left subtree
If data found
return node
endwhile
return data not found
end if
The implementation of this algorithm should look like this.
struct node* search(int data) {
struct node *current = root;
printf("Visiting elements: ");
while(current->data != data) {
if(current != NULL)
printf("%d ",current->data);
//go to left tree
if(current->data > data) {
current = current->leftChild;
}
//else go to right tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
}
//not found
if(current == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
return current;
}
}
To see the implementation of binary search tree data structure, please click here.
Loading [MathJax]/jax/output/HTML-CSS/jax.js](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tree-161223152015/85/Tree-4-320.jpg)