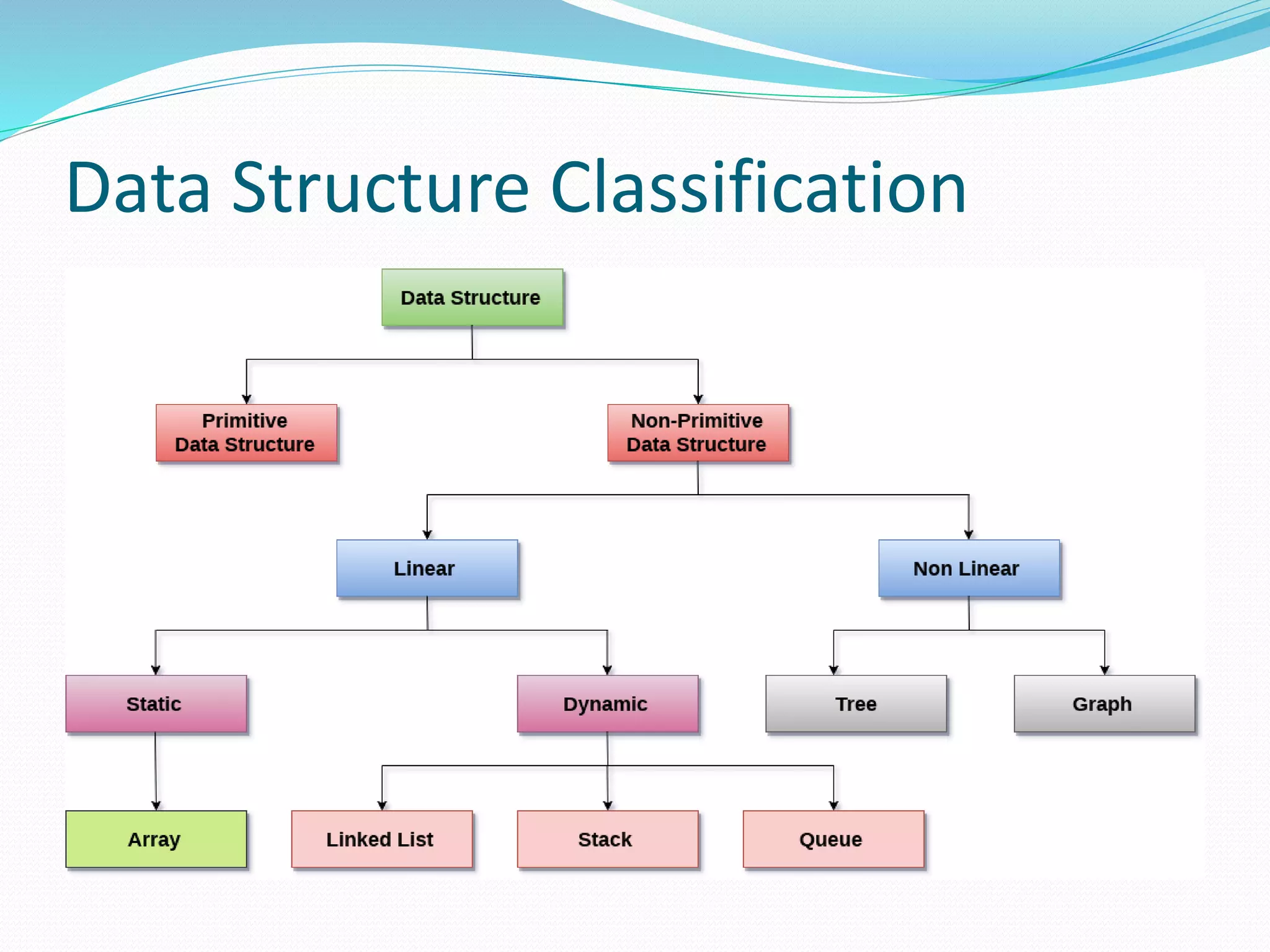
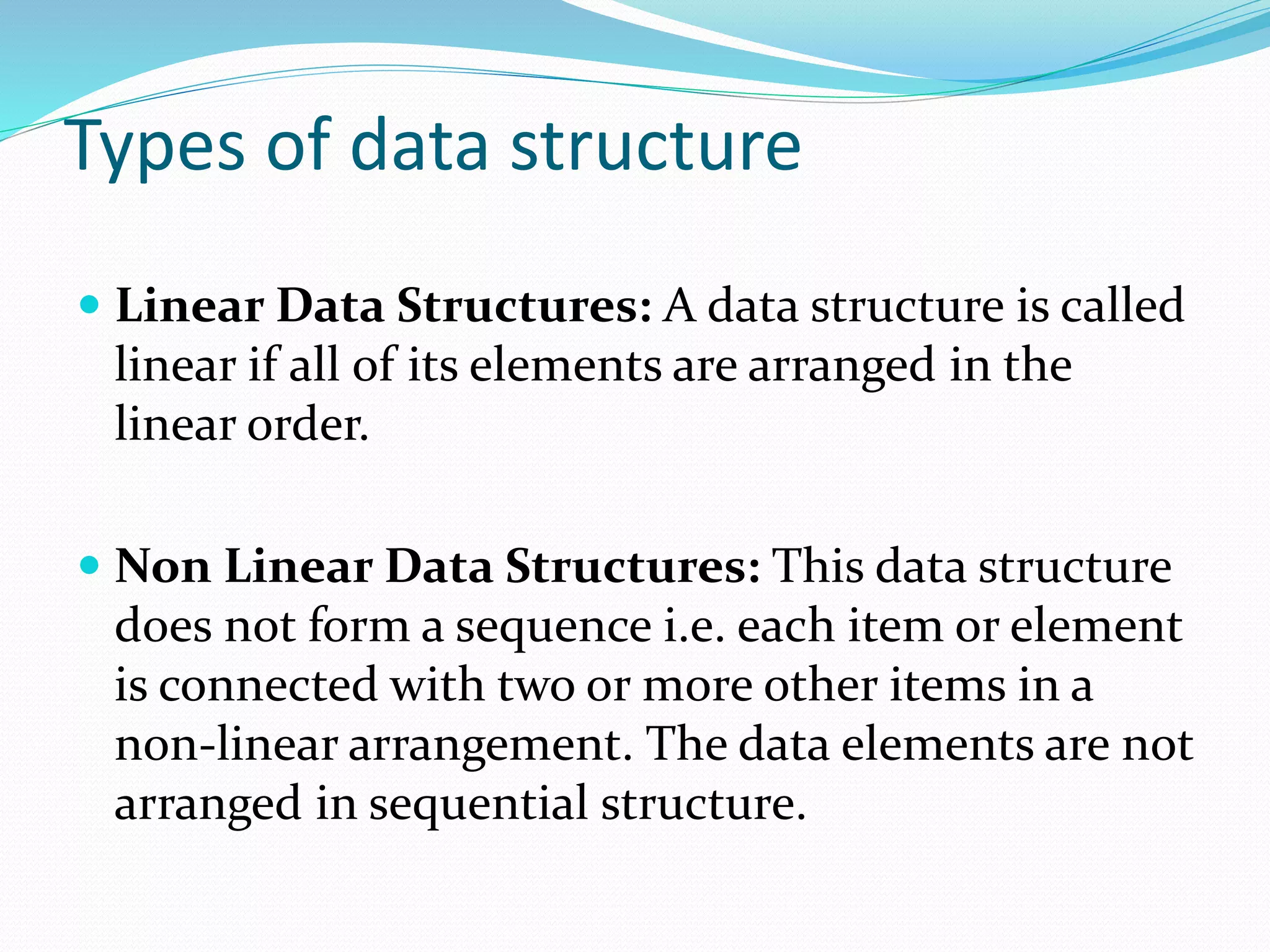
This document introduces data structures and their importance. It defines data structures as organized collections of data that allow efficient storage and retrieval of information. It discusses common data structures like arrays and linked lists. It also covers basic terminology like data, records, files and attributes. The document highlights how data structures enhance software performance by efficiently storing and retrieving user data. It concludes with classifications of linear and non-linear data structures.