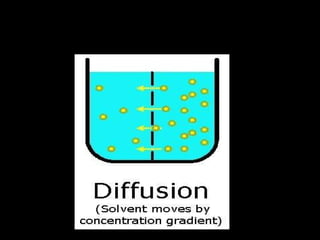
The document describes the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane and different types of transport across the membrane. The cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer that allows for both passive and active transport. Passive transport includes diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion, which move molecules down concentration gradients without energy. Active transport requires energy and transports molecules against concentration gradients using endocytosis, exocytosis, and ion pumps like the sodium-potassium pump.