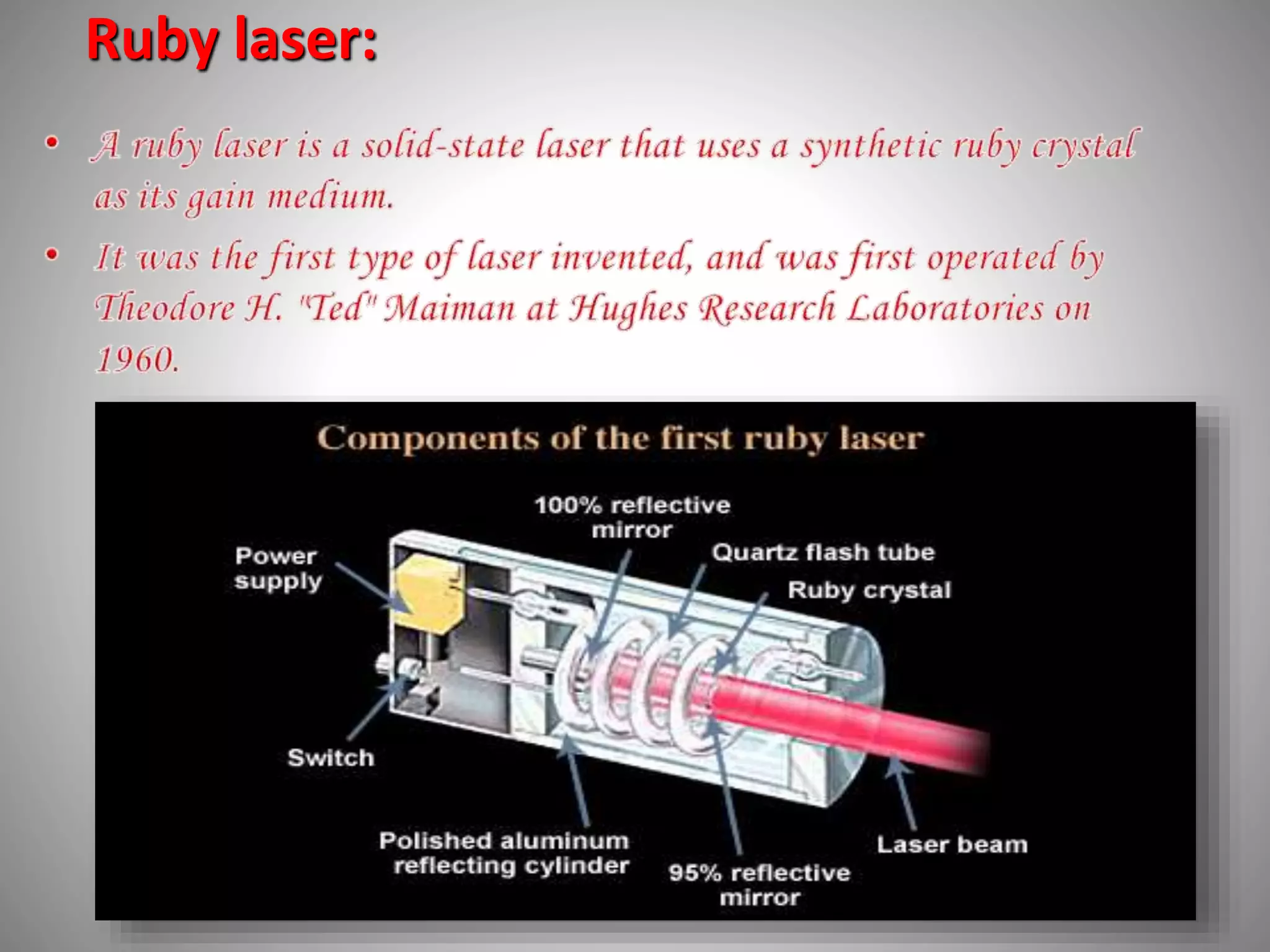
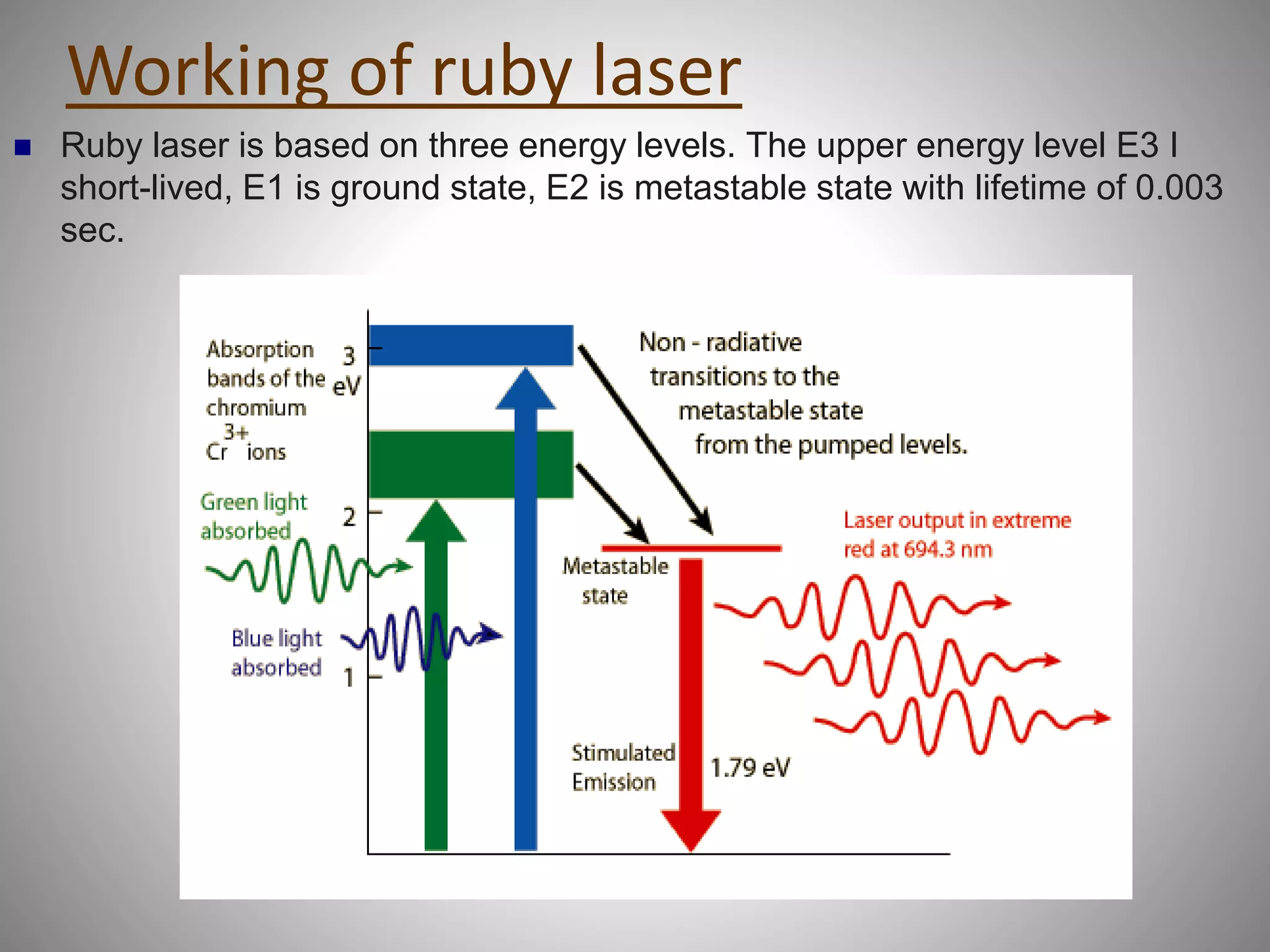
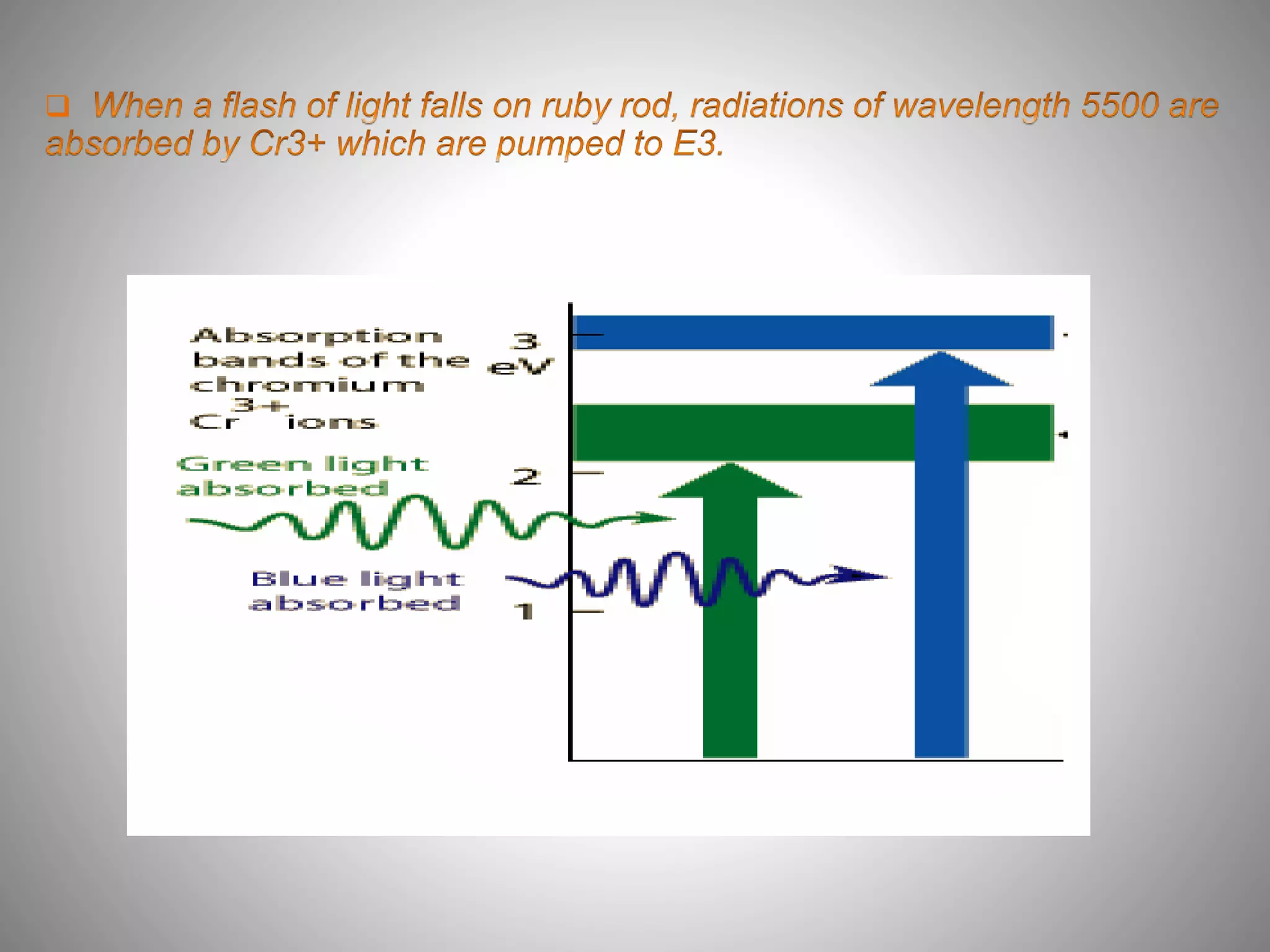
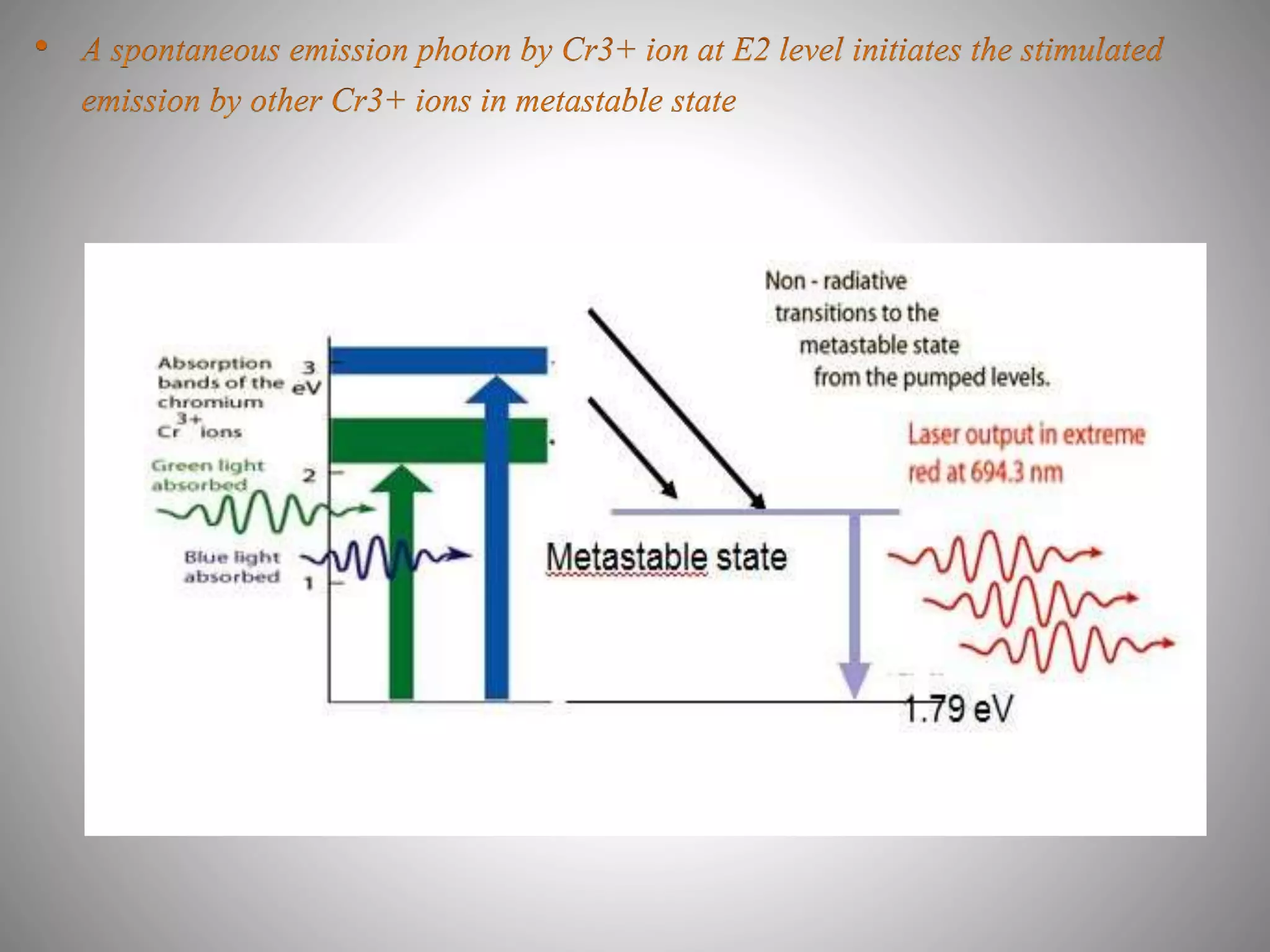
The ruby laser uses a synthetic ruby rod as the active laser medium, which contains chromium atoms that absorb green and blue light and emit red light. The polished ends of the ruby rod form a resonant cavity. A xenon lamp is used to pump ions in the ruby into an excited state. Ruby lasers were used for applications requiring short pulses of red light such as holography and tattoo removal, but have been replaced by better lasing media.