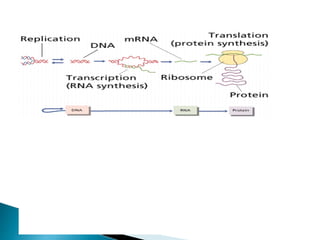
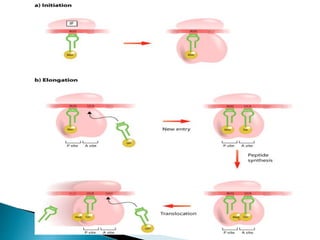
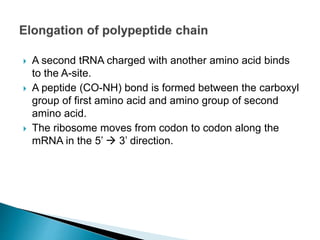
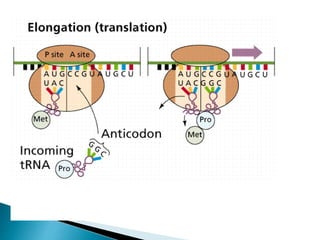
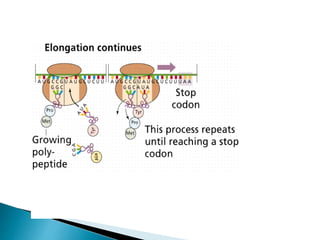
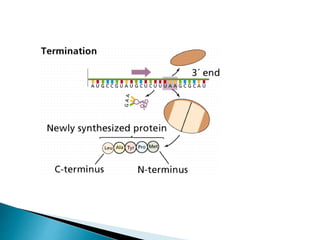
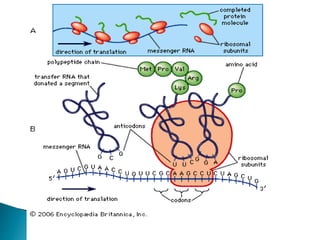
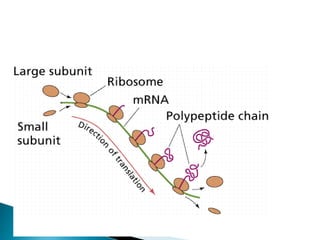
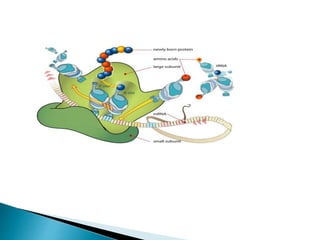
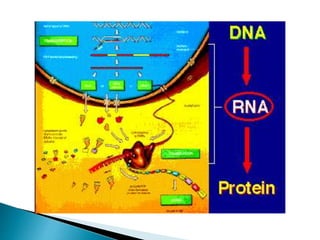
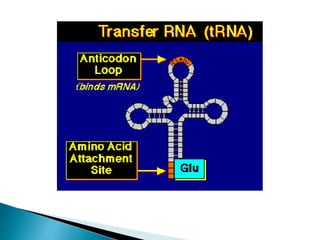
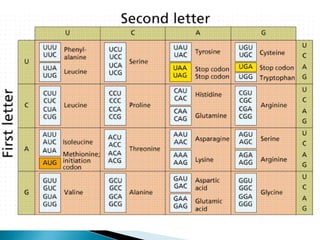
Translation is the process by which the genetic code in mRNA is used to produce a polypeptide chain. It involves mRNA, ribosomes, tRNA, and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. The mRNA codons are read three bases at a time by tRNA molecules carrying complementary anticodons and their attached amino acids. The ribosome facilitates the formation of peptide bonds between incoming amino acids to assemble the polypeptide chain according to the mRNA template. Translation terminates when a stop codon enters the ribosome with no corresponding tRNA.