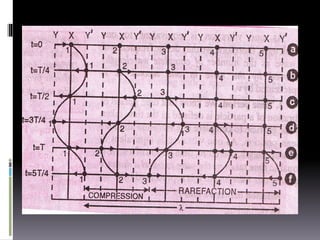
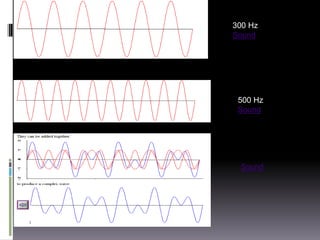
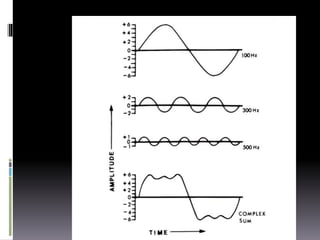
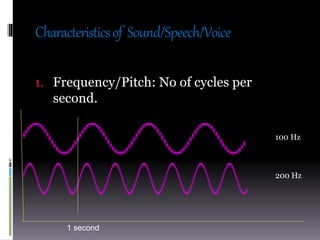
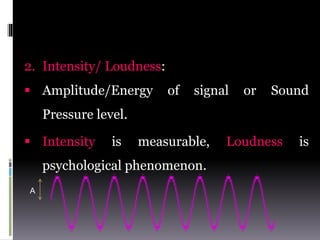
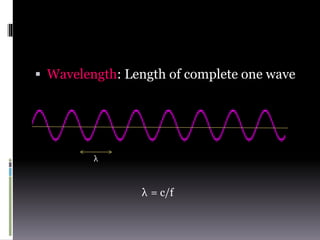
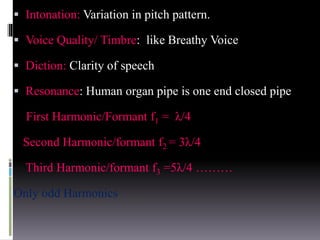
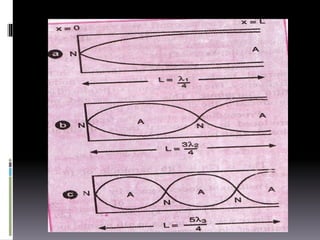
Sound is a vibrational energy that travels through a medium such as air, water or solid material. It is transmitted in the form of longitudinal waves of varying frequency and amplitude. Speech is a complex sound produced by humans for communication that contains different frequencies important for speech between 100-8000 Hz. Forensic voice identification analyzes the unique characteristics of an individual's voice such as fundamental frequency, intensity, wavelength, intonation and timbre to identify unknown speakers, which has applications for criminal cases where only a recorded voice is available as evidence.